Honors Chemistry
advertisement

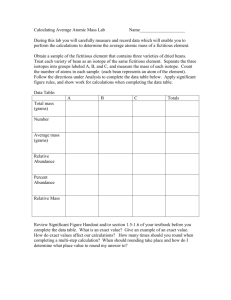
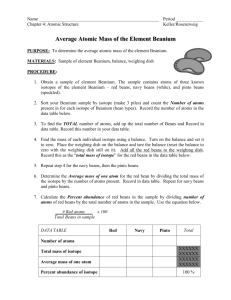
Honors Chemistry Lab Labs Atomic Structure The Average Atomic Mass of Vegium, Vg *You will use the electronic, top-loading mass balance for this exercise. 1.Obtain a sample of the fictitious element vegium containing: black beans, brown beans, and green peas…isotopes of vegium??? 2.Separate the isotopes (black beans, brown beans, green peas) of the vegium into three small beakers. 3.Mass the separate isotopes of all the black beans, all the brown beans, and all the green peas. Record this in your data table as the mass of each isotope. Always record the proper precision of the analytical balance and the correct units. 4.Count all the isotopes (black beans, brown beans, green peas). Record this as the amount (number?) of each isotope. 5.Divide the mass of each isotope (black beans, brown beans, green peas) by the amount of each isotope to get the average mass of each isotope. ave. mass of isotope (black bean) mass of isotope (black beans) amount of isotope (black beans) 6.Divide the amount of each isotope (black beans, brown beans, green peas) by the total number of all the isotopes to get the relative abundance of each isotope. rel. abundance of isotope (black bean) amount of isotope (black beans) total amount of all isotopes (black beans, brown beans, green peas) 7.Multiply the relative abundance by the average mass of each isotope to get the relative mass of each isotope. 8.Multiply the relative abundance of each isotope by 100 to get the percent abundance of each isotope. percent abundance of isotope (black bean) rel. abundance of isotope (black bean) 100 9.Calculate the average atomic mass of the fictitious element vegium. ave atomic mass = rel. mass isotope (black) + rel. mass isotope (brown) + rel. mass isotope (green) Requirements: 1)What are the purposes and learning objectives for this laboratory? 2)Create a data table that can be used to summarize the activity. 3)Draw a labeled diagram (s) that can depict the procedure and apparatus used. This can be done in the form of a flow chart. 4)Complete the calculations outlined throughout the procedure. Organize these in a logical format. 5)What would you do to improve this activity if you could make changes? 6)What did you learn? Lab Atomic Structure-Counting Atoms A. How Many Atoms Are In The Container? *You will use the triple beam balance for this activity. -Determine the number of atoms of each element in the samples provided. Sample A is a common nail. The nail is 94.5 % iron. Container B contains tin. -Handle the solids with a pair of forceps. Return all of the sample to the plastic container when finished. -How many moles of each element are found in the samples? -What volume of iron is found in the nail (Sample A)? -How many atoms of iron are found in the nail? -Suppose the entire sample of tin from Container B reacts with diatomic chlorine according to the following unbalanced equation: Sn(s) + Cl2(g) SnCl4(s) What minimum number of moles of diatomic chlorine must be available to react completely with the tin? B. The Nucleus In A Bag Find the plastic bags numbered 1, 7, 10, 14, and 17. Do not open the bags. Each bag contains a simulated atomic nucleus. The nucleons are represented by the colored marbles: protons = black Protons neutrons = blue After examining the contents of the bag, prepare a table similar to the one below including each of the five bags or isotopes: Neutrons Mass Number Nuclear Symbol Hyphen Notation Requirements for Parts A & B: You may decide on the requirements for this lab. What have I asked you to include before? Remember, a good lab report stands alone as a meaningful document. I should not have to see this lab handout to understand what you did in the lab. Organize and label your work.