PowerPoint
advertisement

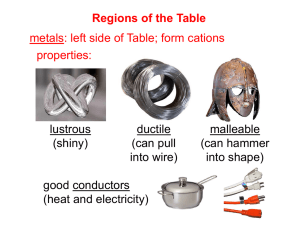
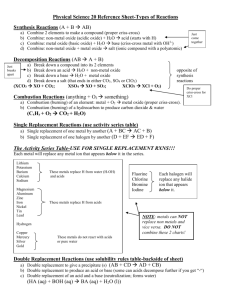
Lesson 4.03/4.04 Single & Double Replacement, Synthesis and Decomposition 4.03 • Double Replacement Reaction: A type of reaction in which the ions of two compounds exchange places in an aqueous solution to form two new compounds. AY + BZ → AZ + BY Double Replacement Reactions: 1. A salt and a base Ca(NO3)2 + 2 NaOH → 2NaNO3 + Ca(OH)2 4.03 2. Two Salts 2 KCl + Pb(NO3)2 → PbCl2 + 2KNO3 3. A Salt and an acid Ba(NO3)2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HNO3 4. Metal Carbonate and an acid MgCO3 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2CO3 5. An acid and a base 2HCl + Mg(OH)2 → MgCl2 + 2H2O 4.03 Sample Problems: 1. KOH + H3PO4 → 2. FeS + HCl → 3. BaCl2 + K2CO3 → 4.03 • Single Replacement Reaction : one element reacts by replacing another element in a compound. A + BY → AY + B To predict whether a single replacement reaction will occur, and what its products will be, you must compare the individual element to the similar element within the compound to determine if the replacement can occur. 4.03 • The activity series of metals can help you identify single replacement reactions and predict the products that will form. • Activity Series of Metals Li, Rb, K, Ba, Sr, Ca, Na, Mg, Al, Mn, Zn, Cr, Fe, Cd, Co, Ni, Sn, Pb, H2, Sb, Bi, Cu, Hg, Ag, Au * In an activity series list, elements are listed from most reactive to least reactive. On the list above, lithium (Li) is most reactive, where gold (Au) is least reactive. 4.03 Single Replacement Reactions: 1. A metal replacing a less active metal 2Na + CuSO4 → Na2SO4 + Cu Sodium can replace copper in the compound because Na is higher on the activity series than Cu. Zn + NaCl → no reaction Zinc cannot replace sodium because Zn is lower on the activity series than Na. 4.03 2. A metal replacing the hydrogen in water • The highly reactive metals (such as the alkali metals in Group 1) react vigorously with water to produce a metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas. 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 • Less active metals, such as aluminum and iron, can react with water under the right conditions to produce a metal oxide and hydrogen gas. Zn + H2O → ZnO + H2 Au + H2O → no reaction 4.03 The halogens decrease in reactivity as you go down the group. F2 + 2NaCl → 2NaF + Cl2 Sample Problems: 1. Ca + H2O → 2. Zn + FeSO4 → 3. Br2 + CaCl2 → 4.03 3. A metal replacing the hydrogen in an acid • The more reactive metals can react with certain acids, such as hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, to form an ionic compound (a salt) and hydrogen gas. Pb + 2HCl → PbCl2 + H2 4. A nonmetal replacing a less active nonmetal • A nonmetals get involved in the replacement as well. A halogen in Group 17 can take the place of a less active halogen within a compound. 4.04 • Synthesis Reaction: involve two or more reactants combining to form one new substance. A + B → AB Synthesis Reactions: 1. Nonmetal oxide with water = oxyacid SO3 + H2O → H2SO4 2. Metal oxide with water = metal hydroxide CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 3. Metal with nonmetal = neutral compound 4.04 Ca + Cl2 → CaCl2 4. Nonmetal and oxygen = nonmetal oxide S + O2 → SO2 5. Metal oxide and nonmetal oxide = salt MgO + SO2 → MgSO3 Sample Problems: 1. N2 + O2 → 4.04 2. Na + Cl2 → 3. MgO + H2O → • Decomposition Reaction: starts with only one reactant but ends with more than one product. AB → A + B Decomposition Reactions: 4.04 1. Binary compound = 2 individual elements 2H2O → 2H2 + O2 2NaCl → 2Na + Cl2 2. Metal carbonate = metal oxide + CO2 CaCO3 → CaO + CO2 3. Metal chlorate = metal chloride + O2 2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2 4. Metal hydroxide – metal oxide + water Ca(OH)2 → CaO + H2O 4.04 5. Oxyacids - nonmetal oxides + water H2SO4 → SO3 + H2O Sample Problems: 1. Ca(ClO3)2 → 2. H2CO3 → 3. Na2CO3 →