Cell Biology - This area is password protected
advertisement

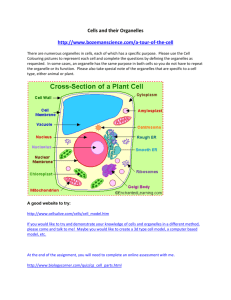
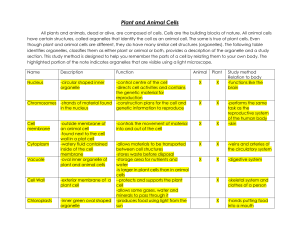
AS Bio 2.4 – Cellular Processes Cell Organelles…(master) Cell wall A rigid structure made of cellulose surrounding plant cells. This provides shape and strength. Cell membrane A layer that encloses the cell contents and controls what enters and exits the cell. It is made of two layers of lipid (fat) molecules with proteins for cell identification, active transport and communication. Cytoplasm fills the interior of the cell. It consists of a liquid (called the cytosol that contains water, proteins and dissolved ions) and cell organelles. It is used to transport substances throughout the cell and create internal pressure and is where most chemical reactions occur. Nucleus contains the genetic material which controls the cells activities. Nuclear membrane separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm. Perforated by pores and continuous with ER. Chromosomes Structures made of DNA and protein containing genes for protein synthesis. Mitochondria Organelles within the cytoplasm for cell respiration where food molecules are broken down to release energy. Chloroplast Organelles in plant cells containing chlorophyll for photosynthesis. Centrioles Produce spindle fibres for separating chromosomes during cell division Vacuole Liquid-filled organelle in cytoplasm for creating pressure and storing water and dissolved substances. Ribosome Organelle found free in the cytoplasm or attached to ER. Used for protein synthesis. Endoplasmic reticulum Is a system of membranes and connecting tubes that provide a surface for chemical reactions and a pathway for moving material within the cell. Lysosome Membrane-bound sac containing digestive enzymes. Breaks down food and worn out cell parts. Cell size Cell size is limited by the rate at which essential nutrients and oxygen can diffuse into a cell and waste products can be removed. Golgi body a series of membrane-bound sacs for producing and releasing secretions. Cell shape is determined by the role of the cell. Nerve cells are long and thin to conduct neural messages around the body. Intestinal cells have frilly edges to increase surface area for rapid diffusion. Plant Cells have: -rigid cell walls giving the cells a geometric shape; -chloroplasts (usually); -starch granules -large central vacuole They are usually larger than animal cells. Become specialised to perform support, absorption of water, conduct liquids, allow gases in and out, manufacture food, form protective surfaces and reproduction. Animal Cells don’t have a cell wall and have centrioles and an irregular shape. Become specialised to perform specific tasks. Humans have over 200 different kinds of cells. Similarities and differences Egg cells are spherical and large to contain organelles and nutrients for the zygote. Sperm cells have a long flagellum and many mitochondria for fast movement. RBC’s are disc-shaped with rounded edges for easy passage through blood vessels. Many cells are flat to increase the surface area, reduce travelling distance and increase diffusion rates Relative numbers of organelles present Secretory cells (e.g. glands) have large numbers of golgi bodies. Highly active cells (e.g. muscle) have larger numbers of mitochondria. Leaf cells contain large numbers of chloroplasts. Root cells have a large surface area for efficient water absorption. AS Bio 2.4 – Cellular Processes Cell Organelles…(Cloze) Structures made of DNA and ____________ containing ____________ for protein synthesis. Cell wall A rigid structure made of __________ surrounding plant cells. This provides shape and strength. Mitochondria Organelles within the cytoplasm for cell _________ where food molecules are broken down to release _________. Cell membrane A layer that encloses the cell contents and controls what _________ and _________ the cell. It is made of two layers of lipid (fat) molecules with proteins for cell identification, active ____________ and communication. Cytoplasm Fills the interior of the cell. It consists of a liquid (called the _________ that contains water, proteins and dissolved ions) and cell organelles. It is used to transport substances throughout the cell and create internal pressure and is where most chemical _______________ occur. Nucleus contains the _________ material which controls the cells activities. Nuclear membrane separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm. Perforated by _________ and continuous with ER. Chromosomes Chloroplast Organelles in plant cells containing _________ for _________. Centrioles Produce s_________ fibres for separating chromosomes during cell d__________ Vacuole Liquid-filled organelle in cytoplasm for creating ____________ and storing water and dissolved substances. Ribosome Organelle found free in the cytoplasm or attached to ER. Used for _______________ _______________. Endoplasmic reticulum Is a system of ____________ and connecting tubes that provide a surface for chemical reactions and a pathway for moving material within the cell. Lysosome Membrane-bound sac containing digestive __________. Breaks down food and worn out cell parts. Golgi body a series of membrane-bound sacs for producing and releasing ____________. Plant Cells have: -rigid cell walls giving the cells a ________ shape; -____________ (usually); -starch _________ -large central _________ They are usually _________ than animal cells. Become specialised to perform support, absorption of water, conduct liquids, allow gases in and out, manufacture food, form protective surfaces and reproduction. Animal Cells don’t have a cell wall and have ____________ and an irregular shape. Become specialised to perform specific tasks. Humans have over 200 different kinds of cells. Similarities and differences Cell size Cell size is limited by the rate at which essential nutrients and oxygen can _________ into a cell and waste products can be removed. Cell shape is determined by the _________ of the cell. Nerve cells are _________ and thin to conduct neural messages around the body. Intestinal cells have frilly edges to increase surface area for rapid _________. Egg cells are spherical and large to contain organelles and nutrients for the _________. Sperm cells have a long flagellum and many ____________ for fast movement. RBC’s are disc-shaped with rounded edges for easy passage through _________ vessels. Many cells are flat to increase the surface area, reduce travelling distance and increase ____________ rates Relative numbers of organelles present Secretory cells (e.g. glands) have large numbers of _________ bodies. Highly active cells (e.g. muscle) have larger numbers of mitochondria. Leaf cells contain large numbers of ____________. Root cells have a large surface area for efficient water absorption.