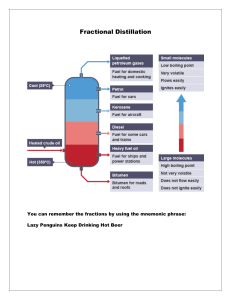
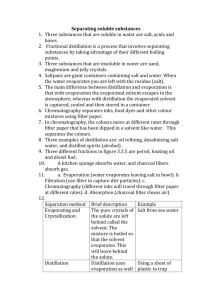
Chemistry Paper 6 Revision (●ˇ∀ˇ●) 1. Name of apparatus(common): - Pipette - Spatula - Fractionating column (present in fractional distillation) - Pestle (the stick to grind solid) and mortar(bowl) - Measuring cylinder (with measurements) - Gas jar (same as measuring cylinder but no measurements) 2. Apparatus to be used when involved with heating: - Test tube & Boiling tube - Beaker and crucible 3. Method of obtaining hot flame: -Open airhole 4. Separation methods(with labelling) :- Filtration - Simple distillation - Fractional distillation - Evaporation - Crystallisation - Chromatography *In simple distillation, there is condenser there are 2 openings and it’s for the constant flow of cold water the direction of water flow is always against the gravity going in from bottom, goes out from top* 5. Chromatography: - Baseline is ALWAYS drawn with pencil (if with ink, it will dissolve in solvent, inaccurate readings) - Apply samples to chromatography paper (on the baseline) - Use of solvent (ex. Ethanol or water) - Solvent below baseline - Check the spots produced - Compare to know Rf values 6. Measurement : - Time(stopwatch) - Temperature(thermometer) - Mass(measuring balance/ weighing scale) - Volume(measuring cylinder, pipette, burette i.e. more accurate) Accuracy increases 7. Experimental setup and drawings :- Electrolysis(cathode, anode, electroplating) - Gas collection(gas syringe, water displacement with measuring cylinder) 8. Dehydrating agents: *function of dehydrating agents is to remove water* - Porcelain chips - Concentrated sulfuric acid 9. Preparation of salts (from ex book) 10. Purpose of using the residue : - If we are using the residue – To remove(wash away) the soluble impurities - If we are going to discard the residue – To ensure all filtrate is obtained 11. 12. Universal indicator: - more than one colour changes - not suitable for titration - very hard to determine and control the end point 13. Titration (refer from ex book) 14. 15. Refer ex book 16. 17. Refer ex book 18. 19.