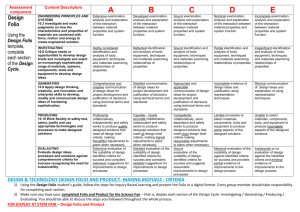
Areas of study
advertisement
Senior school handbook 2005 Contents Subjects are arranged by faculty groupings Subject Units Page Art 1-4 7 Media 1-4 8 Studio arts- printmaking/ drawing 1-4 9 Studio arts- glass 1 -4 10 Studio arts-fashion/ costume design 1-4 11 Studio arts-photography 1-4 12 Visual Communications 1-4 13 Accounting 1-4 14 Business Management 1-4 15 Legal Studies 1-4 16 English 1-4 17 English as a Second Language (ESL) 1-4 18 Literature 1-4 19 Health & Human Development 1-4 20 Outdoor & Environmental Studies 1-4 21 Physical Education 1-4 22 1-4 23 History- Applied history in the local community 1 24 History- Power and people 2 24 History- Australian 3&4 25 History- Revolutions 3&4 25 History- 20th Century 1&2 26 International Studies 1&2 26 ART BUSINESS STUDIES ENGLISH HUMAN DEVELOPMENT HUMANITIES Classical Societies and Cultures Politics 3&4 27 1 -4 28 Information Technology 1&2 29 Information Processing and Management 3&4 29 Information Systems 3&4 30 French 1-4 31 Italian 1-4 31 Philosophy INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY LANGUAGES OTHER THAN ENGLISH (LOTE) MATHEMATICS Deciding which Maths to do 32 Foundation Mathematics 1&2 33 General Mathematics 1&2 33 Mathematical Methods 1-4 34 Specialist Mathematics 3&4 35 Further Mathematics 3&4 35 Drama 1-4 36 Theatre Studies 1-4 38 Music Performance 1&2 39 Music Performance- Group 3&4 40 Music Performance- Solo 3&4 40 Biology 1-4 41 Chemistry 1-4 42 Physics 1-4 43 Psychology 1-4 45 Design and Technology 1-4 46 VOCATIONAL EDUCATION AND TRAINING (VET)/VCE 1-4 48 School Based New Apprenticeships 1-4 48 PERFORMING ARTS SCIENCE TECHNOLOGY STUDIES MEETING THE REQUIREMENTS OF THE V.C.E. & VCAL VCE: Victorian Certificate of Education VCAL: Victorian Certificate of Applied Learning What is the difference between VCE and VCAL? VCE is a valuable pathway to further study at university, TAFE and the world at work. It is possible to complete a school based apprenticeship or traineeship within your VCE. A VCE program will usually consist of 20 –24 semester units taken over two years. VCAL gives practical hands on experience, as well as literacy and numeracy skills and the opportunity to build personal skills that are important for life and work. Like the VCE, it is a recognised qualification. Students who do VCAL are likely to be interested in going on to training at TAFE (Technical and Further Education), doing an apprenticeship, or getting a job after completing school, rather than attending university. However, if you start your VCAL and then decide VCE is the right option for you, you can change your mind. In fact, any VCE units you complete as part of VCAL will count towards your VCE, just as VCAL units will count towards VCE. Structure of the VCE Certificate The Victorian Certificate of Education is a two-year certificate for Years 11 and 12. It is made up of units of study that run for one semester. The studies available come from English, Arts/Humanities and Mathematics/Science/Technology. Students must select 4 units of English To obtain the VCE, students must satisfactorily complete 16 units including: at least 3 units of English (to receive an ENTER score, students must satisfactorily complete English, ESL or Literature, Units 3 & 4) at least 3 sequences at Units 3/4 level (ie. 6 units) in studies other than English, of which 2 may be VCE VET sequences. All students must study English/ English as a Second language and/or English Literature at Year 11 and Year 12 levels. Sequence of Units It is usual for units at the 1/2 level to be taken in Year 11 and Units at the 3/4 level in Year 12. However, some students may take one unit 3/4 sequence in Year 11 (after consultation with coordinators). Some students may choose to study VCE over 3 years, mixing units 1/2 and units 3/4. In Year 11, subjects may be taken for one unit only (ie. changes in subjects can be made for Unit 2). In Year 12 subjects must be taken for the whole year. Assessment At Years 11 and 12 the award of satisfactory completion for a unit is based on a decision that the student has demonstrated the set of outcomes specified for that unit. In making this decision, the teacher will use a selection of designated assessment tasks and course work. For units 3 and 4, levels of performance are assessed by school-assessed coursework (set and marked by the teachers), according to guidelines from VCAA (Victorian Curriculum & Assessment Authority) as well as exams (set and marked by VCAA). For Units 1 and 2, levels of performance are assessed by the designated assessment tasks (set and marked by the teachers) VET (Vocational Education & Training)/VCE VET/ VCE subjects are offered to years 10, 11 and 12. These are usually run by TAFE and are usually held at a campus outside Princes Hill Secondary College on Wednesdays. These units give Nationally Accredited Training Certificates as well as VCE units Equivalent National Tertiary Entrance Rank (ENTER) A mark out of 99.95 is given to all students who complete the VCE and who apply through VTAC (Victorian Tertiary Admissions Centre) for tertiary admission. This is calculated from the student’s scores in Units 3 and 4 of English, Literature or ESL, the student’s next best three scores and 10% of the student’s next two best scores. Further Mathematics and Specialist Mathematics cannot be done in the same year. If they are done studied in separate years, only one can be counted in the primary four and the other would count as an increment. Only one of the following combinations can be used in the best six (that is, in the calculation of the ENTER): English or ESL Chinese (FL) or Chinese (SL) Indonesian (FL)or Indonesian (SL) Japanese (FL) or Japanese (SL) Korean (FL) or Korean (SL) No more than two Mathematics studies, no more than two Music studies, no more than two History studies, no more than two English studies and no more than two LOTEs (Languages Other Than English) can be included in the “primary four”. (Other mathematics, musics, histories, English studies and/or LOTEs can be used as a 10% increment.) A maximum of one sequence of Units 3 & 4 (with a study score) of a VET program may be counted in the primary four, and a total of 2 VET VCE in the program. Units 3 & 4 (with study score) of any VET programs may be used for 5th & 6th study increments for the ENTER. Units 3 & 4 of a VET program where no study scores are available may be used for 5 th and 6th study increments. It will be 10% of the average of the primary 4 score The Relevance of a Study to a Career Some tertiary courses require that students have taken certain units while other units may be recommended. The Victorian Tertiary Admissions Centre (VTAC) has published details of tertiary entrance requirements for 2006 and 2007. All students are advised to obtain a copy of these requirements. Full details are available from the Careers Adviser and at www.vtac.edu.au Students and parents are advised to consider carefully the tertiary prerequisites for the various courses and to consult the VCE Coordinators or the Careers Adviser if there are any doubts about these. VCAL (The Victorian Certificate of Applied Learning) At Princes Hill it is possible to complete a VCAL certificate at Foundation, Intermediate or Senior level – the levels roughly correspond to years 11 and 12. Students complete three compulsory VCAL studies, a VET study and 2 VCE studies. VCE, VET and VCAL are offered to all year 11 and 12 students in the one subject selection grid. The three compulsory VCAL units are indicated on the selection sheet with an asterisk. VCAL units 1. English – Literacy – Foundation, Intermediate or Senior level. The aim of these units is to develop students’ knowledge, skills and understanding in literacy in the contexts of family and social life, workplace and further education settings and in the wider community. The overall purpose is to provide an applied real-life approach to literacy development. This consists of two units, including a reading and writing unit and an oral unit, studied over two semesters. Work Related Skills – Foundation, Intermediate or Senior level. The aims of this unit are: to develop key competencies and employability skills through a workrelated context, to develop and apply critical thinking skills, to develop planning and organisational skills, to provide experiences that prepare students for a vocational context and to develop particular interests and abilities that may link to employment-related goals. This is one unit, studied in conjunction with Literacy. 2. Maths – Numeracy – Foundation, Intermediate or Senior level. The aim of this study is to apply Maths skills to tasks which are part of students’ everyday life, the workplace and the community. Students are asked to develop everyday numeracy to make sense of their personal and public lives. This study is made up of one unit. It will be decided at a later date whether the one unit will be done over a whole year, or whether another unit will be taken. 3. Personal Development – Foundation, Intermediate or Senior level The aim of this study is to develop students’ self esteem and personal growth. Students are asked to develop their skills and abilities in leadership, teamwork, goal setting, time management, accepting responsibility, decision making, problem solving and reflection. This is largely met through the design, implementation and evaluation of individual, group or community-based projects. This study is made up of two units, one undertaken each semester. Industry Specific Skills – Foundation, Intermediate or Senior level Through a VET (Vocational Education and Training) study students develop knowledge and skills in a vocational context, undertake vocational experience in relation to their interests and abilities, and establish pathways to further studies through credits gained that articulate into a VCE or VET course. A VET study is made up of two units, one undertaken each semester. VET may be done as part of the VCE rather than VCAL. These units can also be done through SBNAs (School Based New Apprenticeships). See p. 49 for more details. 5 VCE studies as part of the VCAL qualification Students select two additional VCE studies from the course selection grid. At year 11, these would normally be at Unit 1 & 2 level. At senior level this would normally be Units 3 & 4. Completion To complete a VCAL certificate a student must successfully complete 10 units including: One unit of English – Literacy One unit of Maths – Numeracy One VET study One unit of Work Related Skills One unit in Personal Development Student VCE Handbook 2005 At the start of Term 1, all VCE students will be given a handbook outlining the procedures for assessment and rules for the implementation of the VCE at Princes Hill Secondary College. Subjects offered in 2005 The following pages describe the subjects offered by Princes Hill Secondary College for 2005. These are merely outlines: for further information, you should see the current teacher of the subjects, Subject area coordinators, year level coordinators and the careers coordinator. 6 Visual Arts Unit 1 Art Units 1- 4 Unit 3 Areas Of Study 1. Art Production – Developing ideas and skills This focuses on visual solutions developed through an exploration of techniques and working methods. It explores the characteristics of selected art forms and media. 2. Art Appreciation – Art and Society This focuses on the ways in which art reflects the values, beliefs and traditions of the society for which it was created. Assessment Areas of Study 1. Art Production Investigation and Interpretation This focuses on making personal art responses through a broad investigation, which includes exploration and experimentation in one or more media to prepare and develop a sustained body of work. 2. Art Appreciation – Interpreting Art This focuses on using interpretive frameworks to respond critically to art works from two periods of art: pre 1970 and post 1970 (contemporary). Folio, extended written responses, annotated visual reports and contribution to class discussions. Assessment Students are expected to supply their own materials Art Unit 2 Areas of Study 1. Art Production – Exploring ideas and issues This involves the development of areas of personal interest in visual explorations and the communication of ideas and directions. 2. Art Appreciation – Art and the Individual This area of study focuses on the ongoing interest in artists and their distinctive approaches to creativity and individuality. Assessment Folio of three major art works, analysis of three major works, written reports, short answers and contribution to class discussions. Students are expected to supply their own materials Assessment is based on both practical and analytical work, demonstrating the development of the student’s thinking and work practices. Students are expected to supply their own materials Art Unit 4 1. Art Production – Realisation and resolution the preparation of a final presentation of concepts, ideas and/ or observations developed and refined from the visual directions explored in unit 3. 2. Art Appreciation – Discussing and debating art Exploring the meanings and messages of art through interpretation of selected art works Assessment Assessment is based on exploratory or finished folio, personal substantiated interpretations in selected artworks and an end of year exam. This course is also assessed by School Assessed Tasks and School Assessed Coursework Students are expected to supply their own materials 7 Visual Arts Media Units 1 - 4 Media Unit 1 Presentation and technologies of representation Areas of Study Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Representation Technology New media Assessment Print layouts / posters Photographs / audiovisual multi-media display Tests. Short written reports. Oral report. At least one of the assessment tasks in Unit 1 must be in written form. Media Unit 2 Media Production & The Media Industry 1. 2. Narrative Media Production Design Assessment Written analyses (Outcome 1) Two technical exercises relevant to the specifications identified in the production design plan. School assessed coursework for Unit 3 (Outcomes 1 and 2) contribute 8% to the final assessment. Outcomes 2 & 3 in Unit 3 and Outcome 1 in Unit 4 will be assessed through a 35% school-assessed task. Media Unit 4 Media processes, social values and media influence Areas of Study Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. Media Production Media industry production Australian media organisations Assessment Print layouts / posters Photographs / audiovisual multi-media display Tests. Short written reports. Oral report. At least one of the assessment tasks in Unit 2 must be in written form. 8 Media Unit 3 Narrative and media production design Media Process Social Values 3. Media Influence Assessment School assessed coursework for Outcomes 2 and 3 will contribute 12% to final assessment. Written analyses and texts. A two hour exam contributes 45% to final assessment. Studio Arts Print/ Drawing Unit 1 Artistic Inspiration & Techniques Areas of Study Units 1- 4 1 Developing Art Ideas Investigating sources of inspiration and various methods used to record, interpret and translate observations into visual images. 2. Materials and Techniques Develop skills in printmaking and drawing, using a variety of materials and techniques in the production of art works . 3.Interpretation of art ideas and use of materials and techniques The way artists from different times and locations have interpreted ideas and sources of inspiration and use materials and techniques in the production of art works. Assessment Assessment is based on a folio of printmaking/ drawing work, a folio that documents the development of these pieces and a series of written works investigating the ways in which artists from different cultures have gained inspiration and explored materials and techniques. Unit 2 Design exploration and concepts Areas of Study 1. Design Exploration Developing artworks through a design process of visual research and inquiry. 2.Ideas and styles in artworks Development of skills in the visual analysis of artworks. Assessment Assessment is based on a folio of design explorations and written presentations that analyse artworks from different times and locations and discuss the aesthetic qualities used to communicate the artist’s intention Unit 3 Studio production and Professional practices Areas of Study 1. Work brief – this area of study focuses on the development of a work brief that creates a framework for the design process. 2. Design process – this area of study focuses on the exploration and development of the design process as documented in the work brief. 3. Professional practice – this area of study focuses on professional art practices in relation to particular art forms and the development of distinctive styles in art works. Assessment A written work brief, a developmental folio and two written assignments that research the ways in which artists from different times and locations have developed aesthetic qualities and distinctive styles when making artworks. Outcomes 1 and 2 are subject to external review. (33%) SAT 1 Outcome 3 will form part of the end of year exam. Unit 4 Studio production and art industry contexts Areas of study 1. Focus statement – this area of study focuses on the preparation of visual and written documentation that explains the artwork to be completed for the folio. 2. Folio – this area of study focuses on the production of a cohesive folio of finished artworks developed from potential solutions. 3. Art Industry contexts – this area of study focuses on the presentation of artworks and current art industry issues. Assessment 1. Present a visual and written focus statement, a folio that consists of no less that two finished artworks 2. A 1 ½ hour examination based on work done in Outcome 3 from Units 3 and 4. (34%) Outcomes 1 and 2 are subject to external review. (33%) SAT 2 9 Studio Arts Glass Units 1 - 4 Note: Students are expected to contribute to the cost of materials they use in these units Unit 1 Glass Artistic Inspiration and techniques Areas of study 1. Developing Art Ideas Investigating sources of inspiration and various methods used to record, interpret and translate observations into visual images. 2. Materials and Techniques Developing skills in using materials and techniques in the production of art works . 3.Interpretation of art ideas and use of materials and techniques The way artists from different times and locations have interpreted ideas and sources of inspiration and use materials and techniques in the production of art works. Assessment A folio, the presentation of 2 pieces of glass work and a series of written works Unit 3 Studio production and professional practices Areas of study 1. Work brief Development of a work brief that creates a framework for the design process. 2. Design process Exploration and development of the design process as documented in the work brief. 3. Professional practice Research the work and art practice of a traditional and contemporary designer / artist. Assessment A written work brief detailing how you will structure you design process, a developmental folio that explores the aims and ideas as set out in the work brief and produces a range of potential solutions and two written research assignments. Outcomes 1 and 2 are subject to external review. (33%) SAT 1 Outcome 3 will form part of the end of year exam. Unit 2 Unit 4 Design exploration and concepts Studio production and art industry contexts Areas of Study Areas of study 1. Focus statement Preparation of visual and written documentation that explains the artwork to be completed for the folio. 2. Folio The production of a cohesive folio of two finished artworks developed from potential solutions. 3. Art Industry contexts The presentation of artworks and current art industry issues. 1. Design Developing artworks through a design process of visual research and inquiry. 2. Ideas and styles in artworks Development of skills in the visual analysis of artworks. Assessment A folio of design explorations and the production of a number of related art works and written presentations that analyse artworks. 1. 2. Assessment Present a visual and written focus statement, a folio that consists of no less that two finished artworks A 1 ½ hour examination based on work done in Outcome 3 from Units 3 and 4. (34%) Outcomes 1 and 2 are subject to external review. (33%) SAT 2 Students are expected to supply their own materials 10 Studio Arts Fashion/ Costume Design Unit 1 Artistic Inspiration and techniques Areas of study 1. Units 1- 4 Note: Students will provide the majority of their material needs. Developing art ideas Investigating sources of inspiration and various methods used to record, interpret and translate observations into textile forms. 2. Materials and techniques The exploration of a range of fibres and fabric treatments used in the development of materials and their construction. 3. Interpretation of art idea and use of materials and techniques The work of artists from different locations and times is studied in order to gain an understanding of how artworks are conceived and produced. Assessment Workbook, a folio of completed artworks and a series of investigative written tasks analysing designers’ work. Unit 3 Studio production and professional practices Areas of study 1. Work brief Development of a work brief that creates a framework for the design process. 2. Design process Exploration and development of the design process as documented in the work brief. 3. Professional practice Research the work and art practice of a traditional and contemporary designer / artist. Assessment A written work brief detailing how you will structure you design process, a developmental folio that explores the aims and ideas as set out in the work brief and produces a range of potential solutions and two written research assignments. Outcomes 1 and 2 are subject to external review. (33%) SAT 1 Outcome 3 will form part of the end of year exam. Unit 4 Unit 2 Design exploration and concepts Areas of study 1. Design Developing artworks through a design process of visual research and inquiry. 2. Ideas and styles in artworks Development of skills in the visual analysis of artworks. Assessment A folio of design explorations and the production of a number of related art works and written presentations that analyse designers’ work. Studio production and art industry contexts Areas of study 1. Focus statement Preparation of visual and written documentation that explains the artwork to be completed for the folio. 2. Folio The production of a cohesive folio of two finished artworks developed from potential solutions. 3. Art Industry contexts The presentation of artworks and current art industry issues. 1. 2. Assessment Present a visual and written focus statement, a folio that consists of no less that two finished artworks A 1 ½ hour examination based on work done in Outcome 3 from Units 3 and 4. (34%) Outcomes 1 and 2 are subject to external review. (33%) SAT 2 11 Studio Arts Photography Unit 1 Photography Artistic Inspiration and techniques Units 1-4 Note: Students will be required to pay a paper levy for these units Areas of study 1. Developing art ideas Investigating sources of inspiration and various methods used to record, interpret and translate observations into visual images. 2. Materials and techniques – The use of lens based media (analogue and digital photography and video) used in the production of artworks. 3. Interpretation of art ideas and use of materials and techniques The work of artists from different locations and times is studied in order to gain an understanding of how artworks are conceived and produced. Assessment Workbook, folio, and a series of written works analysing artists’ work Unit 2 Design Exploration and Concepts Areas of study 1. 2. Design exploration Developing artworks through a design process of visual research and inquiry. Ideas and styles in artworks The development of skills in the visual analysis of artworks. Assessment Workbook, folio, and a series of written works analysing artists work Unit 3 Studio production and professional practice Areas of study 1. 2. 3. Work brief The development of a work brief that creates a framework for the design process. Design process exploration and development of the design process as documented in the work brief. Professional practice research the work and art practice of a traditional and contemporary photographers / artists. Assessment A written work brief, a developmental folio and two written assignments that research the ways in which artists from different times and locations have developed aesthetic qualities and distinctive styles when making artworks. Outcomes 1 and 2 are subject to external review. (33%) SAT 1 Outcome 3 will form part of the end of year exam. Unit 4 Studio production and art industry contexts Areas of study 1. Focus statement Preparation of visual and written documentation that explains the artwork to be completed for the folio. 2. Folio The production of a cohesive folio of finished artworks developed from potential solutions. 3. Art Industry contexts The presentation of artworks and current art industry issues. Assessment 1. Present a visual and written focus statement, a folio that consists of no less that two finished artworks 2. A 1 ½ hour examination based on work done in Outcome 3 from Units 3 and 4. (34%) Outcomes 1 and 2 are subject to external review. (33%) SAT 2 12 Studio Arts Unit 1 Visual Representation Visual Communication Units 1- 4 Note: Students are to supply their own folio and special materials such as mountboard, photopaper and computer printing Areas of study 1. 2. 3. 3. Instrumental Drawing Freehand Drawing Visual communication production process Design process Assessment Three folios that demonstrate the range of drawing styles, including technical, rendering, freehand and three dimensional, and a series of report describing the design process. Unit 3 Visual communication practices Areas of study 1. 2. 3. Visual Communications Design Visual Communications Analysis Investigating Professional Practice Assessment A folio and two written reports (33% of final assessment) Unit 4 Unit 2 Communications in context Areas of study 1. Representing and communicating form through freehand and instrumental drawing 2. Developing imagery 3. Developing visual communication solutions 4. Visual communications in context Designing to a brief Areas of study 1. 2. 3. Developing a Brief Solutions to the Brief Final presentations Assessment Preparation of a brief and a folio that fulfils that brief. Two final presentations will be developed to satisfy the brief. (33% of final assessment) End of year exam is worth 34 % of final assessment. Assessment Three folios showing competency in instrumental drawing to Australian Standards and the visual communication of form, space and surface through the use of perspective drawing, rendering, a range of media design elements and design principles. A design exercise. A written and visual presentation that investigates and analyses a design movement or a prominent designer 13 Business Studies Accounting Units 1-4 Accounting Unit 1 Going into business This unit focuses on accounting and financial management of a small business. Areas of study 1. 2. Recording, reporting and understanding accounting information. Decision making. Assessment Assessment tasks for this unit may include: Use of computer software and/or applications such as spreadsheets, to record and analyse data. Test(s). Assignments. Folio of exercises. Classroom presentations. Unit 2 Operating a business This unit focuses on the accounting and financial operations of a sole proprietor trading business. Areas of study 1. 2. Recording, reporting and understanding accounting information. Decision making. Assessment Use of computer software and/or applications such as spreadsheets, to record and analyse data. Test(s). Assignments. Folio of exercises. Classroom presentations. Case Studies. Classroom presentations. Unit 3 Double entry for trading businesses This unit focuses on accounting and financial issues of a small trading business, operating a sole proprietor. 14 Areas of Study 1. 2. Recording, reporting and understanding accounting information. Decision making. Assessment Assessment tasks for this unit may include: Establishing a chart of accounts for a business and recording and reporting a transactions using a double entry computer package Exercises involving manual recording and reporting. Structured questions. Research report. Folio of exercises. Case study. School-assessed coursework for Unit 3 will contribute 17% to the study score. Exams: Mid year exam of 1 ½ hours duration will contribute 33% to the study score. Unit 4 Planning, control and decision making This unit develops the role of accounting in providing information, with the main focus on accounting information for management. Areas of Study 1. 2. Recording, reporting and understanding accounting information. Decision making. Assessment Assessment tasks for this unit may include: Exercises involving manual recording Preparation of budgets using information and communications technology methods. Evaluation of a business School-assessed coursework for Unit 4 will contribute 17% to the study score. Exams: End-of-year exam of 1 ½ hours duration will contribute 33% to the study score. Business Studies Business Management Units 1- 4 Business Management Unit 1 Small business management Areas of study 1. Business Concepts 2. Small business decision making planning and operation. Assessment 1. Business Plan 2. Small school-based business activity. 3. Folio of analytical exercises. Unit 3 Corporate management Areas of study 1. Large scale organisations in context. 2. Organisational elements and the role of management. 3. Management styles and skills. 4. The management of change. Assessment Two written analyses selected from a portfolio. Test – open book analysis of a case study. Essay These tasks will account for 75% Semester exam 25% Unit 2 Management in action Areas of study 1. Management, change and innovation 2. Management and communication 3. Managing the marketing process. Assessment 1. Business research (print and online) 2. Essay 3. Business communications project These tasks will account for 75% Semester exam 25% Unit 4 Human resource and operations management Areas of Study 1. 2. Human resource management. Operations management. Assessment Two written analyses selected from a portfolio. Essay. Test – open-book analysis of a case study. The level of achievement for Units 3 and 4 is also assessed by an end of year examination, which will contribute 50 per cent to the final assessment. 15 Business Studies Unit 1 Unit 3 The individual and the law Making and changing the law Legal Studies This unit introduces sources of law, the need for laws, the nature of criminal and civil law, and the role of law enforcement agencies. Units 1- 4 Areas of study 1. 2. The need for and the nature of law. Criminal law, its enforcement and the individual. 3. Civil law and the individual This unit focuses on the institutions which determine laws and processes by which laws are made. Areas of study 1. Role of Parliament and the courts 2. Relationship between lawmaking bodies. 3. Changing the law. Assessment Structural assignment essay Mock court or role play, folio and report Case study Test Annotated visual display Assessment Folio of three analytical exercises Assignment or essay or report in multimedia format. Essay or written report of research or analysis of legal commentary. (25% of final assessment). Unit 2 Unit 4 The law in operation Evaluation of the legal system This unit explores legal issues relating to the law in society. Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Access to the law The role of the law Change and the law Assessment Structural assignment essay. Action plan and report. Mock court or scripted role-play. Folio and report Case study Test Audio or visual presentation Interview and report. Annotated visual display. This unit focuses on the courts, tribunals, and alternative avenues of dispute resolution and processes and procedures which operate within the legal system. Areas of study 1. Criminal cases and civil disputes. 2. Court processes and procedures 3. Evaluation of the legal system. Assessment Assignment or short-answer test or annotated visual display or report in multi-media format. Test(s) – extended responses to questions. Analysis of contemporary legal commentary or report of an analysis of a case study. (25% of final assessment). Exam: 2 hour examination is worth 50% of final assessment. 16 English English Units 1- 4 Note that all students must do English Units 1 & 2. (or ESL 1 & 2) For units 3 & 4, they can do English Units 3 & 4, (or ESL)and/or Literature units 3 &4 It is strongly recommended that students take English 3 & 4 (or ESL) Units 1-4 encompass a study of a variety of texts, including written, film and media. Students also develop their writing skills in a variety of styles. Units 1 & 2 Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Reading and the study of texts. The craft of writing. Effective oral communication. Assessment There are three outcomes. Text responses will be assessed through a range of written and oral means. Writing will be assessed by the development of a folio of writing pieces. Oral work will be assessed by the student’s participation and leadership in discussions and/ or by role plays or other oral presentations. Unit 4 Areas of Study 1. Reading and the study of texts. 2. The craft of writing. Assessment There are two outcomes. Text responses will be assessed through an analytical response. Students will also develop a writing folio. The final version will contain two pieces of writing written for different specified purposes and audiences. The exam is three hours in length and is worth 50% of the overall assessment. Unit 3 Areas of study 1. Reading and the study of texts. 2. The craft of writing 3. Effective oral communication. Assessment There are two outcomes. Text responses will be assessed through an analytical response. Students will also analyse the way an issue is presented in the media and construct their own point of view. Oral skills will be assessed by the delivery of complex information in an oral presentation. 17 English English as a Second Language Units 1- 4 Students need to meet certain guidelines to be able to study English as a second language. The structure of the units is similar to English, but the assessment guidelines are modified. Units 1-4 encompass a study of a variety of texts, including written, film and media. Students also develop their writing skills in a variety of styles. Units 1 & 2 Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Reading and the study of texts. The craft of writing. Effective oral communication. Assessment There are three outcomes. Text responses will be assessed through a range of written and oral means. Writing will be assessed by the development of a folio of writing pieces. Oral work will be assessed by the student’s participation and leadership in discussions and/ or by role plays or other oral presentations. Unit 3 Areas of study 1. 2. 3. Reading and the study of texts. The craft of writing. Effective oral communication. Assessment There are two outcomes. Text responses will be assessed through an analytical response. Students will also construct their own point of view in response to a current media issue. Oral skills will be assessed by the delivery of complex information in an oral presentation. 18 Unit 4 Areas of study 1. 2. Reading and the study of texts. The craft of writing. Assessment There are two outcomes. Text responses will be assessed through an analytical or creative response. Students will also develop a writing folio. The final version will contain two pieces of writing written for different specified purposes and audiences. The exam is three hours in length and is worth 50% of the overall assessment. English Unit 1 Literature Areas of Study Units 1- 4 1. 2. Reading Strategies Themes and ideas in texts Assessment There are three outcomes. Students will construct a range of analytical, creative and oral responses to a variety of literary texts. Unit 4 Areas of study 1. Literature in the making 2. Views, values and contexts in literature Assessment There are three outcomes. Students will analyse selected texts, discuss the merits of various readings and construct an original piece of writing in the style of a particular text or recreate texts. Unit 2 Areas of study 1. 2. Reading Strategies Themes and ideas in texts Assessment There are three outcomes. These outcomes are assessed in a variety of ways, that may include evidence of participation in on line forums, oral or written reviews, close analysis of selected passages, essay responses and/or dramatic interpretation of texts. Unit 3 Areas Of Study 1. 2. Literature in the making Views, values and contexts in literature Assessment There are three outcomes. Students will be able to express their understandings of the set literature through essays, comparisons, reflection, evaluation and a review of a text of the student’s own choosing. 19 Human development Health and human development Units 1- 4 Unit 1 Unit 3 Youth health and development Nutrition, health and development A study of the transition and challenges from childhood to adulthood which includes physical, social, emotional and intellectual development. A study of the changes in public health that have occurred as a result of changes in understanding about health and health needs. Government and non government initiatives designed to promote health and development will be explored. Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Understanding health and development. Transition to adulthood Challenges for youth Assessment A close study analysis A data analysis A multi media presentation An oral presentation A test A written test Unit 2 Individual and community health and development A study of the organisation and delivery of health care in Australia, inequitable health and development outcomes affected by social and environmental factors and optimal health and development throughout childhood and adulthood. Areas of study 1. Health and development of young Australians 2. Adult health and development 3. Health care in Australia Assessment As unit 1, including a written response.. Areas of study 1. Understanding Australia’s health. 2. Promoting health in Australia Assessment A response in one of the following forms: a written report, a case study analysis, a data analysis or a test A response in written, visual or multimedia format focussing on a diet related issue A rsponse in a written, visual or multimedia format focussing on a non diet related health issue (25% of total mark for the year). . Unit 4 Global health and development A study of health through the lifespan in both industrialised and developing countries. Health care initiatives developed by governments and international agencies to optimise health and development globally. Areas of study 1. Development across the lifespan. 2. Promoting health and development globally Assessment A response in one of the following forms: a written report, a case study analysis, data analysis or a test Two short responses from the following forms: written report, case study analysis, data study analysis or a test. (25% of total mark for the year). Exam: Held in November. 2 hours duration. 50% of final mark for the year. 20 Human development Unit 1 Outdoor & environmental studies Areas of study 1. Humans and nature Humans relate to nature in a variety of ways. The relationships between humans and nature are explored through direct experiences of different outdoor environments. 2. Natural environments This area of study provides an introduction to the characteristics of natural environments and the ways in which they function. It investigates different types of natural environments and interrelationships within them, and how changes to nature affect people. Units 1 – 4 Note: There is a cost of approximately $150 for each unit to cover the costs of camps and excursions Understanding nature Assessment oral presentations practical reports in non-text format such as multimedia, annotated visual display; short reports of outdoor experiences; tests, written responses Unit 2 Areas of study 1. Impact on people Through an understanding of environments, this area of study focuses on the ways in which social humans relate to nature 2. Impact on nature This area of study focuses on identifying human activities and their environmental impacts at local/regional/statewide levels. Assessment oral presentations practical reports in non-text format such as multimedia, annotated visual display short reports of outdoor experiences tests written responses. Unit 3 Relationships with outdoor environments Areas of study 1. Changing perceptions of outdoor environments This area of study focuses on how Australians have understood and interacted with the outdoors over time. 2. Contemporary views of outdoor environments This area of study focuses on the current state of the environment and interrelationships between humans and the environment. Assessment The student's level of achievement in Unit 3 will be determined by school-assessed coursework and an end-of-year examination. School-assessed coursework for Unit 3 will contribute 25 per cent to the final assessment. The level of achievement for Units 3 and 4 is also assessed by an end-of-year examination, which will contribute 50 per cent to the final assessment Unit 4 The future of natural environments Areas of study 1. Interacting with outdoor environments This area of study focuses on approaches to developing interactive practices that maintain natural environments. 2. Sustaining outdoor environments This area of study focuses on the sustainability of natural environments in order to support the future needs of the world's human population. Assessment School-assessed coursework for Unit 4 will contribute 25 per cent to the final assessment. The level of achievement for Units 3 and 4 is also assessed by an end-of-year examination. Assessment tasks consist of any two of the following tasks for both Outcome 1 and 2: a written report or an analysis of data or a short essay or a test. 21 Physical education Units 1- 4 . Unit 1 Unit 3 The nature activity of physical Areas of study 1. Body Systems 2. Involvement in Physical Activity Assessment Written Reports Tests Laboratory Reports Oral reports Video/media analysis Structured questions and participation in practical activity. Areas of study 1. Understanding fitness 2. Physiology needs and responses to activity Assessment School assessed course work for Unit 3 will contribute 25% to the final assessment. End of year examination which will contribute 50% to the final assessment. Unit 4 Unit 2 Analysing physical activity Participation and performance Areas of study Areas of study 1. 2. Skill Acquisition Biomechanics Assessment Written Reports Tests Laboratory reports Oral reports Video/media analysis Structured questions and participation in practical activity 22 The physiology of fitness 1. Participation in physical activity. 2. Physical activity for performance. Assessment School assessed course work for Unit 4 will contribute 25% to the final assessment. End of year examination which will contribute 50% to the final assessment. Humanities Classical societies and cultures Units 1- 4 Unit 1 Unit 3 Myths and legends Classical culture This unit explores the nature of myths and legends focusing on Ancient Greece. Areas of study Areas of Study 1. 2. Communication of Myths and Legends, their historical basis, form and content. Representation of Myths and Legends in art and literature, their context and influence on Western society. 5th C. BCE Greece, specifically Athens 1. 2. Society and Culture – the environment, major events and cultural achievements of 5th C BCE Greece. Ideas, issues and values – the values of the society as expressed in at least three works selected from epic poetry (Homer), tragedy, comedy, history and philosophy, sculpture and ceramics. Assessment Mapping, genealogy and timeline exercises. Oral and written reports and debates. Short analyses of artefacts Essays. Mid year Exam as an assessment task. Assessment School assessed coursework (25%) including written reports or tests, written analyses, open book essays. Unit 2 Unit 4 Emerging societies The classical heritage This unit explores the emergence of Ancient Greek Society from mythological to historical explanations of their world. Areas of study 1. Catalysts of Change – how change came about in Classical Greece. 2. Continuity and the classical heritage – selected works which demonstrate the ongoing significance of Classical Culture. Areas of Study 1. 2. The emergence of a society, from palace to polis, from aristocracy to democracy. Cultural expressions and art forms, festivals ideas. Assessment Timelines and mapping exercises Oral reports and debates Short analyses of artistic/literary works. Essays. End of year exam as an assessment task. Assessment School assessed coursework (25%) including written analyses and a catalogue. End of year exam on Units 3 and 4 (50% of final assessment). 23 Humanities Applied history Unit 1 Power and the people Unit 2 Melbourne’s past contains many struggles over the nature of its future. While the sleazy entrepreneurs who led white settlement imagined Port Phillip merely as a source of rich pasture, others dreamed a different dream. Those choosing this unit will traverse the city’s alleys and lanes to uncover stories of secret police and secret armies, guerrilla artists and underground cells, militant unionists and intransigent peaceniks. Along the way they will ask questions about the kinds of history that we celebrate, and reflect upon what our vision of the important and preservable past says about us in the present day. This unit explores the ways in which struggles, challenges and change are fundamental processes in human history. Conflict between opposing groups in a society actively alters that society with new ideas replacing old. Various concepts such as ‘liberty’, ‘authority’, ‘freedom’, ‘equality’, ‘right’, and ‘truth’ will be analysed both in terms of their modern-day usage and their historical basis. Areas of study 1. People and place 2. Investigating community history 3. The community historian at work 2. History Applied history in the local community. Unit 1 Power and the people Unit 2 It is expected that students will take both of these units Assessment: A range of tasks will be given, that will assess the student’s ability to locate evidence in the local community, analyse written, oral and visual evidence, interpret and research sources and acknowledge sources. Areas of Study: 1. 3. Analyses established political, religious, intellectual and patriarchal authority and the ways in which these have maintained and legitimised themselves over time. Focuses on the reasons why some people and groups challenge established authority. Explores the notion of change and its short and long term impacts. Assessment 24 Short reports Essays Oral presentations Responses to films and texts Multimedia presentations Hypothetical debates Humanities Australian history Revolutions Unit 3 Unit 3 French Revolution History Australian Units 3 & 4 Revolutions Units 3 & 4 This unit focuses on the European experience in Australia from the early years of the Port Phillip District (later Victoria) through the nineteenth century and up to the eve of World War 1. Areas of study 1. A new land: Port Phillip District 1830-1860 2. Nation, race and citizen 18881914 Assessment: Each of the following four assessment tasks must be taken over Units 3 & 4. Research report Analysis of visual and/or written documents Historiographical exercise Essay School assessed coursework for Unit 3 contributes 25 % of the study score. Unit 4 This unit continue the exploration of the ideas and visions underpinning Australian society by offering students the opportunity to examine a time when these visions were under threat. They may choose to focus on World War I, The Depression or World War II.The study concludes with an examination of changing Australian attitudes. Areas of study: 1. Testing the new nation 19141950 2. Debating Australia’s future 1960-2000 Unit 4 Russian Revolution These units look separately at why the French and the Russian revolutions occurred. This will include looking at rising social tensions and conflict and the eroding confidence in the old order. Leaders and ideas are also important in the process of revolution, and students will study the role of leaders and the debate among historians about their importance. Once the new society is established, it has to be maintained and sometimes extreme measures are employed. To what extent are these measures justified? Areas of study (the same for both units) 1. Revolutionary ideas, leaders, movements and events France, 1781-1789 Russia, 1905-1917 2. Creating a new society France 1789-1795 Russia 1917-1924 Assessment: Each of the following four assessment tasks must be taken over Units 3 & 4. Research report Analysis of visual and/or written documents Historiographical exercise Essay School assessed coursework for Unit 3 & 4 contributes 50 % of the study score. Assessment: See unit 3. School assessed coursework for Unit 4 contributes 25 % of the study score. 25 Humanities History 20th Century Units 1 & 2 International Studies 20th Century History Unit 1 1900- 1945 Patterns of daily life were changed as a result of political and social developments in the first half of the 20th century. This unit considers the way that society responded to these changes and how they affected people’s lives. Areas of study 1. Crisis and conflict 2. Social life 3. Cultural expression Assessment A variety of tasks will be used. At least one of the tasks must be in written form and one must include an analysis of visual evidence. Unit 2 1945-2000 This unit considers some of the major themes and principal events of post World War II history, and the ways in which individuals and communities responded to the political, economic, social and technological developments in domestic, regional and international settings. Areas of study 1. Ideas and political power 2. Movements of the people 3. Issues for the millennium Assessment A variety of tasks will be used. At least one of the tasks must be in written form and one must include an analysis of visual evidence. International Studies Unit 1 International perspective This unit investigates differences between nations and the causes of such differences Areas of Study 1. An International Profile: global inequality, third world debt. 2. Globalisation: migration, multinationals, tourism, aid Assessment Assessment tasks for this unit may range from: Annotated records of texts, articles, radio and television programs, class discussions. Mapping exercises with commentary. Design of an index of well being with a written analysis. Graphic representation of the links which exist across national boundaries with commentary. Analytical profiles. Oral reports. Unit 2 Internationalism This unit examines the history and workings of international organisations such as the UN and Amnesty. It includes studying current issues of international concern such as terrorism. Areas of Study 1. International organisations and the ideals of internationalism. 2. International issues and the conflict between International organisations and Nation States. Assessment As for unit 1 26 Humanities Political Studies Units 3 & 4 Unit 3 The Australian Political System Investigates the operation and effectiveness of the Australian political system. Areas of Study 1. The Structure of the Australian Political system 2. The Australian Constitution 3. Parliament and the Executive 4. Voting and Elections Assessment Two of the following: a short report, a test or short answer questions. An essay. A short report, a test or short answer questions (25% of final assessment) Unit 4 The Australian Political Process Investigates the Australian political process Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Political parties and pressure groups. Australian foreign policy. Politics, issues and the media (compulsory). Assessment A short report or a test or short answer questions . A short essay for and a short report or a test or short answer questions. A case study for Politics, issues and the media. (25% of final assessment) End of year exam 50% of final assessment. 27 Humanities Philosophy Units 1-4 Unit 1 Introduction to philosophical enquiry This unit engages students in philosophical enquiry through active, guided investigation and discussion of three key areas of philosophy: 1. Judgements about what is right and wrong (ethics) 2. The ways in which we analyse knowledge (epistemology) 3. The connections between theories of human nature and the ways we behave. (metaphysics) The emphasis in the exploration of these three fields is philosophical enquiry. Areas of study 1. Fields of philosophical enquiry 2. Methods of philosophical enquiry Assessment Assessment tasks may include a short written analysis, a written reflection, an oral analysis, an essay, an oral reflection/ response, short written exercises Unit 2 Philosophical issues in practice This unit explores a range of problems in applied philosophy and involves formulating and defending philosophical positions in relation to practical issues. The examination of examples of philosophical thought, both contemporary and historical, is also undertaken. Areas of study 1. Problems in applied philosophical thought 2. Positions in applied philosophical thought Assessment As for unit 1. 28 Unit 3 The good life In this unit students explore ideas concerning the nature of the good life as developed by ancient and modern philosophers. Students compare these with notions found in familiar traditions, such as Buddhism, Christianity and Confucianism. Areas of study 1. Ancient Greek conceptions of the good life 2. Nineteenth and twentieth century discussions of the good life Assessment Assessment tasks may include short answer responses, an essay, a written exercise, a test. Unit 4 Mind and knowledge In this unit students look at two areas of contemporary philosophical debate, mind and knowledge, and their historical development. It involves the study and evaluation of contemporary arguments in these debates and their relationship to historical arguments. Areas of study 1. Mind, body and soul 2. Science, knowledge and dogma Assessment Assessment tasks may include short answer responses, a test, an essay, a written essay. Information technology Information technology Unit 1 Information technology The basis of this unit is how individuals use, and be affected by, information technology in their daily lives Units 1 & 2 Information processing and management Units 3 & 4 Areas of Study 1. IT Techniques: solutions and outputs 2. IT: possibilities and consequences 3. IT: components of computer systems Assessment Designing and developing a solution in response into a design brief, using information technology tools and techniques Tests (short answer, open book, practical) Short written reports oral reports supported by visual presentation Unit 2 The basis of this unit is the study of how individuals and organizations use and can be affected by information systems. Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. IT: techniques processes and management. IT: applications and implications IT: information systems. Assessment Designing and developing solutions in response to a design brief, using information technology tools and techniques. Visual presentations. Short written reports. Oral reports supported by visual presentation. Tests (short answer, open book, practical) Information processing and management Unit 3 The focus of this unit is why information is used in organisations and d the ways in which it is processed and managed. Areas of Study 1. IT techniques: solving information problems 2. Organisations and information 3. Information systems Assessment A short, practical test, including a written response. An information technology solution in response to a design brief and a report as either a written report or a visual presentation. Written report or test (open book, short answer . (25% of final assessment). Unit 4 The focus of this unit is on a range of techniques, procedures and strategies to solve information problems efficiently and effectively, and to manage the development, implementation and evaluation of a new or modified information system Areas Of Study 1. 2. 3. Problem solving Managing change Information systems (networks) Assessment Information technology solution in response to design brief. Students annotate the solution to indicate how it meets the decision-making needs of the organisation. Written report or test (open book, short answer.) ( 25% of final assessment). Examination of two hours duration worth 50% of final assessment. 29 Information technology Information systems Units 3 & 4 Information systems Unit 3 This unit focuses on techniques and procedures to analyse and design information systems and to partially develop a software design specification through the use of a programming language. Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Information systems and networks Information systems engineering (analysis and design) Software development Assessment Visual presentation Written report An information technology solution in response to a system design, including a written report (25% of total assessment) Unit 4 This unit focuses on techniques, procedures and strategies to develop, implement and evaluate a proposed networked information system. Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Software engineering Information systems engineering Information systems: networks Assessment An information technology solution A written report or test (25% of total assessment) Exam: 2 hour exam worth 50% of final assessment 30 LOTE (Languages other than English) French Units 1- 4 Italian Units 1- 4 French Units 1 & 2 Italian Units 1 & 2 Areas of Study Areas of Study 1. Themes There are three prescribed themes in the VCE French course: The individual The French-speaking communities 1. Themes There are three prescribed themes in the VCE French course: The individual The Italian-speaking communities The changing world 2.Text types and kinds of writing Students are expected to be familiar with a variety of text types 3.Vocabulary and Grammar Students are expected to be familiar with a range of vocabulary and idioms relevant to the topics and to develop the necessary skills to use dictionaries effectively. Students are expected to recognise and use a wide range of grammatical items. The changing world 2.Text types and kinds of writing Students are expected to be familiar with a variety of text types 3.Vocabulary and Grammar Students are expected to be familiar with a range of vocabulary and idioms relevant to the topics and to develop the necessary skills to use dictionaries effectively. Students are expected to recognise and use a wide range of grammatical items. Assessment Four assessment tasks will be undertaken, which will include conversation, understanding of information in written texts and oral presentations. Assessment Four assessment tasks will be undertaken, which will include conversation, understanding of information in written texts and oral presentations. French Units 3 & 4 Areas of study As for units 1 & 2 Assessment School assessed coursework 50% Unit 3 250-word personal or imaginative written piece. Response to spoken texts. Three to four minute role-play. Unit 4 Response to written texts. 250-300 word informative, persuasive or evaluative written piece. Three to four minute interview. End of Year Examinations Oral Examination: 12.5% Written Examination Listening & Responding Part A: Response in English 10% Part B: Response in French Reading & Responding Part A: Response in English 10% Part B: Response in French 5% Writing 7.5% Italian Units 3 & 4 Areas of study As for units 1 & 2 Assessment School assessed coursework 50% Unit 3 250-word personal or imaginative written piece. Response to spoken texts. Three to four minute role-play. Unit 4 Response to written texts. 250-300 word informative, persuasive or evaluative written piece. Three to four minute interview. End of Year Examinations Oral Examination: 12.5% Written Examination Listening & Responding Part A: Response in English 10% Part B: Response in Italian 5% Reading & Responding Part A: Response in English 10% Part B: Response in Italian 5% Writing 7.5% 31 Mathematics: Deciding which subject(s) to do. In selecting their Mathematics Units students should first: 1. Decide how many units of Mathematics they wish to do (usually 2 or 4 Mathematics units per year). 2. Check that the units they select will allow them to do the Units 3 and 4 at Year 12 that they need to proceed to their preferred courses at tertiary colleges and universities. VCE Mathematics units are arranged in seven blocks: four blocks in Units 1 and 2 and three blocks in Units 3 and 4. YEAR 11 VCAL Numeracy Intermediate (1) Foundation Maths (1 and 2) YEAR 12 General Mathematics (1 and 2) Mathematical Methods (1 and 2) Further Mathematics (3 and 4) Mathematical Methods (3 and 4) Specialist Mathematics (3 and 4) The following table shows your possible options for Units 3 and 4 considering the Units 1 and 2 completed: UNITS 1 AND 2 General Mathematics 1 and 2 only Foundation Maths leads on to leads on to Mathematical Methods 1 and 2 only leads on to one of General Mathematics 1 and 2 and Mathematical Methods 1 and 2 leads on to one of Units 3 & 4 UNITS 3 AND 4 Further Mathematics 3 and 4 only NO MATHS POSSIBLE (except in very special cases) Mathematical Methods 3 and 4 only Further Mathematics 3 and 4 only Mathematical Methods 3 and 4 and Specialist Mathematics 3 and 4 Mathematical Methods 3 and 4 and Further Mathematics 3 and 4 Mathematical Methods 3 and 4 only Further Mathematics 3 and 4 only Further Maths 3 & 4 Maths Methods 3 &4 Unit 2 Unit 1 VCAL Numeracy (Intermediate) 32 Foundation Maths 2 General Maths 2 Foundation Maths 1 General Maths 1 + Maths Methods 2 Maths Methods 1 + Specialist Maths 3 &4 Mathematics Foundation Mathematics Units 1 & 2 General Mathematics Units 1 & 2 Foundation Mathematics Units 1 & 2 The Foundation Mathematics course does not usually lead to any Units 3 and 4 in VCE Mathematics. It may not fulfil the requirement for “any Maths” Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. 4. Space and shape Patterns in number Handling data Measurement and design. Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for each unit have been met through completion of schoolassessed coursework. This work will mostly be assignments and will include: 1. Tests 2. Projects 3. Problem –solving tasks General Mathematics Unit 1 Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. 4. Statistics Algebra – linear Functions and graphs Variation Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for each unit have been met through completion of schoolassessed coursework. This work will include: 1. Exercises 2. Tests 3. Exam 4. Project or problem-solving task Unit 2 Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. 4. Trigonometry Measurement Coordinate geometry Linear programming Assessment Same as for Unit 1. 33 Mathematics Mathematical Methods Units 1- 4 Mathematical Methods Unit 1 Unit 3 Areas of Study Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. 4. Functions and graphs Polynomials Exponential and logarithmic functions Circular functions Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for each unit have been met through completion of schoolassessed coursework. This work will include: 1. Tests 2. Exam 3. Project or problem solving task. Mathematical Methods Unit 2 Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Relations and functions Rates of change Calculus Probability Combinatorics Assessment As for unit 1 1. 2. 3. 4. Coordinate geometry Circular (trigonometric) functions Calculus Algebra Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for each unit have been met through completion of schoolassessed coursework. This work makes up 60% of the internal assessment and contributes 20% to the final assessment. It consists of: 1. Project 40 marks 2. Tests - two 10 marks each Unit 4 Areas of Study 1. 2. Calculus Statistics and probability Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for each unit have been met through completion of schoolassessed coursework. This work makes up 40% of the internal assessment and contributes 14% to the final assessment. It consists of: Analysis tasks – two 20 marks each The external assessment consists of the following tasks under examination conditions, each contributing 33% of the final assessment: Examination 1 – Facts, skills and application task (multiple choice and short answer questions) Examination 2 – Analysis task (extended-answer questions) Final Assessment: Exams 66% School-assessed coursework 34% 34 Mathematics Specialist Mathematics Further Mathematics Specialist Mathematics Not to be done with Further Mathematics in the same year Not to be done with Specialist Mathematics in the same year Unit 3 Unit 3 Units 3 & 4 Areas of Study Areas of Study 1. 1. 1. Further Mathematics Units 3 & 4 2. 3. 4. 5. Coordinate geometry Circular (trigonometric) functions Algebra Calculus Vectors in two and three dimensions Mechanics Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for each unit have been met through completion of schoolassessed coursework. This work makes up 40% of the internal assessment and contributes 14% to the final assessment. It consists of: Analysis tasks – two: 20 marks each Data analysis (Core) 2. Networks and decision mathematics (Applications) Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for each unit have been met through completion of schoolassessed coursework. This work makes up 60% of the internal assessment and contributes 20% to the final assessment. It consists of: 1. Application task: 40 marks 2. Analysis task – test or assignment of 2-4 hours duration: 20 Marks Unit 4 Areas of Study Unit 4 1. Areas of study As for unit 3 2. Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for each unit have been met through completion of schoolassessed coursework. This work makes up 60% of the internal assessment and contributes 20% to the final assessment. It consists of: 1. Problem-solving or modelling application task 40 marks 2. Tests – two: 10 marks each Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for each unit have been met through completion of schoolassessed coursework. This work makes up 40% of the internal assessment and contributes 14% to the final assessment. It consists of: 1. Analysis Task 1- test or assignment of 2-4 hours duration: 20 marks. 2. Analysis Task 2 – test or assignment of 2-4 hours duration: 20 Marks The external assessment consists of the following tasks under examination conditions, each contributing 33% of the final assessment: Examination 1 – Facts, skills and application task (multiple choice questions) Examination 2 – Analysis task (extended-answer questions) Final Assessment: Exams 66% School-assessed coursework :34% The external assessment consists of the following tasks under examination conditions, each contributing 33% of the final assessment: Examination 1 – Facts, skills and application task (multiple choice and short answer questions) Examination 2 – Analysis task (extended-answer questions) Final Assessment: Exams 66 % School-assessed coursework 34% Geometry and trigonometry (Applications) Graphs and relations (Applications) 35 Performing arts Drama Unit 1 Unit 3 Ensemble performance Character development Drama Units 1- 4 This unit focuses on the art of transforming into imagined characters, examining the place of role and status in characterisation, and using performance structures such as solo or ensemble performance. The origins of performance from a range of cultures and their significance in a variety of social, political and historical contexts are examined. This unit also involves analysis of student performances and of professional performance work. Areas of Study 1. Creating characters 2. Analysing characters Assessment 1. Character-based performances to an audience. 2. & 3. Student's performance on a selection of the following assessment tasks Assessment tasks for this unit are: analytical exercises; short reports; essays; oral presentations; multimedia presentations; tests One of the assessment tasks must be completed in writing. Unit 2 Interpreting drama This unit focuses on the differing perspectives and interpretations that drama can give to play scripts and stimulus material selected from a range of cultures. The application of dramatic elements and stagecraft and the development of expressive skills to create and communicate dramatic form will be explored in the student's own work and in a professional performance work. Areas of Study 1. Creating dramatic performance 2. Analysing dramatic performances Assessment 1. An ensemble performance 2 & 3 As for unit 1 36 This unit focuses on the nonnaturalistic drama from a diverse range of traditions. Nonnaturalistic performance styles and associated theatrical conventions are explored in the development of ensemble performance. A nonnaturalistic work selected from the prescribed play list will also be analysed. Areas of Study 1. 2. Creating ensemble performance Analysing non-naturalisitc performance Assessment The student's level of achievement in Unit 3 will be determined by school-assessed coursework and an end-of-year examination. Contributions to final assessment School-assessed course work for Unit 3 will contribute 35 per cent to the final assessment. The level of achievement for Units 3 and 4 is also assessed by two end-of-year examinations, which will contribute 60 per cent to the final assessment Unit 4+ Solo performance This unit focuses on the performance styles, theatrical conventions and stimulus materials from a variety of cultural sources in the development of a solo performance. The processes involved in the development of solo work are also analysed and evaluated. Students will select one solo performance from a list published annually in the VCE Bulletin. Areas of Study 1. 2. Creating a solo performance Analysing a solo performance Assessment School-assessed course work for Unit 4 will contribute 5 per cent to the final assessment. Performing Arts Drama Unit 4 (continued) Theatre Studies Units 1 & 4 The level of achievement for Units 3 and 4 is also assessed by two end-of-year examinations, which will contribute 60 per cent to the final assessment. Units 3 and 4 written examination contributes 25 percent and Unit 4 performance examination contributes 35 per cent. Theatre studies Unit 1 Theatrical form This Unit focuses on studying theatrical form and working with plays in both their written form and in performance, with emphasis on the use of stagecraft. This Unit provides the opportunity to enhance acting skills, apply other aspects of stagecraft and develop knowledge of the nature of specific performance styles. Theatre history is introduced through text realisation, focusing on works prior to the 1880s. Stagecraft includes: acting, direction, dramaturgy, state management, set design, costume, lighting, properties, make-up and sound. Unit 2 Text interpretation This unit focuses on the study of works of the modern era, from the 1880s to the present. Acting and use of other aspects of stagecraft focus on naturalistic and nonnaturalistic forms which characterise the times and which make meaning for contemporary audiences. Theatre history is explored through selected texts, emphasising the works’ placement within their historical contexts. Students also learn about theatre as industry and develop knowledge of the workings of modern theatre companies. Analytical and evaluate skills are developed to enable students to demonstrate their knowledge of performance processes. Areas of Study 1. 2. The Modern Era and performance Theatre Companies Assessment As for unit 1 Areas of Study 1. 2. Text interpretation Analysing a play in performance. Assessment Performance interpretation through the use of stagecraft. Analytical exercises Theatre history reports Essays Oral presentations Multimedia presentations Tests. One of these assessment tasks must be completed in writing. 37 Performing arts Theatre studies Unit 3 Theatre studies Play production Units 3 & 4 This unit focuses on the interpretation and production of a play(s). It involves all aspects of production processes. Specialised areas in stagecraft are developed. Acting skills focus on specific styles used in the interpretation of the play and enable students to demonstrate knowledge of particular performance styles and theatrical conventions. Theatre history is studied in the context of the selected play(s) with a focus on the playwright, traditional performance styles and conventions, interpreted performance styles and conventions and the use of a range of stagecraft. Analysis of the play from the prescribed play list is enhanced through the evaluation of the production. Stagecraft includes: acting, direction, dramaturgy, stage management, set design, costume, lighting, properties, make-up and sound. Students should specialise in two areas of stagecraft in Unit 3. Unit 4 The actor in performance This unit focuses on a prescribed play that involves individual students working in the areas of text research, interpretation and performance. Each student selects a scene containing a prescribed monologue from a play and , using acting skills and other stagecraft, develops the scene. The scene interpretation involves ensemble work and dialogues, as appropriate, and is accompanied by contextual analysis, which comprises the stages of development of a student’s interpretation of the scene. Acting skills focus on rehearsal of the scene with other students, culminating in the student’s performance of a monologue from that scene. Students investigate the context of the play. This research informs their work. The performance of actors in the play selected from the prescribed play list is also analysed. Areas of study 1. 2. 3. Scene Interpretation Context Investigation The actor Assessment Areas of Study 1. 2. Production and Performance Theatre Criticism Assessment Assessment of levels of achievement The student’s level of achievement in Unit 3 will be determined by school-assessed coursework and an end-of-year examination. Contributions to final assessment School-assessed coursework for Unit 3 will contribute 30 percent to the final assessment. The level of achievement for Units 3 and 4 is also assessed by two end-of-year examinations, which will contribute 55 per cent to the final assessment. 38 Assessment of levels of achievement The student’s level of achievement for Unit 4 will be determined by school-assessed coursework and two end-of-year examinations. Contributions to final assessment School-assessed coursework for Unit 4 will contribute 15 percent to the final assessment. The level of achievement for Units 3 and 4 is also assessed by two end-of-year examinations, which will contribute 55 percent to the final assessment. Performing arts Music performance Units 1 & 2 Music performance Unit 1 This unit focuses on developing skills in practical music and performance in solo and group contexts, studying performance and performing, and developing skills in aural comprehension and organisation of sound. Students will present a solo and a group performance, demonstrate prepared technical work and perform previously unseen music. A written report or an oral presentation or a multimedia presentation. A test that includes written, aural and practical components. Areas of Study 1. Performance Skill Development 2. Music Craft 3. Organisation of sound Assessment A solo performance recital, a group performance, technical work and unprepared performance test A written report, or An oral presentation, or A multimedia presentation Aural written and practical test Composition and/or improvisation exercises. Unit 2 The Unit further develops skills in practical music and performance in solo and group contexts. Students present a prepared program(s) of solo and group works, demonstrate prepared technical work, perform previously unseen music and develop skills in aural comprehension. Selected works are analysed to enhance performance interpretation and to understand their context, influences, characteristics and styles. This unit also focuses on music theory relevant to performance and used in the analysis of music. Areas of Study 1. Performance skill development 2. Background of music works 3. Music craft Assessment A solo performance recital; a group performance; technical work and unprepared performance test(s). 39 Performing arts Unit 3 Group performance Units 3 & 4 Solo performance Music performance group This unit focuses on developing skills in an ensemble context. It includes developing skills in either part-writing or improvising and knowledge of the processes involved. Aural comprehension and critical listening skills used by ensemble performers are also developed. These units focus on the preparation and presentation of solo works. Students use performance techniques to develop understanding of interpretation of a range of styles. Ensemble performance, solo technical work and unprepared performance, broaden music performance skills, Aural comprehension skills and understanding of the structure and characteristics of a group work are also developed. Units 3 & 4 Music performance solo Units 3 & 4 Areas of Study 1. Performance skill development 2. Part-writing or improvisation 3. Aural comprehension Assessment Unit 4 Group performance This unit focuses on developing performance skills in interpreting styles and applying a range of technical and artistic techniques to present a program of works in an ensemble context. It involves analysis of strategies and techniques for preparing and presenting ensemble performances. This unit further develops aural comprehension and critical listening skills used by ensemble performers to prepare and present performances of music in a range of styles. Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Performance skill development Aspects of performance Aural comprehension Assessment School Assessed Coursework (SAC) includes Harmony SAC, Performance Style SAC and two Aural SACs. There are also Performance and Aural/ Written exams 40 Areas of Study 1. Performance skill development This area of study involves the development of skills in performing on an instrument or singing in solo and ensemble contexts. 2. Interpretation This area of study involves differentiating structures of works and styles represented, and exploring with interpretation through performance. 3. Aural comprehension This area of study focuses on aural comprehension of music. Development of knowledge and skills in this area of study should be undertaken in a systematic manner across Units 3 and 4. 4. Analysis of ensemble work This area of study focuses on analysis of music through identifying and describing musical characteristics in an ensemble work that are relevant to performance of the work. Assessment Two Technical SACs Performance Exam Aural Written exam Science Unit 1 Unit 3 Organisms in their environments Challenge to survival Biology Areas Of Study 1. 2. Units 1 – 4 1. 2. The nature of ecosystems Changes in ecosystems Areas Of Study 3. Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit have been met through completion of assessment tasks, which are: Cells in their environment Surviving under changing conditions Surviving challenges from organisms that cause disease Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit has been met through completion of school assessed coursework. This contributes 17% to the study score and includes at least five practical activities, at least one of which should be the student's own design. Practical activities Questions and problems Tests Design and implementation of field-based investigations Short reports of ecological investigations Outcome 1: At least three practical activities (45 marks) Presentation of a structured written report of field studies Outcome 2: At least two practical activities (30 marks) Presentation of practical reports in non-text formats such as poster, multimedia Functioning Organisms Outcome 3: A short presentation (eg poster, webpage, report in multimedia format) or a short research report (25 marks) The mid-year examination (1 1/2 hours) contributes 33% to the study score. Areas Of Study Unit 4 1. 2. Biological continuity and change Oral presentations Unit 2 Requirements for life Reproduction and development Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit have been met through completion of assessment tasks, which are: Areas Of Study 1. 2. Genetic inheritance Variation, natural selection and evolution Assessment Practical activities Questions and problems Tests Presentation of a structured written practical reports Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit have been met through completion of school assessed coursework. This contributes 17% to the study score and is: Oral presentations Presentation of practical reports in non-text formats such as poster, multimedia Outcome 1: At least two practical activities (30 marks) and a short presentation or research report (25 marks) Outcome 2: At least two practical activities (30 marks) and a short presentation or research report (15 marks) The end-of-year examination (1 1/2 hours) contributes 33% to the study score. 41 Science Unit 1 Unit 3 Chemistry Areas Of Study Units 1- 4 1. 2. 3. Units 1 and 2 are not prerequisites for Unit 3; however, students who enter Chemistry at Unit 3 may need to undertake preparatory work in view of the sequenced nature of the study. Introduction to materials Water Chemistry of surfaces Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit have been met through completion of assessment tasks, which are: Experimental reports Homework sheets End-of-topic tests Assignments End-of-unit examination Unit 2 Unit 1 is not a prerequisite for Unit 2; however, students who enter Chemistry at Unit 2 may need to undertake preparatory work in view of the sequenced nature of the study. Areas Of Study 1. 2. 3. Analytical Chemistry Equilibrium Industrial Chemistry Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit have been met through completion of school assessed coursework, which is the completion of practical activities and reports: Outcome 1 – 40 marks Outcome 2 – 30 marks Outcome 3 – 30 marks School assessed coursework contributes 17% to the study score and the mid-year examination (1 1/2 hours) contributes 33%. Areas Of Study 1. 2. 3. Acids in the environment The atmosphere Corrosion of metals Assessment As for Unit 1. Unit 4 Students must undertake Unit 3 prior to undertaking Unit 4. In view of the sequenced nature of the study, it is advisable that students undertake Units 1 to 4. Areas Of Study 1. 2. 3. Supplying & using energy Food Chemistry The periodic table: an overview of Chemistry Assessment As for Unit 3. The end-of-year examination (1 1/2 hours) contributes 33% to the study score. 42 Science Unit 1 Unit 2 Physics Areas of study Areas of study 1. 2. Wave–like properties of light Nuclear and radioactivity physics 3. Detailed study Three detailed studies are available in Unit 1. One detailed study is to be selected from: 1. Movement 2. Electricity 3. Detailed study Three detailed studies are available in Unit 2. One detailed study is to be selected from: Astrophysics Astronomy Investigations: Aerospace Medical Physics Energy from the nucleus Investigations: Alternative energy sources Units 1 & 2 Assessment Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit have been met through completion of assessment tasks, which are: Practical investigation (studentdesigned or adapted) and A selection from the following: Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit have been met through completion of assessment tasks, which are: Practical investigation (studentdesigned, adapted or extended) and A selection from the following: An annotated folio of practical activities An annotated folio of practical activities A data analysis A data analysis A multimedia or webpage presentation A multimedia or webpage presentation A response to a media article A response to a media article A summary report of selected practical investigations including maintenance of a logbook A summary report of selected practical investigations including maintenance of a logbook A written report A written report A test (short answer and extended response) A test (short answer and extended response) 43 Science Physics Units 3 & 4 Unit 3 Unit 4 Areas of study Areas of study 1. Motion in one and two dimensions 2. Electronics and photonics 3. Detailed study Three detailed studies are available in Unit 3. One detailed study is to be selected from: 1. Interactions of light and matter 2. Electric power 3. Detailed study Three detailed studies are available in Unit 4. One detailed study is to be selected from: Synchrotron and applications Einstein's relativity Photonics Investigating structures and materials Recording and reproducing sound Further electronics Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit have been met through completion of school assessed coursework, which is: A student-designed extended practical investigation and At least two different tasks selected from the following: Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit have been met through completion of school assessed coursework, which is: A summary report of selected practical activities from the student's log book and At least two different tasks selected from the following: A multimedia presentation A multimedia presentation An annotated folio of practical activities An annotated folio of practical activities A summary report of selected practical activities from the student's log book A student-designed extended practical investigation A data analysis A data analysis A report (written, oral, annotated visual) A report (written, oral, annotated visual) A test (short answer and extended response) A test (short answer and extended response) A response to a media article School assessed coursework for Unit 3 contributes 17% to the study score and the marks allocation is: Outcome 1 – 40 marks Outcome 2 – 30 marks Detailed study – 30 marks The mid-year examination (1 1/2 hours) contributes 33% to the study score. 44 Assessment A response to a media article School assessed coursework for Unit 4 contributes 17% to the study score and the marks allocation is: Outcome 1 – 30 marks Outcome 2 – 40 marks Detailed study – 30 marks The end-of-year examination (1 1/2 hours) contributes 33% to the study score. Science Unit 1 Unit 3 Psychology Areas of Study Areas of Study Units 1- 4 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. Introduction to Psychology Social relationships Development of individual behaviour Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit have been met through completion of school assessed coursework, which is assessment tasks selected from the following: Brain and nervous system Visual perception States of consciousness Assessment Satisfactory completion is based on demonstrating that the learning outcomes for the unit have been met through completion of school assessed coursework, which is at least three different tasks selected from the following: Essay Essay Empirical research activity Annotated poster Annotated poster Multimedia presentation Multimedia presentation Empirical research activity Test - short answer and extended response Summary and evaluation of data and methods from two or more related studies Summary of research findings in at least two related studies Unit 2 Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Introduction to neurons and nervous system Individual differences Social attitudes Assessment As for Unit 1. Test (multiple choice, shortanswer and extended response) School assessed coursework contributes 17% to the study score and the marks allocation is: Outcome 1 – 40 marks Outcome 2 – 30 marks Detailed study – 30 marks The mid-year examination (1 1/2 hours) contributes 33% to the study score. Unit 4 Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Memory Learning Research investigation Assessment As for Unit 3. The end-of-year examination (1 1/2 hours) contributes 33% to the study score. 45 Technology studies Design and technology Units 1-3 Unit 1 Materials, processes and design While students in this area will be encouraged to use a range of materials, the main materials areas will be wood and metal. Areas of Study Note: Students are expected to supply their own materials. 1. 2. 3. Properties and uses of materials Methods of communicating ideas Production processes Assessment Assessment will be based on the demonstration of outcomes through design folio production plans production task and evaluation short written reports Costs: Students are expected to supply their own materials Unit 2 Designers are restricted by various boundaries and limitations. These boundaries and limitations may be set by the consumer, manufacturer, social conventions or the law and constrain the actions of the designer throughout the design and production processes. This unit focuses on the origins of products, the considerations and constraints that may be imposed as products are developed and the impact of these constraints on product solutions. Areas of Study 1. 2. 3. Design considerations and constraints. Materials in design, development and production. Design and realization Assessment As for unit 1 46 Unit 3 Product development The design and development of a product for the mass market is subject to a range of complex forces. These include client requirements, social and economic trends, availability of resources and technological developments in industry. Design and production in industry provides a marked contrast to that in a ‘one-off situation’ in a school workshop. Areas of Study 1. 2. Designing for others Product development in Industry Assessment Assessment for Outcomes 1 and 2 will be based on a satisfactory completion of coursework and two written reports. Outcome 3 is a school assessed task and subject to external review. Students will produce a design folio, production plan and commence production. Technology studies Unit 4 Note: Students are expected to supply their own materials. Unit 4 Product evaluation and marketing This unit focuses on how judgements of the success of products can be informed by a comparison of products in terms of their quality, usefulness and appeal. The role and influence of product promotion and marketing are also considered. Areas of Study 1. Product Comparison 2. Marketing Products Assessment Outcomes 1 and 2 will be assessed on the satisfactory completion of coursework and two written reports. Outcome 3 is a school assessed task and subject to external review. Students will produce a design brief for a client, a design folio, production work and an evaluation report. End of year Examination Description of task Students will answer questions set by an examination panel about product development in industry and the marketing of products. In addition, students will respond to design briefs. 47 VET VCE Units of study. (Vocational Education and Training) These are VCE units that also give students a TAFE (Technical and Further Education) qualification. They are usually studied at another host school or a TAFE for a half day on Wednesdays and usually involve some work placement during the year. ET VCE units 3 and 4 contribute to the ENTER score and students can graduate with their VCE and a TAFE Certificate. The Department of Education subsidises the TAFE delivery costs, but students must pay the rest. In 2005 Princes Hill will be asking for the full estimated cost of a year of VET training before the end of 2004 as places in classes cannot be held without payment. Please note VCAL students MUST do a VET VCE subject as part of their VCAL. Of course if students drop out before a date set in February 2005 this money will be refunded. Below is a list of VET VCE subjects offered at PHSC in 2005 and the approximate cost to students for one year. Certificate II in Broadcasting $200 Certificate III in Clothing/ Concept Development $490 Certificate III in Community Services $200 Certificate I in Engineering $600 Certificate II in Fitness and Recreation $200 Certificate II in Furnishings $250 Certificate II in Horticulture $440 Certificate II in Hospitality $310 Certificate II in Information Technology $240 Certificate III in Multimedia $150 Certificate III in Music Industry (Technical Production ) $250 IMPORTANT: These subjects are offered to our cluster of schools so there can be lots of competition. To enrol students MUST fill in a VET enrolment form or they will not be included in the class. They must also attend a compulsory Orientation evening in Term 3 and pay fully by December 10, 2004. Details of all these courses are in the VET handbook available from the Careers Office. SBNAs (School Based New Apprenticeships). Theses are part time apprenticeships. Students are paid as they train. The SBNAs also contribute units to the VCE or the VCAL. Students spend 1 to 2 days per week at the work place or in training. Students must apply as soon as possible on a particular application form to register their interest. (Available from the Careers Room). In this case they might not get the SBNA, and must choose subjects this year as if they don’t have an SBNA. The SBNAs offered are Certificate II in Agriculture (Access to a rural property in the holidays is mandatory.) Certificate II in Automotive Certificate II in Business Certificate II in Hospitality Certificate II in Retail Certificate II in Retail (Hungry Jack’s) Certificate II in Sport and Recreation Details of all these courses are also in the VET handbook available from the Careers Office. There is also a themed VCAL course available in Hospitality (chef) 48