Bones of the Skull
advertisement

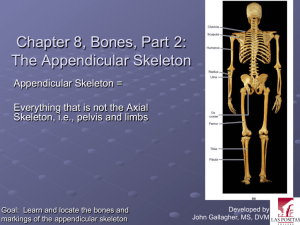
Bones of the Appendicular Skeleton Body Region Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Arm or brachium Forearm Hand & wrist Bone Location Markings Clavicle (“little keys”) Superioranterior thorax; articulates medially with sternum and laterally with scapula Posterior thorax; forms part of the shoulder; articulates with the humerus & clavicle Acromial end; sternal end Humerus Sole bone of arm; between scapula & elbow Ulna (“elbow”) Medial bone of forearm between elbow & wrist; forms elbow joint Radius (“rod”) 8 carpals (16) scaphoid lunate triquetral pisiform trapezium trapezoid capitate hamate Lateral bone of forearm; carries wrist Form a bony crescent at the wrist; arranged in 2 rows of 4 bones each Head; greater & lesser tuberosities; intertubercular sulcus; deltoid tuberosity; trochlea; capitulum; coronoid and olecranon fossa; radial groove; epicondyles (trochlea = “pulley”; capitulum = “small head”) Coronoid process; olecranon process; radial notch; trochlear notch; styloid process; head (coronoid= “crown-shaped”; stylod= “stake-shaped”) Radial tuberosity; styloid process; head; ulnar notch To help you remember the carpals in the order given: 5 metacarpals Form the palm; one in line with each digit Form the fingers; three in digits 2-5; two in digit 1 (the thumb) Scapula 14 phalanges (28) distal middle proximal Scaphoid = “boat-shaped” Lunate= “moon-like” Triquetral = “triangular” Pisiform = “pea-shaped” Trapezium = “little table” Trapezoid = “4-sided” Capitate = “head- shaped” Hamate = “hooked” Phalanx= “closely knit row of soldiers” Glenoid cavity; spine; acromion; coracoid process; infraspinous, supraspinous, and subscapular fossa (acromion = “apex of shoulder”; corac= “like a crow’s beak”) Sally left the party to take Carmen home. The first letter of each word is the first letter of each carpal bone. Body Region Pelvic girdle Lower limb Thigh Kneecap Leg Ankle and foot Bone Location Markings Coxal bone or os coxae (os=bone; coxa=hip) Formed by the fusion of an ilium, ischium, and pubic bone; the coxal bones fuse anteriorly at the pubic symphysis and form sacroiliac joints w/the sacrum posteriorly; girdle consisting of both coxal bones is basinlike Iliac crest; anterior and posterior iliac spines; auricular surface; greater and lesser sciatic notches; obturator foramen; ischial tuberosity and spine; acetabulum; pubic arch; pubic crest; pubic tubercle Femur Sole bone of the thigh; between the hip joint and knee; largest bone of the body Head; greater and lesser trochanters; neck; lateral and medial condyles and epicondyles; gluteal tuberosity; linea aspera Patella (“small pan”) Tibia (“shinbone”) Sesamoid bone lodged in the tendon of the quadriceps muscles Larger and more medial bond of leg; between knee and foot Fibula (“pin”) 7 tarsals (14) talus calcaneus navicular cuboid lateral cuneiform intermediate cuneiform medial cuneiform Lateral bone of the leg; sticklike Tarsals are 7 bones forming the proximal part of the foot; the talus articulates with the leg bones at the ankle joint; the calcaneus, the largest tarsal, forms the heel 5 metatarsals (10) 14 phalanges (28) distal middle proximal 5 bones numbered 1-5 (m l) Phalanges for the toes; three in digits 2-5, two in digit 1(the great toe) Talus = “ankle” Cuboid = “cube-shaped” Cuneiform = “wedge-shaped” Medial and lateral condyles; tibial tuberosity; anterior border; medial malleolus Head; lateral malleolus