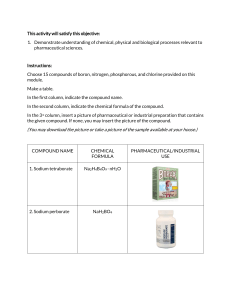
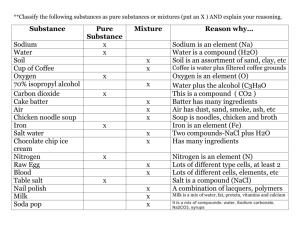
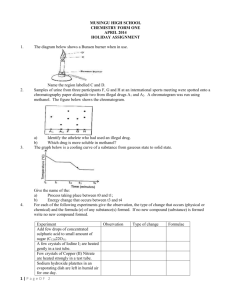
Acid A compound that produces hydrogen ions in solution, is a
advertisement

Acid A compound that produces hydrogen ions in solution, is a hydrogen-ion donor, or an electron-pair acceptor • Base These are chemical substances with a measurable pH above that of 7.0 on a 0-14 scale. • Boiling Point This is a temperature where the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the atmospheric pressure. • Chemical Property This is the ability of matter to change in to a different substance. Example:flammability, reaction to an acid • Compound This is two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio. Example:water, carbon dioxide, sodium chloride. • Conductivity The ability or power to transmit heat, electricity, or sound. Example:Metals transfer heat, electricity, and soundbetter than nonmetals • Chemical Property This is the ability of matter to change in to a different substance. Example:flammability, reaction to an acid • Compound This is two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio. Example:water, carbon dioxide, sodium chloride • Conductivity The ability or power to transmit heat, electricity, or sound. Example:Metals transfer heat, electricity, and soundbetter than nonmetals. • Density This is a measure of mass per unit volume. Example:the reason oil floats on top of water • Element This is a substance that cannot be broken down further by chemical means. Example:sodium, tungsten, iodine Gas This is the phase of matter with no fixed shape or volume. Example:Air, water vapor • Heterogeneous This is a mixture that has different properties throughout. Example:a chocolate chip cookie, salad dressing,pizza • Homogeneous • This is a mixture that has the same composition throughout. Example:sweetened iced tea (without the ice),vinegar, saltwater • Inorganic This usually refers to any element or compound that does not contain carbon. Example:water, zinc metal, sodium chloride • Liquid This is the phase of matter with no fixed shape but fixed volume. Example:water at room temperature