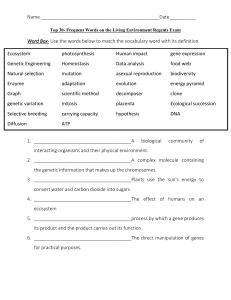
Getting Desired Traits Flipbook
advertisement
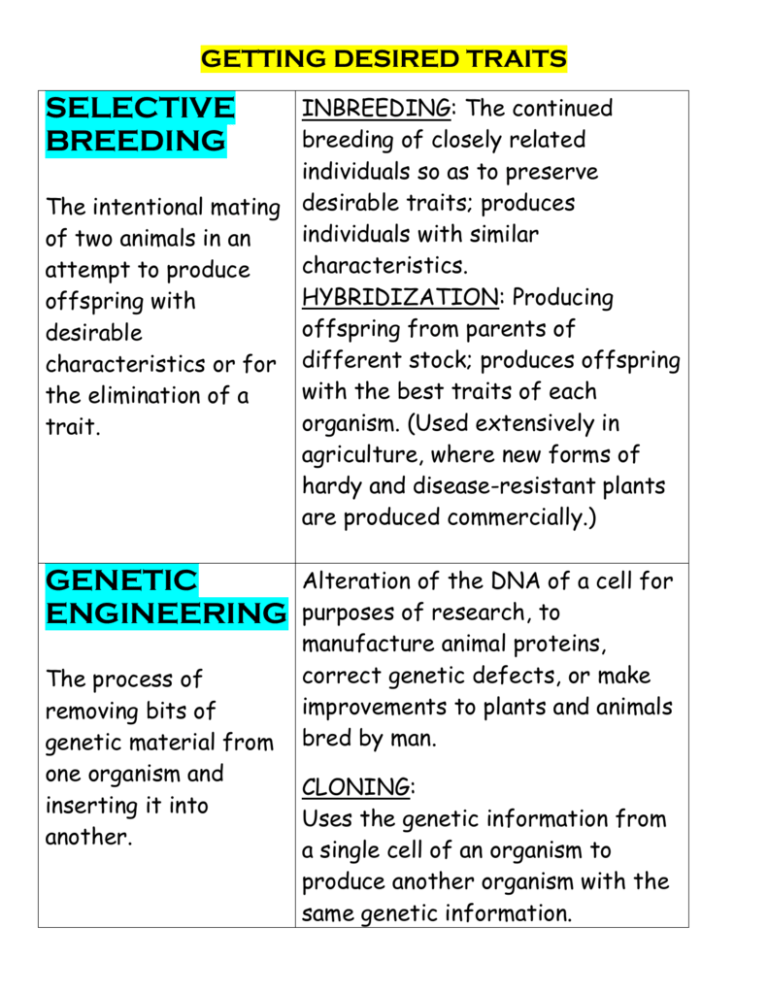
GETTING DESIRED TRAITS SELECTIVE BREEDING INBREEDING: The continued breeding of closely related individuals so as to preserve The intentional mating desirable traits; produces individuals with similar of two animals in an characteristics. attempt to produce HYBRIDIZATION: Producing offspring with offspring from parents of desirable characteristics or for different stock; produces offspring with the best traits of each the elimination of a organism. (Used extensively in trait. agriculture, where new forms of hardy and disease-resistant plants are produced commercially.) GENETIC ENGINEERING The process of removing bits of genetic material from one organism and inserting it into another. Alteration of the DNA of a cell for purposes of research, to manufacture animal proteins, correct genetic defects, or make improvements to plants and animals bred by man. CLONING: Uses the genetic information from a single cell of an organism to produce another organism with the same genetic information. MUTATIONS A change in the number, type or order or nucleotide-base sequence on a gene or DNA molecule deletion, insertion, substitution. SEX-LINKED DISORDERS Any disease or abnormal condition that is determined by the sex chromosomes or by a defective gene on a sex chromosome: Colorblindness, Hemophilia, Turner Syndrome, Klinefelter’s Syndrome