File
advertisement

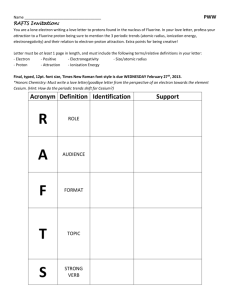
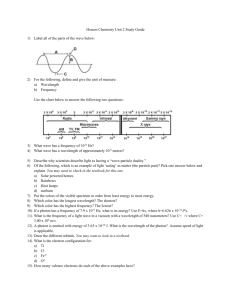
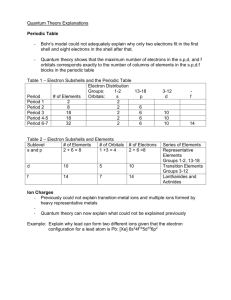
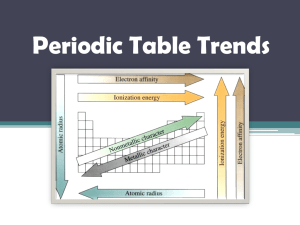
Chemistry Unit 4 Quantum Theory Study Guide Name ___________________ Period ____ Date __________ Answer each question on a separate piece of paper. All calculations must be accompanied by work. 1. Briefly describe the atomic models proposed by each scientist and describe the major contribution each made. a. Dalton b. Thomson (plum pudding) c. Rutherford d. Bohr (planetary) e. Schrodinger (wave-mechanical) 2. Write the formulas for the following: a. energy of a photon in terms of frequency b. speed of light in terms of wavelength and frequency 3. Explain why a series of colored lines are seen when light from a glowing bulb filled with neon is examined through a prism (explain the mechanism for this). 4. Explain why the Bohr model eventually failed. 5. How was the Schrodinger (wave-mechanical) model different from the Bohr model? 6. (a) Find the energy of a photon whose frequency is 1.58 x 1016 s-1. (b) Using the frequency from 6(a), calculate the wavelength of the photon in meters. 7. What does the principle quantum number, n, represent? 8. List all the possible subshells (or sublevels) in the following energy levels: n=1, n=2, n=3, n=4? 9. What is the maximum number of electrons that may fit in the following energy levels: n=1, n=2, n=3, n=4? 10. Define the following: Aufbau Principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle, Hund's Rule 11. Draw the orbital energy diagram for phosphorus, illustrating all electrons in their ground state. 12. a) Write the full electron configuration for sulfur. b) Underline the subshells that constitute the valence electron shell for sulfur. 13. Copper has an electron configuration of 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s1. Is this expected?___. If not, explain why the electron configuration is different from what you would expect. 14. An element has an electron configuration of [Ne]3s23p2. What element is this? 15. An element has 2 electrons in its 5s subshell and 3 electrons in its 4d subshell. What element is it? 16. What is unique about the electron configurations of the Noble Gases? 17. What trends are observed in atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity of the elements as you go across a period (left to right)? Explain why we observe these trends. 18. What trends are observed in atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity of the elements as you go down a group? Explain why we observe these trends. 19. Circle the atom or ion with the larger radius and explain your choice. a. Na or K ? b. P or Cl ? c. Li or Li+ ? d. Cl or Cl- ? 20. Circle the element with the larger 1st ionization energy and explain your choice. a. Al or Mg ? b. Mg or Sr ? 21. Which element has the highest electronegativity?____. Why? 22. Which element has the lowest 1st ionization energy? ____. Why?