Course:
advertisement

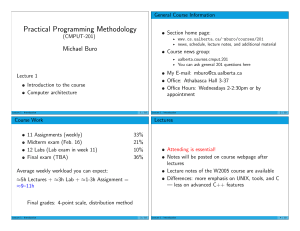
Course: Term: Format: Computers: Instructor: Phone: Email: Textbook: CSCI 490 Special Topics: Introduction to Parallel Programming Full Summer 2006 Online (Web) Remote login to MCSR supercomputers for assignments Jason Hale 662-915-3922 jghale@olemiss.edu Description: Introduction to Parallel Programming Prerequisites: Experience programming in Java, Fortran, or C/C++ (Preferred). "Parallel Programming: Techniques and Applications Using Networked Workstations and Parallel Computers" by Barry Wilkinson and Michael Allen. Prentice Hall. http://vig.prenhall.com/catalog/academic/product/0,1144,0131405632,00.html Course Description: This course will introduce students to the rationale, concepts, and techniques for writing parallel computer programs. Students will be given accounts on a supercomputer and cluster computer at the Mississippi Center for Supercomputing Research (http://www.mcsr.olemiss.edu), and will use these accounts to complete five programming assignments. Distributed memory (message passing) techniques will be featured in some of the assignments. Shared memory techniques (threads) will be featured in others. In addition to learning the programming techniques for sending messages between processes, and for coordinating access to shared memory locations between threads, students will learn how to think about restructuring a computing problem in such a way as to keep all available processors gainfully employed in collectively reaching a solution as fast as possible. Students will learn to evaluate the potential speedup of a computing problem, as well as how to measure the actual speedup of a problem on a given architecture, and to measure how efficient the computer is in solving the problem. This will be a somewhat self-paced course. Course Topics: Introduction to Linux/Unix O/S environment Rationale for Parallel Computers; Grand Challenge Problems Estimating and Measuring Speedup of a Program on a Supercomputer Measuring the Efficiency of a Parallel Computation on a Supercomputer Design Tradeoffs of Major Classes of Parallel Computing Architectures Submitting Batch Jobs to a Scheduler on a Supercomputer (using PBS) Static vs. Dynamic Process Creation Single Program Multiple Data (SPMD) vs. Multiple Program Multiple Data (MPMD) Approaches Message Passing (MPI) Techniques and Concepts: Communicators, Tags, Blocking vs. Non-blocking Messages, Collective Communication Constructs (Reduce, Gather, Broadcast, Scatter) Shared Memory Computing via Unix/Linux Heavyweight Processes Shared Memory Computing via Unix/Linux Lightweight Threads OpenMP Message Passing Interface for Creating Shared Memory Programs Static Work Partitioning Dynamic Work Allocation/Load Balancing Grading Policy: 5 Programs (100 points each): Several Homework Assignments: Two Tests: (100 points each): 500 points 300 points 200 points