PLATE TECTONICS REVIEW - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
advertisement

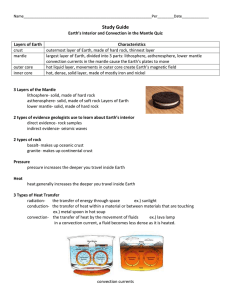
PLATE TECTONICS REVIEW (part 1) 1. Describe the direct and indirect evidence used by geologists to determine the layers of the Earth. DIRECT- ROCK SAMPLES INDIRECT- SEISMIC WAVES 2. What are the 4 layers of the Earth? (starting from the surface) CRUST, MANTLE, OUTER CORE, INNER CORE. 3. Describe each layer in terms of being made of rock or metal and if they are solid or able to flow. CRUST- SOLID ROCK MANTLE- HOT ROCK THAT CAN FLOW OUTER CORE- HOT METAL THAT CAN FLOW INNER CORE- HOT SOLID METAL 4. What is it called when energy moves from a hot object to a cooler one? (ex: you touch a hot pan). HEAT TRANSFER 5. Describe the 3 types of heat transfer. RADIATION- THROUGH SPACE 9NO TOUCHING) CONDUCTION- OBJECTS ARE TOUCHING CONVECTION- HEAT TRANSFER IN A FLUID 6. What would happen to convection currents in a liquid if we removed the heat source? THEY WOULD STOP. 7. Who developed the theory of continental drift? What evidence did he use to support the theory? WEGENER- PIECES FIT TOGETHER, EVIDENCE FROM CLIMATE, EVIDENCE FROM FOSSILS. 8. Why was the theory of continental drift rejected at first? WEGENER COULD NOT IDENTIFY A FORCE THAT COULD MOVE THE CONTINENTS. 9. What technology did geologists use to map the mid-ocean ridge? SONAR 10. In sea floor spreading where does molten material rise up and erupt along? ALONG EITHER SIDE OF THE MID OCEAN RIDGE. 11. Describe the process of subduction. AT A CONVERGENT BOUNDARY WHERE ONE PLATE DIVES DOWN BELOW ANOTHER. 12. Why is old oceanic crust more dense than new oceanic crust? OCEANIC CRUST IS MORE DENSE BECAUSE IT IS COOLER. 13. What do most geologists think causes the movements of the plates? CONVECTION CURRENTS IN THE MANTLE. 14. What is the theory of plate tectonics? THE THEORY OF PLATE TECTONICS STATES THAT THE EARTH’S EXTERIOR CRUST IS BROKEN INTO PIECES CALLED PLATES THAT MOVE. 15. What causes the Earth’s magnetic field? CONVECTION CURRENTS IN THE OUTER CORE 16. What layers of the Earth do convection currents flow in? MANTLE AND OUTER CORE. 17. What is a fossil? A TRACE OF AN ANCIENT ORGANISM THAT HAS BEEN PRESERVED IN ROCK.