Name
advertisement

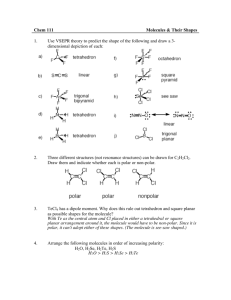
Name:________________________________________ Date:_____________________________ Blk:____ Intra and Intermolecular Bonding: A Review of Unit 3 and 4 1. Distinguish between the following types of bonding: a) inter and intra molecular b) ionic and covalent c) polar and non-polar d) covalent and metallic 2. a) Describe the trends in electronegativity as you go L---->R across a period and down a family in the PT. b) Determine the EN difference, dipoles, directionality and character of the following bonds. i) C-----I b) Sr-----O c) P-----N 3. a) List four properties of ionic substances. b) Describe a simple test to distinguish between polar and non-polar substances. c) Describe a simple test to distinguish between ionic and polar substances. 4. a) Describe three things Lewis theory allows us to predict. b) Draw the Lewis structures for: i) Sr ii) Se2- iii) CaF2 5. a) What additional information about molecular structure is provided by VSEPR? b) Using the best Lewis structure, draw molecular shapes for each of the following. Include the egp geometry name, molecular geometry name, class, angles and indicate if the structure is polar or non-polar. i) COCl2 ii) SOF4 iii) CO32- iv) PH4+ c) How do formal charges help you predict the Best Lewis structure? Calculate the formal charges for CO 32-. d) Draw resonance structures for CO32-. 6. Suppose that a molecule has the formula AB3. Sketch and name two different shapes that this molecule may have. For each of the two shapes, give an example of a known molecule that has that shape. For one of the molecules you have named, interpret the shape in the context of a modern bonding theory. 7. How do pure and hybrid valence bond theory enhance VSEPR? 8. Explain the difference between a bond and a bond. 9. Using pure valence bond theory draw orbital overlap in F2. 10. Using hybrid valence bond theory draw orbital overlap for: a) COCl2 b) CO32- 11. What hybrid orbitals are used by sulphur in SOF4? ________________ 12. Discuss briefly the relationship between the dipole moment of a molecule and the polar character of the bonds within it. With this as the basis, account for the difference between the dipole moments of CH 2F2 and CF4. 13. Consider the molecules SCl2, F2, CS2, CF4, and BrCl. a) Which has the most polar bonds? _________ b) Which are polar molecules? ________________ 14. a) Use Lewis structures to compare the length, strength and order of the N---N bond in N2, N2H4, and N2H2. b) Calculate the Horxn for the following reaction: N4H4 ----> N2H4 + N2 (N4H4: H2NNNNH2) 15. a) Describe the two factors that influence the strength of ion-dipole interaction. b) Which of the following in each list would be expected to have the strongest IMF? H H H i) Na+ --- O , Li+ --- O , F- --- O __________ H H H ii) Na+ --- O H , Mg2+--- O H H , Al3+--- O H H ________ H 16. Which of the following in each pair would you expect to have the higher boiling point? a) CH3CH3 or CH3CH2F ______________ b) CH3CH3 or CH3(CH2)4CH3 _______________ 17. a) Describe the conditions necessary for H-bonding. b) H2O has a lower mass than H2S, H2Se or H2Te and yet its boiling point is significantly higher. Why? 18. For each pair, identify the most important IMF in each substance and then select the substance with the higher boiling point. a) MgCl2 and PCl3 b) CH3NH2 and CH3F c) CH3OH and CH3CH2OH d) CH3(CH2)4CH3 and CH3C(CH3)2CH2CH3 19. What is polarizability and what factors influence the degree of polarizability? 20. What IMF allows non-polar molecules like O2 to dissolve to a small extent in polar water? ________________ 21. Data on the solubilities in water of butane, chloroethane, acetone, and 1-propanol are listed in the table below. On the basis of dipole moments (molecular polarities) and/or hydrogen bonding, explain in a qualitative way the differences in: Solubility a) water solubilities of butane and 1-propanol. Compound Formula in water Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3 insoluble Chloroethane CH3CH2Cl insoluble O Acetone b) water solubilities of chloroethane and acetone. || CH3C C CH3 1-Propanol CH3CH2CH2OH completely miscible completely miscible 22. What IMF allows us to liquefy non-polar gases like N2? _____________________ 23. a) What three factors affect viscosity? b) Rank the following in order of decreasing viscosity: CH 3CH2CH2OH, HOCH2CH2OH, HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH 24. a) Distinguish between adhesive and cohesive properties. b) What happens to the height of a liquid in a tube if cohesive forces are stronger than adhesive forces? 25. Define vapour pressure and describe what happens to vapour pressure as strength of IMF increases? 26. a) Define lattice energy and describe how it is affected by ionic size and charge. b) Which member of each of the following pairs would have a higher melting point? i) SrF2 or MgF2 ii) SrO or RbF 27. Describe the relationship amongst Hosubl, Hofus, and Hovap