Exam Review - Petoskey Public Schools
advertisement

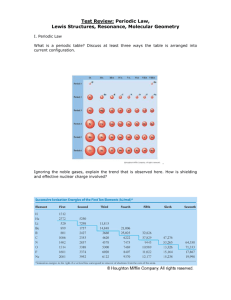
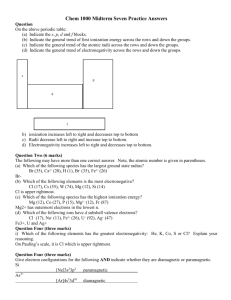
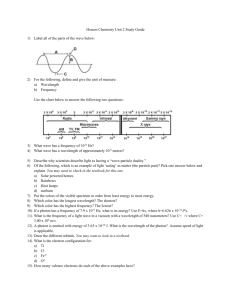
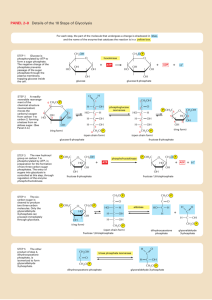
What are the base units for scientific measurements? Convert the following units. 21.7 cm -> ________ m 1.18 km -> _______ m 2.23 mL -> ______ L 35.2 mL -> _____ cm3 How many significant figures are in the following numbers. 414.76 m ____ sig fig 1.0001 km ____ sig fig Calculate the following with correct sig figs. 2.215 cm X 1.1 cm ______________ Calculating the densities 54 g, 1.4 cm X 4.2 cm X 2.2 cm ____________________ 23.3 g, 35.6 mL ____________________ Rewrite in scientific notation. 1,202,000,000 .0000007080 12,676,230 Name the parts of an atom, their locations, and their charges Find the atomic number, mass number, # protons, neutrons, and electrons for Neon – 23. Define isotope. Find how many moles and # molecules in 51.9 g NaCl. Name and explain the three phases of property. Describe both chemical and physical changes. Be able to distinguish both. .000016 Explain the laws of conservation of matter. Contrast accuracy and precision. Compare and contrast qualitative and quantitative observations. Explain the work of Dalton, Rutherford, and Bohr. Explain nuclear instability and radioactive decay. What keeps the protons and neutrons together? Valence electrons – what they are and how to determine how many an atom has What do the quantum numbers s, p, d, and f refer to and how many electrons can each hold? Explain Aufbau’s principle, Hund’s rule, and the Pauli Exclusion principle. What is the relationship between wavelength, frequency, energy, and light color. Electron Configurations – what they are and be able to draw some for main group and transition metals Where are the following families of the periodic table – Alkali, Alkali Earth, Halogen, Noble Gases, Main Group, Transition Metals? Determine the electron configuration for the following atoms Mg _______ Cu _______ Br ______ Where are the S, P, D, and F block elements Definitions of Effective Nuclear Charge, Ionization Energy, Electron Affinity, and Electronegativity. Relationship between Effective Nuclear Charge and the following – atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization energy, electron affinity Trends in the periodic table in relation to Effective Nuclear Charge, Ionization Energy, Electron Affinity, and Electronegativity. Bond types- explain them, types of elements involved, what electrons are doing in each, how to determine (element types and electronegativities) What is the bond length and energy relationship Explain the octet rule and how it is met with bonds Explain Resonance structures Draw electron dot diagrams and find lewis structures for the following compounds CH2O PH3 SiO2 SiH4 Impacts of bond types on characteristics – melting point, solubility, conductivity Naming compounds, polyatomic ions, and acids SCl2 Molar mass, % composition Chemical vs. empirical formula Use electronegativity to determine the bond type for the following. CO2 H2O PCl3 NH3 CuPb NaF Explain VSEPR and use it to determine the shape of the following. CO2 H2O BCl3 NH3 SiCl4 CH2O Using bond types and molecule shape to determine molecule polarity for the following. CO2 H2O PCl3 NH3 SiCl4 CH2O Name the three intermolecular forces and list them from strongest to weakest. Determine the intermolecular forces in the following. CO2 H2O PCl3 NH3 SiCl4 CH2O Name, structure, and formulas for organic compounds Calculate the % composition for the following chemicals: (6 points) Fe(NO4)3 C6H5COOH Mg ________________ C ________________ N ________________ H ________________ O ________________ O ________________ What is the Empirical Formula for a compound that is 38.29% iron, 12.35% carbon and 49.36% oxygen? (2 points) Give the names and letters for the four quantum numbers, then describe what each number is labeling. Write the electron configuration and the noble gas notation for elements from anywhere on the periodic table. What is half-life? Determine how long it will take for a 30 g sample of caffeine to decrease to less than 4 g if the half-life is 4.5 hrs.