Evolution Study Guide Answer Key
advertisement

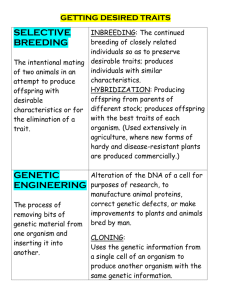
Name: Unit 8 Study Guide | Test Date: _________________________ 1. What is biological evolution? Change in gene frequency in a population over time. It has shaped changes in organisms from their earliest beginnings to now. 2. Compare microevolution vs. macroevolution. How are they different? Microevolution is evolution of a single population (caused by genetic variability), whereas macroevolution is the evolution of an entire species (because of the environment). 3. What is a common ancestor? An ancestor that is shared by two similar species. 4. Biological evolution occurs through natural selection. What is natural selection? Survival of the fittest – whoever is most fit to survive in the environment will live and make more babies. 5. What are the four principles of natural selection? Overproduction of offspring, variation, adaptation, and descent with modification. 6. How does overproduction of offspring influenced by natural selection? The more offspring an organism has, the more likely some will survive to reproduce. 7. How does variation influenced by natural selection? Good genes and physical characteristics will be passed on while bad ones die out. 8. What is adaptation? Developing traits that make an organism more fit to survive in its environment. Ex: camouflage 9. How does adaptation influenced by natural selection? Natural selection favors good adaptations – those that help the organism survive. Bad adaptations will lead to the organism’s death. 10. FYI: All life that exists or has existed on earth share the same nucleic acids and the same proteins. 11. What are the two types of reproduction? Sexual and asexual reproduction 12. How does genetic variability occur in sexual reproduction? Crossing over, gene shuffling, mutations 13. How does genetic variability occur in asexual reproduction? Only mutations 14. Contrast sexual and asexual reproduction. How are they different? Sexual reproduction requires two parents, meiosis to make gametes, lower reproduction rate, lower offspring produced at a time, and offspring that are genetically different from parents and each other. Asexual requires only one parent, mitosis to reproduce, higher rate, higher offspring, genetically identical offspring. 15. What is a species? A group of similar organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. 16. What is a gene pool? The collection of all of the genes in a population. 17. How does diversity affect natural selection or evolution? The more diverse a population is, the more likely that some will survive via natural selection. Those survivors will shape the new population – evolution. 18. Genetic variability leads to microevolution. What are the 5 factors that influence genetic variability in a population? Describe them. Genetic drift (small population, random change in alleles over time), gene flow (migration), mutation (change in DNA), nonrandom mating (sexual selection), natural selection (survival of the fittest) 19. When there is no change in the allele frequencies within a species, the population is in genetic equilibrium. What is another name for this? Hardy-Weinberg principle 20. What are the 5 requirements of genetic equilibrium, or Hardy-Weinberg principle? Large population with no genetic drift, no gene flow, no mutation, random mating, no natural selection 21. What is speciation? Formation of a new species 22. What causes speciation? What are some examples of environmental factors that affect evolution? Speciation is caused by members of a population becoming isolated, preventing the new population from mating with the original population. Environmental factors that affect evolution include climate change, catastrophic events, and continental drift. 23. What are some patterns of macroevolution caused by the environment? Describe each. Convergent evolution (species become more similar due to similar habitats), divergent evolution (one species branches into two; also called adaptive radiation or speciation), coevolution (two organisms that rely on each other to survive evolve in response to each other) 24. What are analogous structures? Created by convergent evolution; structures that are similar in function but not in structure (body shapes of sharks and dolphins, wings of birds, bats, and bugs) 25. What is the difference between gradual and mass extinction? Gradual extinction occurs slowly, mass extinction is caused by one large event that affects many species. 26. What four fields of study have given us evidence for evolution? Anatomy, biochemistry, embryology, paleontology 27. What is anatomy? Study of structures of organisms 28. What are homologous structures? Generated by divergent evolution; similar structures as a result of common ancestry, like the forelimbs (arms) of humans, cats, horses, birds, whales, etc. May not have the same function. 29. What are vestigial organs? Organs that are no longer useful to the current organism, but were to the ancient organism. Example: human appendix and tailbone, ostrich wings, etc. 30. What is embryology? Study of the development of embryos 31. Why is embryology helpful for studying evolutionary history? Species that are more similar to each other have more similar stages of development 32. What is biochemistry? All of the chemical reactions that occur in living things 33. What molecule do we usually compare in organisms to trace evolutionary history? DNA and proteins 34. What is paleontology? Study of prehistoric life – fossils 35. What do fossils show us? Similarities between ancient and current species 36. What is phylogeny? Evolutionary history 37. Can we get a good picture of evolutionary history from one piece of evidence? Why or why not? NO – there’s not a large enough sample size. The more evidence you have, the more reliable your data is. 38. What are phylogenetic trees? Diagrams that help show evolutionary relationships between organisms through time. 39. What can phylogenetic trees tell us? Common ancestry, extinction, speciation, etc. 40. What are cladograms? A type of phylogenetic tree that isn’t very specific – it shows basic relationships based on a few traits rather than all traits. 41. What are the three domains of life? Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya 42. What are the six kingdoms of life? Eubacteria (Domain Bacteria), Archaebacteria (Domain Archaea), Protista, Animalia, Plantae, Fungi (all Domain Eukarya)