Alkane, Alkene, Alkyne Reactions: Chemistry Notes
advertisement

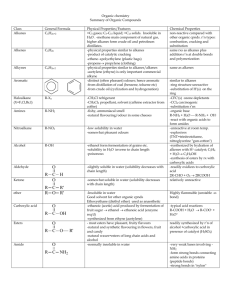
Reactions with Alkanes A. The alkanes undergo complete and incomplete combustions. Approximately 95% of crude oil serves as combustibles. CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) 2 C3H8(g) + 7 O2(g) CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) complete combustion CO2(g) + 8 H2O(g) + 4 CO(g) + C(s) incomplete combustion B. The alkanes also undergo substitution reactions substitute hydrogen one at a time for halogens or <<nitro>> forming organo-halides and another product H l H-C-H l H H l H - C - Cl l H + Cl – Cl + Cl - Cl H l H - C - Cl l H + H l H - C - Cl l Cl HCl + This also occurs with other halogens (F2, Br2, I2) and H-OH & H-NO2. HCl etc. C. Cracking was first introduced in Sarnia, Ontario. This process uses heat (or catalysts) to break larger hydrocarbon molecules into smaller gasoline molecules. Cracking is done in the absence of air and can produce different types of hydrocarbons. C17H36(l) C9H20(l) + C8H16(l) D. Reforming is another technique that uses heat, pressure, and catalysts to convert straight chain alkanes to branched chains and also convert cyclic alkanes into aromatic compounds. C5H12(l) + C5H12(l) C10H22(l) + H2(g) Reactions with Alkenes A. The alkenes also undergo complete and incomplete combustions as the alkanes. B. The alkenes can be formed during cracking. C2H5OH(l) acid C2H4(g) + H2O C. In an addition reaction, atoms are added to a multiple bond. One bond of the multiple bond breaks so that two new bonds can form. H H \ / C=C / \ + Br - Br H H l l H-C-C-H l l This also occurs with other halogens (F2, Cl2, I2) and H-OH & H-NO2 and H2. H H H H \ / C=C / \ H H + H H \ / C=C / \ H H H-H + H - OH Br Br H H l l H-C-C-H l l H H H H l l H-C-C-H l l H OH This is known as hydrogenation. This is one formation for alcohols. D. Alkenes also undergo additional polymerization: a reaction in which monomers with double bonds are joined together, through multiple addition reactions, to form a polymer (chain). Various products such as polyester, polystyrene, latex, polyethylene, and polyvinylchloride are produced in this method. n H H \ / C=C / \ H H ethene (ethylene) H H l l -C–Cl l H H n n represents the number of alkenes with ruptured bonds allowing the formation of the polymer chain. polyethylene (plastic) Reactions with Alkynes A. The alkynes will also undergo complete and incomplete combustions as the alkanes and alkenes. B. The alkynes also demonstrate addition reactions as the alkenes. H–CC–H Cl Cl l l H–C=C–H H–CC–H + + + Cl – Cl Cl – Cl 2H–H Cl Cl l l H–C=C-H Cl l H–C– l Cl Cl l C–H l Cl H l H–C– l H H l C–H l H This also occurs with other halogens (F2, Br2, I2) and H-OH & H-NO2. One bond at a time.