Scalp, Cranial Cavity, Meninges & Brain
advertisement

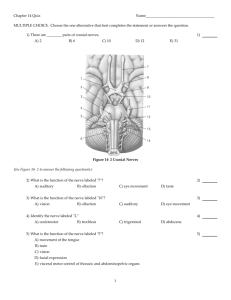
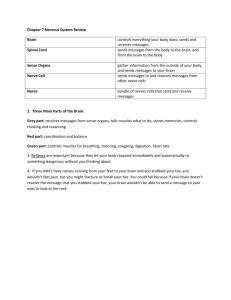
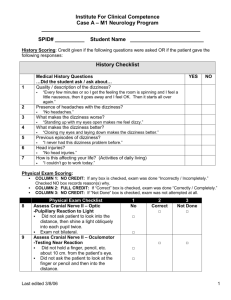
OBJECTIVES EXAM 4 Scalp, Cranial Cavity, Meninges & Brain: Define the scalp, its structural layers, muscles, nerves, and vessels. Identify the prominent landmarks on the internal surface of the skull base. Identify the major blood vessels of the brain, the specializations of cranial meninges, and cranial dural modifications. Identify the cranial nerves on the brain and their courses through the skull base. Identify the parts of the ventricular system and trace the flow of cerebrospinal fluid from production to reabsorption. Parotid Gland & Face: Identify three main neurovascular structures that traverse the parotid gland: the facial nerve, the retromandibular vein and external carotid artery. Identify the branches of the facial nerve in the face. Identify muscles of facial expression and nerve supply. Describe blood supply to the face. Describe cutaneous nerve supply to the head and face. Eye: Describe the components of the eyelids with associated muscles, tarsal glands, connective tissue fascia and conjunctiva. Identify the extraocular and intraocular muscles, their function and innervation. Identify all sensory, motor and autonomic nerves of the orbit and trace their routes to and within the orbit. Identify branches of ophthalmic arteries and veins. Ear & Nasal Cavity: Define the three parts of the ear and the function of each part. Describe each of the four walls of the middle. Describe the structure and actions of the tympanic membrane, the auditory ossicles, and the muscles of the middle ear. Trace the course of the facial nerve through the temporal bone and give the origin, course, and functional components of each of its intracranial branches. Identify the auditory tube and explain its function. Describe the maxillary nerve, its distribution and functional significance. Describe the nasal cavity, openings, nasal septum, conchae, meatuses, and its general neurovascular supply. List the paranasal sinuses and where each opens into the nasal cavity. Describe the hard and soft palate. Infratemporal Fossa & Oral Cavity: Identify the masticatory muscles and give their functions. Define the boundaries and contents of the infratemporal fossa. Identify the branches of the trigeminal nerve and their functions related to mastication and sensation from the face. Identify the chorda tympani nerve and give its function. Describe the structure and function of the temporomandibular joint. Describe the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands and give their innervations. List the muscles of the tongue and their innervation. Describe the oral cavity, its oral vestibule and dental arches, and the hard and soft palate. Anterior Triangle: Identify and list the attachments, innervation and action of the sternocleidomastoid, digastric and infrahyoid (strap) muscles. Identify the boundaries of the anterior and posterior cervical triangles and their subdivisions. Describe the cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus and identify their areas of distribution. Identify the deep cervical fascia, its various component layers and the resulting compartmentalization of the neck. Locate and describe the specific features of the thyroid gland. Give the position of the parathyroid glands and consider the thyroid/parathyroid gland relationship in terms of vascular supply and surgical intervention. Recognize and describe the contents of the carotid sheath and their relationships with surrounding structures. Locate the vagus nerve and give its relationships to the fascia, vessels and viscera of the region. Posterior Triangle: Identify the boundaries of the posterior cervical triangle and its subdivisions. Identify the scalene muscles and the first rib and relate them to the neurovascular structures at the root of the neck. Identify and list the parts and branches of the subclavian artery and vein, and describe their course in the neck. Identify the neurovascular entities that have different relationships to structures on the right and left sides of the root of the neck. In the root of the neck, locate the vagus and phrenic nerves and describe their relationships to the organs, fascia, vessels, and viscera of the neck. Identify the deep cervical lymph nodes and explain their significance. Viscera of Neck (Carotid Sheath, Pharynx, & Larynx): Review the arrangement, distribution and function of the cervical sympathetic trunk. Review the carotid sheath and contents. Identify, trace and describe the general functions of cranial nerves IX (glossopharyngeal), X (vagus), XI (spinal accessory), XII (hypoglossal). Describe the pharynx, its anatomical architecture and action of its musculature during swallowing. List the basic functions of the larynx. Identify the main cartilages and membranes that form the internal framework (skeleton) of the larynx. Describe the actions of the intrinsic muscles of the larynx in tensing, relaxing, abducting or adducting the vocal folds. Describe the innervation and vascular supply of the larynx. Cranial Nerves: List cranial nerves, Indentify origin and course of each nerve List functional components of each nerve and their innervation Identify the branches of each cranial nerve List parasympathetic ganglia and cranial nerves related to them (pre synaptic & post- synaptic) Identify clinical conditions related to specific cranial nerve injuries