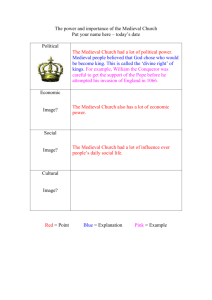
Early Medieval Europe Chapter 11 Study Guide cloissonné fibula
advertisement
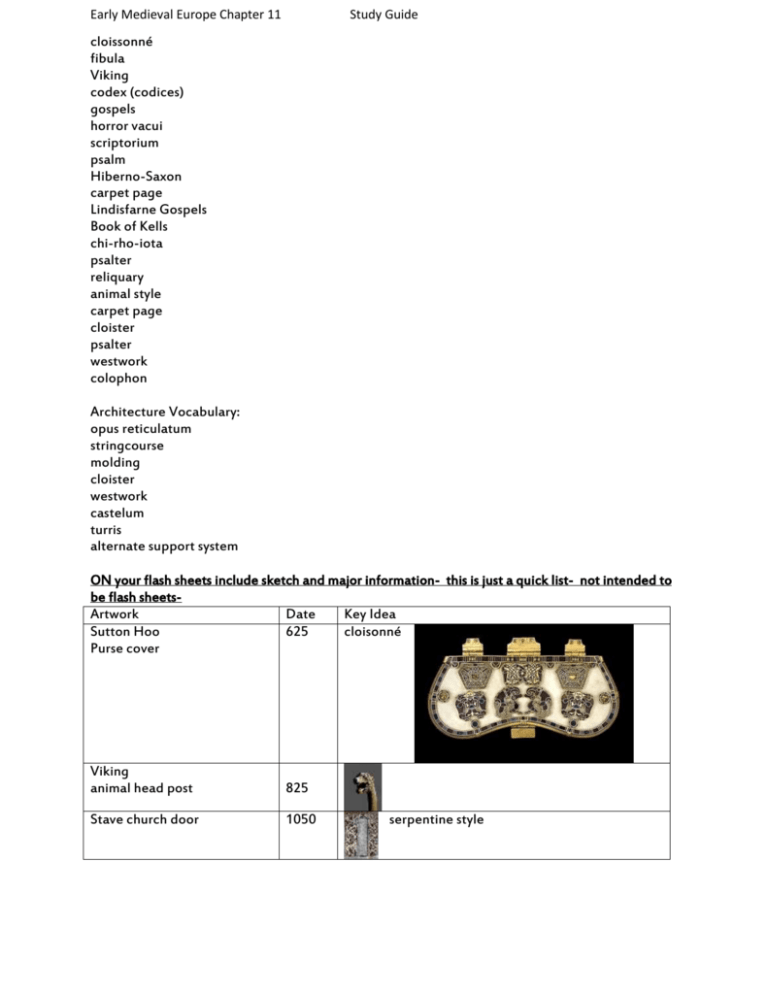
Early Medieval Europe Chapter 11 Study Guide cloissonné fibula Viking codex (codices) gospels horror vacui scriptorium psalm Hiberno-Saxon carpet page Lindisfarne Gospels Book of Kells chi-rho-iota psalter reliquary animal style carpet page cloister psalter westwork colophon Architecture Vocabulary: opus reticulatum stringcourse molding cloister westwork castelum turris alternate support system ON your flash sheets include sketch and major information- this is just a quick list- not intended to be flash sheetsArtwork Date Key Idea Sutton Hoo 625 cloisonné Purse cover Viking animal head post 825 Stave church door 1050 serpentine style Early Medieval Europe Chapter 11 Study Guide Hiberno-Saxon St. Matthew 698 abstract design Book of Kells 428 Caroligian Charlemagne equestrian statue 9th C St. Matthew 800810 St. Matthew 816835 Psalm 44, Detail of Folio 25 Recto of the Utrecht Psalter, from Hautvillers ca. 820– 835 Chi-rho-iota page classicism frenzy(?) style, Ebbo Gospels The drawings in the Utrecht Psalter are rich in anecdotal detail and show figures acting out—literally—King David’s psalms. Palatine Chapel 792805 copy of St. Vitale Torhall 9c Early Medieval Europe Chapter 11 Study Guide Saint Gall 819 Ottonian Saint Michael’s new church 10011031 ANave, Saint Michael’s, Hildesheim, 1001– 1031 Bernward’s doors 1015 God Accusing Adam and Eve, Detail of the Left Door of Saint Michael’s, Hildesheim, Germany 1015 medieval monastery Hildesheim bronze-caster recounted the story of original sin with a flair for anecdote. With vivid gestures, God accuses Adam, who passes the blame to Eve, who points in turn to the serpent. Early Medieval Europe Chapter 11 Study Guide Crucifix 970 Annunciation 10021014 Otto III 9971000 Expressionism Byzantine style Medieval style Questions 1) Identify the following: • Charlemagne: • Otto III: • Viikings: • Hiberno-Saxons: • Carolingians: 2. Name three traditions which fused to create early medieval society in Western Europe: 3. Briefly describe the style of the decoration of the Meroviangian fibula. 4. What was found at Sutton Hoo and what was its importance? 5. The conflict between __________________ and ___________________ set the medieval world of Western Europe apart from the Byzantine and Islamic worlds. 6. The Celts were converted to Christianity in the _________________century. Early Medieval Europe Chapter 11 Study Guide 7. List 3 characteristics of the style utilized on the Chi-rho-iota page from the Book of Kells. a. b. c. 8. List the 4 evangelists: a. b. c. d. 9. Why did medieval manuscript illuminators copy earlier examples rather than working directly from nature? 10. When was Charlemagne crowned as head of the Holy Roman Empire? 11. The Palatine Chapel of Charlemagne resembles the church of ____________________________ in Ravenna, but is distinguished by: a. b. 12. Who was Bishop Bernward? 13. The style of figures on the bronze doors at St. Michael’s at Hildesheim probably derives from manuscript illumination of the period. In what major way does it differ from its prototype? 14. List 3 features of the Gero crucifix that contribute to the expression of suffering. a. b. c. Early Medieval Europe Chapter 11 Study Guide DISCUSSION QUESTIONS: 15. Compare the abstract decorative art of the Early Middle Ages in Europe as seen in the ornamental pafe from the Book of LIndisfarne with the Islamic decorative style as seen in the Ardebil Carpet (page 374). In what ways do they resemble each other? What is distinctive about both? 16. Discuss Charlemagne’s role in the history of art. 17. In what ways did medieval European art and architecture depart from classical Roman art and architecture? Did any of the civilizations retain characteristics of Roman art and architecture? Explain. 18. What previous styles of art influenced medieval art? 19. Describe the style of the decoration on the panel from Urnes and the animal head post of Viking ship found near Oseberg Norway.