Philosophical Foundations - Foundations of Curriculum

Philosophical Foundations
Foundations of Curriculum
Philosophy
-
Study of wisdom (Love of wisdom)
Philosophy fundamental question:
Metaphysic - What is real?
Epistemology - What is truth?
Axiology - What is of value?
Philosophy and Curriculum
“Philosophy is the beginning point in curriculum decision making and is the basis for all subsequent decisions regarding curriculum” –
John Goodland
As cited on page 31
Tyler’s view of philosophy in relationship to school purpose
Suggestions from
Subject
Specialists
Studies of
Learners
Studies of
Contemporary
Life
School
Purposes
Use of
Philosophy
Use of
Psychology of
Learning
Major Philosophies
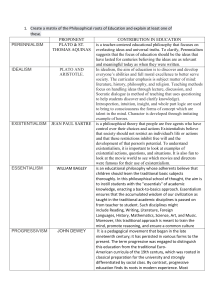
Idealism
Realism
Pragmatism
Existentialism
Idealism
Highest aim is the search for truth and values that will stand the test of time
Truth and values are seen as absolute, timeless, and universal
Idealism curriculum
Curriculum is hierarchical. Concept and abstract subjects are the top subjects. (Philosophy, theology)
Promotes abstract thinking
(Mathematics is considered important because it cultivates the power to deal with abstract thinking)
Language subject is important
Realism
People can come to know the world through their senses and reason.
Things happen according to purpose and in an orderly way (Natural law).
Truth emanate from both science and art
Realism Curriculum
Logic and lessons that exercise the mind and that cultivate rational thought are streessed.
Three R’s (Reading, Writing,
Arithmatics)
Ethical, political, economic thought
Has organized separate subjects curriculum. For example study of humankind experience becomes history subject.
Pragmatism
Referred to as experimentalism, based on change, process, and relativity.
Construes knowledge as a process in which reality is constantly changing
Nothing can be viewed intelligently except in relation to a pattern
Truth is no longer absolute or unversal
Pragmatism Curriculum
Views teaching as more exploratory than explanatory
Considers teaching and learning as process of reconstructing experience according to scientific method
Focuses on problems solving
Existentialism
Stress in individualism and personal self-fulfillment
Prefer to free learner to choose what to study and determine what is truth
Recognizes few standards, customs or tradition.
Existentialism Curriculum
Consists of experiences and subjects that lend themselves to philosophical dialogue and acts of choice making: Literature, drama, filmaking, art, etc.
Classroom would be rich in materials.
Stresses self-expressive activities, experimentation, and methods and media.
Focuses on learner’s feelings, emotions, and insights.
Educational Philosophies
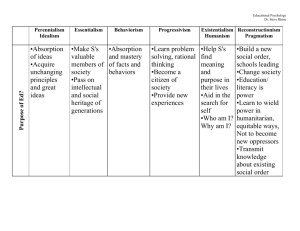
Perennialism
Essentialism
Progressivism
Reconstructionism
Perennialism
Philosophical Base: Realism
Aim: To educate the rational person
Knowledge: Focus on past and permanent studies. (Preserving the past knowledge)
Role of teacher: Helps students to think rationally. Teacher is an authority in the field (Unquestionable)
Teaching method: Socratic method, oral exposition (lecture), explicit teaching of traditional values
Perennialism Curriculum
Classic subjects: Literature, language, mathematics,
Constant curriculum (Unchanged)
Common curriculum for all (Little room for electives and vocational)
Students has no freedom to choose
Perennialism Curriculum
Paideia proposal
Liberal Arts
Essentialism
Philosophical base: Realism and Idealism
Aim: To promote intellectual growth and educate the competent person
Knowledge: Essential skills, master of concepts, and principles
Role of teacher: Authority in the field.
Teaching method: explicit teaching of traditional values. Tough discipline.
Essentialism Curriculum
Essential skills (Three R’s)
Essential subjects: English, Science, history, math, foreign language
Affected by the demand of the public to raise the academic standards and to improve students’ work and minds
Subjects that have contents are emphasized rather than process
Essentialism Curriculum
Back-to-basic curriculum
Excellence in education
Cultural literacy
Progressivism
Philosophical base: Pragmatism
Aim: To provide democratic, social living
Knowledge: Growth and development, living learning process, focus on active and relevant learning
Role of teacher: To guide
Teaching method: Problem solving and scientific inquiry.
Progressivism Curriculum
Curriculum should be based on student’s interests. Should be applicable for human affairs (solving problem).
Interdisciplinary subject matter.
Focus on activities and projects.
Reality is changing therefore no need to focus on fixed body of knowledge.
Process is more important than content
Progressivism Curriculum
Relevant curriculum
Humanistic education
Radical school reform
Reconstructionism
Philosophical base: Pragmatism
Aim: To improve and reconstruct society.
Education is for change and social reform
Knowledge: Skills and subjects that identify problems of society. Active learning with focus of contemporary and future.
Role of teacher: Agent of change and reform
(Project director)
Teaching method: Case study, involve students for social responsibilities. Neutrality is not an option. Social analysis, interpretation, and evaluation activities
Reconstructionism Curriculum
Emphasis on social sciences and social research methods
Examination of social, economic and political problem
Focus on present and future as well as local and global issues
Reconstructionism Curriculum
International education
Equality of educational opportunity
Adventist Philosophy
Philosophical base: Theism
Aim: Restoration of man to God’s image
Knowledge: Bible Values.To prepare responsible citizen for the world today and the world to come. Balance
Education- Spiritual, Physical, Mental,
Social (Wholistic Education)
Role of teacher: Lead student for Christ
Teaching method: Faith Integration, practical, living by example (modeling).
Adventist Curriculum
Curriculum Focus: Salvation,
Redemption.
Subjects: Bible subjects in every program, health subject, vocational, work education, service learning, outreach.
Curriculum Trends
Adventist curriculum trends?
Health message
Vegetarianism
Sanitarium
Academy (Boarding School)
Isolated schools.
Educational Excellence.
Integration of Faith and Learning.