CHEM 2050/2130 Quiz 1 Review Sheet Review the front material
advertisement

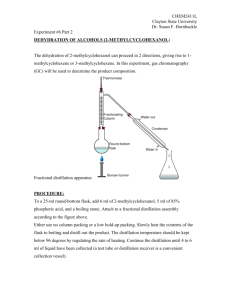
CHEM 2050/2130 Quiz 1 Review Sheet Review the front material we see in the lab experiments: the “big questions” about this quiz point to “why” and “what” questions: i.e. why do we use . . . . , or what is the purpose of . . . . Recrystallization: Characteristics which are desirable for a recrystallization solvent can be found in the beginning of the recrystallization experiment. We perform mixed melting points to ID the proper material and rules out incorrect materials. When using a Melt-Temp, the temperature rise in the melting range, do heat too quickly. The range of heating should be 3 – 5 degrees/minute. Extraction: Understand the basic idea of a distribution coefficient: In the expression Korganic/water = [A]organic/[A]water is a measure of the tendency for the solute to reside in one phase versus the other and is equal to the ratio of solubility’s for A in the respective solvents. Understand why the various chemicals or solutions could be used in an extraction, for example, sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), HCl, NaOH, and MgSO4 or Na2SO4 Basic Ideas for Chromatography: In the column chromatography we use silica (SiO2) as the stationary phase, which is a solid, inert material that contains a polar functional group. The solvent is a less polar material. We use the general idea of solubility to separate components in a mixture: polar materials are more attracted to the stationary phase while less polar materials are more attracted to the mobile phase. Be able to properly calculate Rf’s. Distillation: Distillation is a technique used to separate mixtures into separate fractions. Some different types of distillation include simple distillation, fractional distillation and steam distillation. Understand the differences we see in the two types of distillation we perform in lab.