Day 3 - HO - Types of Reactions
advertisement

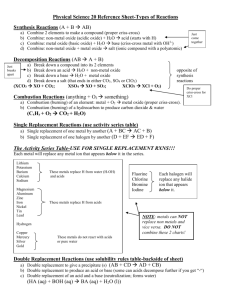
4.2 Types of Reactions Synthesis Reaction: Two or more elements or compounds combine to form a new product. General: A + B C Types of Syntheses: (1) Direct union of two elements produces a binary compound. ** i.e. Mg + O2 MgO (2) Metallic oxides and carbon dioxide produce carbonates. i.e. CaO + CO2 CaCO3 (3) Metallic oxides and water produce metallic hydroxides (a base). ** i.e. CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2 (4) Non-metallic oxides and water produce an acid. i.e. SO3 + H2O H2SO4 ** N2O5 + H2O HNO3 P2O5 + H2O H3PO4 (5) Binary salts and oxygen react to produce a chlorate. i.e. KCl + O2 KClO3 Decomposition Reaction: A compound breaks down into elements or simpler compounds. Opposite of a synthesis reaction. You can recognize this because there is only ONE substance on the left side of the arrow. General: C A + B Types of Decomposition: (1) All binary compounds break down into their elements. i.e. HgO Hg + O2 ** (2) All carbonates break down into the oxide and CO2 i.e. Na2CO3 Na2O + CO2 (3) All chlorates break down into the binary salt (metal and nonmetal put together) and O2 i.e. Ba(ClO3)2 BaCl2 + O2 (4) Metal hydroxides (bases) break down into the metal oxide and water. i.e. NaOH NaO + H2O (5) When you see hydrogen bonded with a polyatomic ion (an acid), it breaks into the non-metal oxide and water. i.e. H2SO4 SO3 + H2O ** * Binary: two elements put together ** Binary salt: One is a metal; the other is a non-metal.