Educational Philosophies: Perennialism to Pragmatism
advertisement

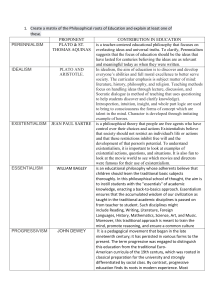
Purpose of Ed? Educational Psychology Dr. Steve Rhine Perennialism Idealism Essentialism Behaviorism •Absorption of ideas •Acquire unchanging principles and great ideas •Make S's valuable members of society •Pass on intellectual and social heritage of generations •Absorption and mastery of facts and behaviors Progressivism •Learn problem solving, rational thinking •Become a citizen of society •Provide new experiences Existentialism Reconstructionism Humanism Pragmatism •Help S's find meaning and purpose in their lives •Aid in the search for self •Who am I? Why am I? •Build a new social order, schools leading •Change society •Education/ literacy is power •Learn to wield power in humanitarian, equitable ways, Not to become new oppressors •Transmit knowledge about existing social order Educational Psychology Dr. Steve Rhine Methods/Learn best? Perennialism Idealism •Begin with subject matter, not student •Correct and critical thinking •Teacher as example of values and ideas •Emphasize rational thinking •"Sage on the stage, not guide on the side" Essentialism •Hold natural, nonproductive instincts in check •Develop rational thinking skills Behaviorism Progressivism •Individualized program •Teacher as mental disciplinarian, leader/model •Education is training •Begin with student, not subject matter •Teacher as challenger, inquiry leader •Learning is active not passive •Teachers provide experiences so S's learn by doing •Continual selfanalysis and reflection •Teacher as facilitator "guide on the side, not sage on the stage" Existentialis Reconstructionism m Pragmatism Humanism •Teacher as noninterfering sounding board •T's allow for freedom of choice •T's provide s's with experience s that help them find meaning in their lives •Teacher as project director and research leader •S's research ideas •Discussion of new perspectives, extensive interactions experiences •Literacy (Freire) •Experience is important, studentcentered Educational Psychology Dr. Steve Rhine Skills or knowl? Perennialism Idealism •Great ideas from scholars, poets •Great principles (as opposed to specific content) •"Truth" •Rational thinking processes Essentialism Behaviorism Progressivism •Our culture has a core of common knowledge that schools are obligated to transmit-our social and intellectual heritage •Back to basics •Intellectual and moral standards •Communica te clearly, logically •Arts=frills •Facts •Learned behaviors •Control of behavior •Problem finding and solving skills •Content determined by students' interests •Humankind and knowledge are constantly changing, so prepare S's for future with problem solving strategies to cope with life •Learn what is important to them, not "enduring truths" Existentialism Humanism •What is important to the individual •Individual meaning •Respect for others freedom Reconstructionism Pragmatism •Openmindedness, ability to think from multiple perspectives •Problem solving skills •Literacy Educational Psychology Dr. Steve Rhine People Perennialism Idealism Essentialism Mortimer Adler (Paideia Proposal), Robert Hutchins (Great Books Program), Augustine, Plato, Aristotle, St. Thomas Acquinas E.D. Hirsch (Cultural Literacy), William Bagley, Rickover, Horace Mann B A Behaviorism John Watson, B.F. Skinner, Ivan Pavlov E Progressivism John Locke, John Dewey, William Glasser (Quality School), Maria Montessori C Existentialism Humanism Reconstructionism Pragmatism Sartre, Maxine Greene, Carl Rogers, John Holt (Home Schooling), A.S. Neill Brameld, Paolo Freire (Pedagogy of the Oppressed), Jonathon Kozol (Savage Inequalities), Michael Apple D