Exam 1 Answer Key
advertisement

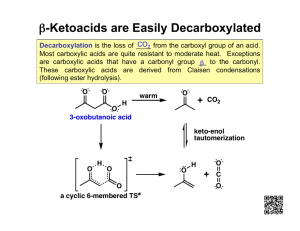
CHEMISTRY 213 EXAM 1 Fri., April 18, 2003 Answer all 18 questions (150 pts). Name . Answer Key 1. (3) True or False. The compound shown would lose CO2 on treatment with H 3 O+ and heat. COCH3 CO2Ph 2. (3) True or False. The hydrogens to the carbonyl of an ester are less acidic than those to a ketone. 3. (3) True or False. The compound shown is malonic ester. O O Et OEt 4. (7.5) For each of the following reactions, state whether the step shown is an addition, elimination, rearrangement, or substitution. O a) O substitution OMe O b) NHMe O elimination Ph Se O O c) O substitution 5. (12) In each of the following molecules, identify all the acidic hydrogens with pKa values <25. Note, you may have to draw in the appropriate hydrogen atoms. Additionally, give the approximate pKa value for each proton you have indicated. a) b) O O H pKa = 10 O O H pKa = 20 HO pKa = 5 O c) HO H pKa = 20 pKa = 17 H pKa = 20 6. (7) Draw two other resonance forms for the following anion. O O O 7. (38) Provide the structures of the major organic products expected, or provide the reactants and / or reagents necessary to effect the following transformations: a) COOH COOH heat COOH b) O excess NaOH Ph Ph excess I 2 O c) O H+ O 1) Br 2 , PBr3 HO 2) H2O HO Br CO2Me d) OH CO2Me 1) LiOMe CO2Me CO2 Me 2) 1-bromo-3methylbutane H3O+, heat COOH e) O Ph O O O KOEt Ph Ph O OEt + O Ph f) O OH 1) 2 MeMgCl Cl 2) H+ O g) 1) LDA O 2) Br 8. (4.5) Assign the relative reactivity of each of the following to nucleophiles (use #1 for most reactive to #3 for the least). O O O O NH H3 C 3 CH3 O O 2 CH3 CH3 1 9. (9) Answer the following questions related to the malonic ester synthesis. a) What solvent would be used for the reaction of malonic ester with NaOEt ? Ethanol b) Why can malonic acid itself (HOOCCH2COOH) not be used as the starting material ? The base would react with the carboxylic acid protons rather than the alpha proton c) Why can NaOH not be used as a base for the reaction with malonic ester ? The hydroxide ion would attack the C=O carbon and displace RO10. (3.5) Explain briefly but clearly why LDA would never be used in ethanol as solvent. LDA is a very strong base and would easily abstract the alcohol proton, generating Alkoxide anion and forming diethylamine 11. (3.5) Explain briefly but clearly why it is necessary to use an acid catalyst for the hydrolysis of an amide. Water would not be a strong enough nucleophile to displace the amine anion from the amide. If an acid catalyst is used, the amide becomes a better electrophile and the leaving group is improved drastically, becoming a neutral amine rather than its anion 12. (9) State whether each of the following normally would act as a nucleophile or electrophile. You need not explain your answer. a) b) c) O Al KOCH2CH2CH3 H nucleophile electrophile nucleophile 13. (15) From the list given, choose the best reagent for each transformation shown. Write the appropriate letter above the reaction arrow. It is possible to use the same reagent more than once. A. NaCN then H2 / Pd E. NaCN then H3O+ C. NaBH4 D. Me2CuLi then H+ G. LiAlH4 then H3O+ H. H3O+ B. NaOH, Br2 F. MeMgBr then H3O+ H CONHCH3 COOH H CO 2CH 3 COOH D COCl COCH3 G PhCH2CONHCH3 PhCH2Br PhCH2CH2NHCH3 E PhCH 2CO 2H 14. (10) In each of the following examples, draw the 2 key starting materials (not bases or solvents) required to form the products shown by C-C forming reactions. a) from a nitrile, Grignard, + then H 3 O Ph O Ph C N + EtMgBr O b) OH Br + H2C(CO2 Me)2 15. (4) The first step of the hydrolysis of a nitrile under basic conditions (HO-, water) is attack by hydroxide on the C of the CN, with breaking of the CN pi bond. What is the second step? Attack by the resultant nitrogen anion upon the H of water 16. (12) Show the first complete step of the arrow-pushing mechanism for each of the following: O a) OEt NaOMe MeOH b) OH Li NiPr2 H Li NiPr2 O H c) O 17. (3) True or False. Treatment of malonic ester with NaOMe gives 100% of the corresponding anion. 18. (3) True or False. Treatment of acetone with NaOMe gives 100% of the corresponding anion.