VVV

6.
CHEMISTRY 204 Spring 2006
HOUR EXAM I
Dr. Christine Yerkes NAME _______________________________
February 15, 2006
SIGNATURE _________________________
QUIZ TA _____________________________
Test Form A
A. DO NOT open the exam until you are instructed to do so.
B. The exam has 7 pages. After you are instructed to begin the exam, please check to see that you have all 7 pages.
C. You should also have a list of helpful information and equations and a periodic table.
D. The exam contains 40 questions. The point value of each question appears next to the question number.
E. Academic dishonesty.
If cheating is observed, any students involved will receive a zero on the exam.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE ANSWER SHEET.
1. Use a soft lead pencil and make dark marks. Do NOT use a pen. Erase all changes completely.
2. Print your Name in the appropriate designated spaces, then blacken in the letter boxes below each printed letter, last name first, then your first name initial.
3. Under Network ID print your University Network ID starting from box #1, then blacken in the corresponding letters, numbers and/or dashes.
4. Sign your name (do not print) on the line provided. Your signature indicates that this is your work. Print your name underneath it.
5. Put your section number under course code:
AQA = 00001
AQF = 00005
AQB = 00002
AQG = 00006
AQC = 00003
AQI = 00007
AQD = 00004
AQJ = 00008
Mark only one answer for each question.
CHEMISTRY 204 Spring 2006
HOUR EXAM I page 1
Questions 1-5 are true/false questions. Answer a) for true and b) for false.
1. (2) Oxygenated hemoglobin is red and deoxygenated hemoglobin is blue. This is
because oxygen is a weak-field ligand and water is a strong-field ligand for Fe
2+
.
2. (2) In the separation of chloroform, CHCl
3
and ethanol, CH
3
CH
2
OH, by fractional distillation, chloroform is the product collected from the condensation tube.
This is because it is the larger of the two compounds, with stronger London
Dispersion Forces.
3. (2) Tetrahedral complex ions always show a larger d orbital splitting than octahedral complexes, with the same ligands.
4. (2) On the basis of the following vapor pressure data,
T ( o
C) P
H2O
(torr) P
D2O
(torr)
20 17.5 15.2
30
H
31.8 28.0 vap
for D
2
O is greater than that for H
2
O.
5. (2) A 5.0 M NaCl solution will have a lower freezing point than expected from ideal behavior.
6. (3) Potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) is the compound: a) K
4
[Fe(CN)
6
] b) KFe(SCN)
4 d) K
3
[Fe(SCN)
6
] e) K
4
[Fe(NCO)
6
] c) K
3
[Fe(CN)
6
]
7. (3) The magnetic moment of the square planar complex, Ni(CN)
4
2-
(in Bohr
Magnetons) is: a) 0 b) 1.4 c) 1.7
8. (3) Which of the following complexes is diamagnetic ? d) 2.8 e) 3.9 a) Ni(en)
3
2+
b) Cu(NH
3
)
4 d) Fe(CN)
6
4-
e) Co(Cl)
6
2-
2+ c) Ti(H
2
O)
6
3+
9. (3) The empirical formula for a coordination complex is Cu NO
2
.
6H
2
O. How many isomers can exist with this formula? (Consider all s tructural and stereoisomers). a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 e) 6
1
CHEMISTRY 204 Spring 2006
HOUR EXAM I page 2
Classify the following three compounds as: a) weak field b) strong field c) impossible to tell
10. (3) [Co(en)
3
]Cl
2
1 unpaired electron
11. (3) K
4
[Fe(OH)
6
] 4 unpaired electrons
12. (3) [Ni(CO)
6
](OH)
2
2 unpaired electrons
13. (3) A compound has the empirical formula Co(NH
3
)
5
Cl
3
. When an aqueous solution of this compound is mixed with excess silver nitrate, 2 moles of AgCl precipitate per mole of compound. When excess sulfuric acid is added to this compound, no
NH
4
+
ions are detected in the resulting solution. The correct name for this compound is: a) tetramminedichlorocobalt(III)ammonium chloride b) triamminetrichlorocobalt(III) c) ammonium pentaamminetrichlorocobaltate(III) d) pentaamminechlorocobalt(III) chloride e) none of these names (a - d) are correct
14. (3) Which of the following complexes exists as a pair of optical isomers? a) trans -tetraamminedichlorochromium(III) chloride b) cis -diamminedibromocobalt(III) chloride c) trans -diamminedibromocobalt(III) chloride d) transdiamminebis(en)cobalt(III) chloride e) tris(en)platinum(II) chloride
15. (3) Dilute, equimolar solutions of the following compounds are prepared. Arrange these compounds in order of increasing freezing points of the solutions, (lowest freezing point first).
I Na
3
[Co(NO
2
)
6
] II K[Cu(en)
2
Cl
2
] III Co(NH
3
)(CN)
3
IV [Cr(NH
3
)
5
Cl]Cl
2
V [ Pt(NH
3
)
6
]Br
4 a) V < I < IV < III < II b) I < II < III < IV < V c) III < II < IV < I < V d) V < I < IV < II < III e) II < III < IV < I < V
16. (3) Which of the compounds (I - V) in the previous question would be colorless? a) I b) II c) III d) IV e) V
2
CHEMISTRY 204 Spring 2006
HOUR EXAM I page 3
17. (3) The compound, [PtBrCl(NH
3
)
2
] exists as a pair of geometric isomers. Which energy diagram, below, correctly represents this compound? b) c) a) d) e) none of these (a-d) are correct
Hexaaquachromium(III) is a violet solution. In the next two (2) problems, predict how each of the treatments will affect the color of this compound.
18. (2) Oxidizing the chromium, to get hexaaquachromium(VI), will give a solution that a) appears more green b) appears more yellow c) remains violet, with a less intense color d) is colorless e) is apparently unchanged
19. (2) Replacing some or all of the H
2
O with cyanide, CN
-
, will give a solution that a) appears more green b) appears more yellow c) remains violet, with a less intense color d) is colorless e) is apparently unchanged
20. (3) How many unpaired electrons in the tetrahedral FeCl
4
-
complex? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3` d) 4 e) 5
21. (2) Potassium metal crystallizes in the body-centered cubic structure. The number of nearest neighbor atoms for each potassium atom in the solid is: a) 4 b) 6 c) 8 d) 10 e) 12
3
CHEMISTRY 204 Spring 2006
HOUR EXAM I page 4
22. (2) A compound contains two types of atoms, X and Y. Its crystal structure has a simple cubic lattice structure, with X atoms at the corners of the unit cell and Y atoms at the body centers. The simplest formula for this compound is: a) X
8
Y b) X
2
Y c) XY d) XY
2 e) XY
8
23. (2) The intermolecular forces in liquid A are considerably larger than the intermolecular forces in liquid B. Which of the following properties is expected to be smaller for A than for B? a) The vapor pressure at 20 o
C b) The temperature at which the vapor pressure is 100 torr c) The critical temperature d) the heat of vaporization e) the normal boiling point
24. (2) At a specified value of temperature and pressure, which of the following gases will show the greatest deviation from the ideal gas law? a) N
2 b) NH
3 c) NO d) Ne e) NF
3
25. (2) The normal boiling point of a liquid a) Is the temperature at which liquid and vapor are in equilibrium b) Varies with the atmospheric pressure c) Is the temperature at which the vapor pressure is 1 atm. d) Is the temperature at which the vapor pressure equals external pressure e) Is directly proportional to the molecular weight of the liquid
26. (2) The vapor pressure of a given liquid will decrease if a) the liquid is moved to a container in which its surface area is much smaller b) the volume of the liquid in the container is decreased c) the volume of the vapor phase is increased d) the temperature is decreased e) the number of moles of liquids is decreased
27. (3) BeCl
2
crystallizes in a face-centered cubic unit cell. The ionic radius of Be
2+ is 27 pm and the ionic radius of Cl
-
is 181 pm. With Cl
-
at the lattice points, which positions will be occupied by the Be 2+ ions? a) ¼ of the tetrahedral holes c) ½ of the tetrahedral holes e) all of the octahedral holes b) ¼ of the octahedral holes d) ½ of the octahedral holes
4
CHEMISTRY 204 Spring 2006
HOUR EXAM I page 5
28. (3) You are given a small bar of an unknown metal, X. You find the density of the metal to be 7.14 g/cm
3
. An x-ray diffraction experiment measures the edge of the unit cell as 291 pm. Assuming that the metal crystallizes in a body-centered cubic lattice, what is X most likely to be? a) Mg b) Ag c) Pt d) Cr e) none of these
Shown below is a graph of the vapor pressure of water, dichloromethane and chloroform as a function of temperature. Use this information to answer the next 2 (two) questions.
29. (2) Identify the compound which corresponds to each curve:
I II III a) H
2
O CHCl
3
CH
2
Cl
2 b) CH
2
Cl
2
CHCl
3
H
2
O c) CHCl
3
H
2
O CH
2
Cl
2 d) CHCl
3
CH
2
Cl
2
H
2
O e) CH
2
Cl
2
H
2
O CHCl
3
1000
800
600
400
200
I II III
20 40 60 80 100 120
30. (2) The normal boiling point of dichloromethane, CH
2
Cl
2
, is approximately: a) 40 o b) 60 o c) 80 o d) 100 o e) can't be determined from the data
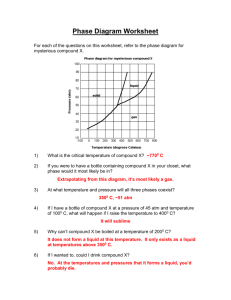
Use the phase diagram, shown below (not drawn to scale) to answer the following two (2) questions.
31. (2) Which of the following statements (a-d) is false , ?
4 a) This substance cannot exist as a liquid above 400K b) The normal boiling point is at about 100 K c) The solid is more dense than the liquid
P
(atm)
3
2 d) A pressure of at least 3 atm is required to condense
the gas at 400K
1 e) none of the statements (a-d) are false.
150
T (K)
32. (2) When a sample of this compound, kept at 2 atm pressure and at 100 K, is placed on a lab bench, at room temperature, it will a) vaporize b) melt c) sublime d) condense e) remain in the same phase
400
5
CHEMISTRY 204 Spring 2006
HOUR EXAM I page 6
33. (3) An aqueous solution of acetone, CH
3
COCH
3
, is 10.00% acetone by weight. What is the mole percentage of acetone in this solution? a) 3.3325% b) 5.000% c) 10.00% d) 11.11% e) 17.22%
34. (3) The freezing point of a solution prepared by dissolving 20.5461 g of a nonvolatile non-electrolyte with the empirical formula (C
3
H
2
) n
in 400.0 g of benzene is
4.33
o
C. The freezing point of pure benzene is 5.48
o
C, and the K f
= 5.1 kg K/mol.
The correct molecular formula of this compound is: a) C
3
H
2 b) C
6
H
4 c) C
9
H
6 d) C
15
H
10 e) C
18
H
12
35. (2) The value of K b
for water is 0.51 kg K/mol. The boiling point of a 1.00 m solution of CaCl
2
should be elevated by: a) exactly 0.51
o c) exactly 1.02
o e) exactly 1.53
o
C b) somewhat less than 1.02
o
C d) somewhat less than 1.53
o C
36. (3) The liquids benzene (78.11 g/mol) and toluene (92.14 g/mol) form ideal solutions.
At 35 o C the vapor pressure of benzene is 160.0 torr and the vapor pressure of toluene is 50.0 torr. If 64.05 g of benzene and 106.2 g of toluene are poured into a large container, which is covered and maintained at 35 o
C, what is the mole fraction of toluene in the vapor phase when the system comes to equilibrium? a) 0.305 b) 0.584 c) 0.624 d) 0.695 e) 0.762
37. (3) The concentration of a saturated solution of a certain non-electrolytic polypeptide is 1.0 x 10
-3
M at 25 o
C. The osmotic pressure, in torr, of this solution is: a) 0.0245 b) 0.760 c) 18.6 d) 24.5 e) 156
6
CHEMISTRY 204 Spring 2006
HOUR EXAM I page 7
Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
38. (3) At 35 o C, the vapor pressure of pure X is 512 torr and of pure Y is 344 torr. A solution of X and Y in which the mole fraction of X is 0.25 has a total vapor pressure of 600 torr. Which of the following statements about solutions of X and
Y is true ? a) A mixture of 100.00 mL of Y and 100.00 mL of X has a volume of
200.00 mL. b) When Y and X are mixed at 35 o C, heat must be absorbed in order to produce a solution at 35 o
C. c) When Y and X are mixed at 35 o
C, heat is released d) Raoult's law is obeyed by both X and Y for this solution. e) A mixture of 100.00 mL of Y and 100 mL of X will have a volume of significantly less than 200.00 mL
39. (2) What are possible identities of X and Y?
X Y a) CH
3
COCH
3
CH
3
OH b) CH
3
OH c) CS
2
CH
CH
3
3
COCH
COCH
3
3 d) CH
3
COCH
3
CS
2 e) CH
3
OH CH
3
CH
2
OH
40. (2) Which combination of compounds would give the vapor pressure diagram shown below (P solution
= ----)?
X Y a) CH
3
COCH
3
CH
3
OH
X Y b) CH
3
OH c) CS
2
CH
3
COCH
3
CH
3
COCH
3 d) CH
3
COCH
3
CS
2 e) CH
3
OH CH
3
CH
2
OH
XXX
X x
0
0 1
X
Y
7
CHEMISTRY 204 Spring 2006
HOUR EXAM I page 8
8