Q and A
advertisement

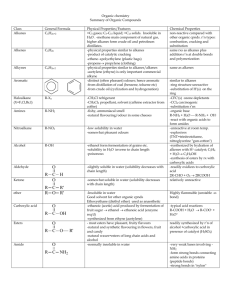
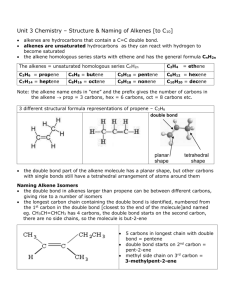
Topic 6 – Hydrocarbons – Q and A 1 What are the alkanes? A family of hydrocarbons 2 Which of the following are alkanes: ethene, propyne, butane, ethanol, decane, propene? butane and decane because they end in -ane 3 Name the first 8 alkanes. (If you don't remember them they are in the data book). methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane, heptane, octane (nonane, decane) 4 Give uses for: a) methane b) propane c) butane d) octane methane – cookers, heating propane: portable heaters butane – lighter fuel octane – petrol 5 Name the following alkanes: CH4, C5H12, C7H16, C3H8 methane, pentane, heptane, propane 6 What is the general formula of the alkanes? CnH2n+2 7 Work out the molecular formula of the alkanes with: a) 2 carbons b) 6 carbons c) 8 carbons C2H6 C6H14 C8H18 8 Which of the following are alkenes: ethene, propyne, butane, ethanol, decane, propene? ethene and propene (end in –ene) 9 Name the first 5 alkenes. ethene, propene, butene, pentene, hexene 10 Name the following alkenes: C2H4, C6H12, C5H10, C3H6 ethene, hexene, pentene, propene 11 What is the general formula of the alkenes? CnH2n 12 Work out the molecular formula of the alkenes with: a) 2 carbons b) 6 carbons c) 8 carbons C2H4, C6H12, C8H16 13 Draw molecular formulae and full structural formulae for the following hydrocarbons: C2H4 C4H10 ethene, ethane, butane, pentene 1 C2H6 C5H10 Topic 6 – Hydrocarbons – Q and A 14 What is meant by a saturated hydrocarbon? A hydrocarbon with single bonds only between carbons 16 What is meant by an unsaturated hydrocarbon? A hydrocarbon with at least one C=C double bond 17 Which of the following are saturated: ethane, ethene, propane, butene? ethane and propane are saturated (alkanes have single bonds) 18 What chemical test is used to distinguish between a saturated and an unsaturated hydrocarbon? State the result of the test. Bromine water when added to an unsaturated hydrocarbon is decolourised quickly. 19 State the type of reaction that occurs between bromine and an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Addition reaction. 20 Does fractional distillation of crude oil give adequate supplies of short chain hydrocarbons for uses such as petrol. No it gives too much of the less useful bigger molecules. 21 What is the name of the industrial method for producing smaller, more useful molecules? Catalytic cracking or thermal cracking. 22 In what 2 ways are the products of cracking different from the original molecules? The molecules are smaller and lighter. Alkenes are always produced. 2 Topic 6 – Hydrocarbons – Q and A Credit Questions 1 What is meant by a homologous series? A family of related compounds with similar properties. Alkanes, alkenes (also cycloalkanes) 2 Give 2 examples of homologous series. 3 What is the general formula of a) the alkanes b) the alkenes 4 The first three members of a homologous series are: C2H2, C3H4, C4H6 What is the general formula of this series? 5 Name the first five members of the cycloalkanes. cyclopropane, cyclobutane, cyclopentane, cyclohexane, cycloheptane 6 Explain what is meant by isomers. Molecules with same molecular formula and different structural formulae. 7 Draw extended structures for 2 isomers with the formula a) C4H10 b) C5H12 8 Explain why the boiling point increases steadily as we go from methane to octane. The molecules are getting bigger and so are harder to separate – more energy needed. 9 In thermal cracking, why does use of a catalyst represent a cost saving? Less heat is needed using a catalyst, so energy is saved. CnH2n+2 CnH2n-2 a) 10 What types of molecules are produced from the cracking of long chain alkanes? b) Smaller molecules always including alkenes. 12 Copy and complete this equation for cracking putting in numbers for x and y and suggest possible names for all the products. C10H22 CnH2n C3H6 Butane, propene and propene C4H10 + C3H6 + CxHy (one of the propenes might be cyclopropane) 3