Study Guide Answers Unit 4
advertisement

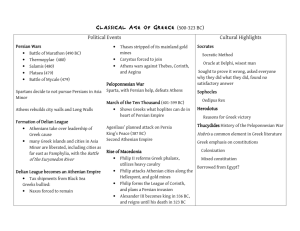
Ancient Greece Study Guide GREEK GEOGRAPHY 1. Large sea located south of Greece Mediterranean Sea 2. Small sea located east of Greece Aegean Sea 3. Prevented the Greeks from uniting and slowed travel and communication Mountainous terrain 4. Limited fertile land forced Greeks to use this for a living. The Sea for trade and food 5. These were communities created along the coast of the Mediterranean; designed to send crops back to Greece. Colonies **** Know the map of Greece**** GREEK ECONOMY and SOCIETY 1. name given to Greek culture “ Hellenic Culture” 2. economy based on ______trade_____ instead of agriculture POLITICAL DEVELOPMENT 1. Name for a Greek city-state polis 2. Greek cities were designed to encourage civic life and commercial (trade) life. 3. Why were colonies created along the Mediterranean Sea? Overpopulation and lack of arable (farmable) land in Greece 4. Different forms of Greek government: a. Name for the rule of kings Monarchy b. Rule by a few noble families Oligarchy c. Rule by a single leader, usually military Tyranny d. Government by the people Democracy 5. What describes a Greek “citizen” Male, from that city-state, not a slave, 18 and over 6. Three (3)groups of people with NO political rights in Greece: slaves, women, foreigners ATHENS 1. Two tyrants who worked for reforms: ____Solon and Draco___________ 2. Principles of Democracy: a)________Citizens have duties (like voting and serving int the military, paying taxes)_____ b)________Direct democracy: every citizen can vote_ c)________Public Debate___________________ 3. Name of the Athenian alliance during the Peloponnesian War: ______Delian League_______________________________ SPARTA 1. Type of government ____oligarchy______________ (small group) 2. society centered around the Spartan ____army _____________ 3. Name for the Spartan alliance during the Peloponnesian War: _____ Peloponnesian League ____________________________ GREEK MYTHOLOGY 1. Greek religion was ____polytheistic______. 2. They used myths to explain __natural phenomena (weather, sea storms, thunderstorms, etc.)_____. 3. Chief god ___Zeus_________________ 4. the god of the sun _Apollo______ 5. Protector of Athens Athena 1. Historical enemy of all Greek city-states Persia 2. Greeks who had a militaristic society Spartans 3. War between the Greeks and the Persians Persian Wars 4. Greek city that grew in power and influence over its allies Athens 5. Leader of Athens after the Persian War Pericles 6. Time period of growth and prosperity for Athens_____ the Golden Age _____ 7. War fought between 431 BC and 404 BC Peloponnesian Wars 8. The former ally but later an enemy of Athens Sparta 9. Building constructed at the time of Pericles Parthenon 10. Writers of tragedies Aeschylus (Orestia) and Sophocles (Oedipus) 11. Historians of Greece Herodotus (Persian Wars) and Thucydides (Peloponnesian Wars) 12. Two famous epic poems by Homer Iliad and Odyssey 14. Father of Geometry, wrote “Elements” Euclid 15. Famous Greek philosopher; killed by the government of Athens Socrates___ 16. Student of the man listed in No. 15, Wrote the Republic Plato 17. Student of the man listen in No. 16, tutored Alexander the Great ___ Aristotle _____ 18. Who was the Greek who developed the way to measure volume of irregular objects and a screw to lift water? ____ Archimedes ___ 19. Who was the father of medicine? ____ Hippocrates ______ 20. Who developed a theory about right triangles? ___ Pythagoras ____ A Herodotus and Thucydides B Pythagoras C Archimedes D Pericles E Peloponnesian Wars F the Golden Age G the Age of Growth H Aeschylus and Sophocles I Socrates J Athens K Sparta L Iliad and Odyssey M Parthenon N Plato O Spartans P Persians Q Persian War R Aristotle S Hippocrates T Euclid Greek Architecture can be seen in its styles of columns. They are (in order) A) Doric B) Ionic C) Corinthian 1. What war made it easier for the Macedonians to conquer Greece? _________Peloponnesian War_________ 2. What Macedonian conquered most of Greece? _____Phillip II______________________ 3. Name 3 areas controlled by Alexander the Great. _____Persia, Egypt, Inida, Greece______ 4. What did Alexander the Great spread? __Hellenic _CULTURE_ 5. What was Hellenistic culture? _____a mix of Greek, Perisan, and Egyptian culture___ 6. How did Alexander inspire loyalty among the people he conquered? He adopted some of their cutoms, let people in the Persian empire keep their system of satrapies, he worshipped the gods of the people he conquered, he kept his Macedonians in charge of the army and taxes to prevent revolt, he destroyed cities that revolted, he spread Greek culture, and he promoted himself as a god.