Bacteria notes
advertisement

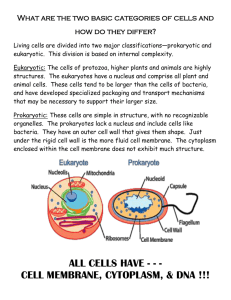
Name: Date: Period: Kingdom Eubacteria and Kingdom Protista Remember the classification: LIFE PROKARYOTE – NO Nucleus in cell 3 DOMAINS ARCHAEA EUKARYOTE – HAS A Nucleus in cells BACTERIA EUKARYA ARCHAEBACTERIA EUBACTERIA (MONERANS) ANIMALIA 6 KINGDOMS PLANTAE PROTISTS FUNGI We will be focusing this unit on the Kingdoms: Eubacteria and Protista Archaebacteria: the oldest bacteria; found in extreme environments – hot springs, our intestines, bottom of swamps, sewage Eubacteria: do not live in extreme environments, but live everywhere else – on us and in our bodies, some are autotrophs that float on water I. Characteristics of Eubacteria Characteristic My definition My drawing or examples Autotroph Can make food through ________________________, like a plant. Heterotroph Must get food from outside source. Can not complete photosynthesis Unicellular Made up of _________ cell. Prokaryote Does not contain a ______________ in its cell. II. Two types of Eubacteria Types of Monerans: My definitions: Good bacteria helps make: 1) Bacteria Bad bacteria can cause: 2) Blue green algae Can complete ________________________. We know it commonly as pond scum. III. Classification of Bacteria by their shape Name (suffix) Shape My Drawing Can be in chains: -coccus ROUND Can be in pairs: Can be in clumps: -bacillus ROD -spirilla SPIRAL Write the scientific name of the following bacteria: Underline the scientific name. Genus name is capitalized Species name is lower case Rod Round Spiral IV. Organelles of a bacteria cell Organelle Function My Drawing (structure) 1. Capsule Keeps the cell from drying out. 2. Cell Wall Maintains the __________ of the cell. Located just inside the capsule 3. Ribosomes 7. 5. Makes __________ for the cell. 1. 6. 4. DNA Controls the cell – NO NUCLEUS 2. 3. 5. Cilia 6. Flagella 7. Cytoplasm Hair-like structure for movement and attachment Whip-like tail for movement Jelly-like inside of cell (environment of the cell) 4. V. Reproduction of Bacteria 1) Asexual Reproduction: a. Reproduction of a living organism from only __________ parent. 2) Binary Fission: a. Process of _________ organism dividing into _______ organisms. VI. Draw a picture of Binary Fission below: Antibiotics 1) Antibiotics: a. Chemical substances used to _________ or slow the growth of bacteria. b. Anti = _____________ c. Bio = ____________ 2) What is wrong with overusing antibiotics? _____________________________ KINDOM PROTISTA What is a protist? Microscopic ______________organisms that contain a nucleus (_____________) Characteristics of protists Most of them are unicellular, and usually do not have a cell wall Able to move Take in oxygen and give off carbon dioxide through cell membrane (__________________) React to changes in their environments – move to better environmental conditions Can be Autotrophs or Heterotrophs WORD BANK FOR THE CELL PARTS: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Cell membrane Nucleus Nuclear membrane Chromosomes Ribosomes Chloroplasts Mitochondria 8) Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 9) Cytoplasm 10) Vacuole Cell membrane – surround the cell and give it its’ __________. Nucleus – control center of the cell. Nuclear membrane – surrounds and protects the _______________. Chromosomes – the DNA of the cell (information) Ribosomes – make protein for the cell. (remember, DNA makes RNA, RNA moves out of the nucleus and carries the message to the ribosomes) Chloroplasts – ONLY found in PLANT cells or cells that complete PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Make _____________ for the cell by completing photosynthesis. Mitochondria - ______________ producers of the cell. This is where RESPIRATION occurs – the cell takes in the food and breaks it down using oxygen, to release ENERGY! Endoplasmic Reticulum – the proteins (and other small molecules) are transported by the ER to a place for packaging (called the Golgi Bodies) to head out of the cell. Cytoplasm – environment of the cell (jelly-like inside of cell) Vacuole – many types of vacuoles are found in a cell, mostly used as storage… a. food vacuoles hold food b. waste vacuoles hold waste c. contractile vacuoles excrete excess water from the cell Cellular Processes: Cell Transport - MOVEMENT We talked about making proteins in the cell and nutrients needed, but how do we get them to other areas of the body? PASSIVE TRANSPORT: NO ENERGY 1. Diffusion Molecules of a substance _____________________________________________________ _________________ to reach an equilibrium. **Small molecules such as food molecules, oxygen, and water diffuse into the cell (through the selectively permeable membrane) and Carbon Dioxide diffuses out of the cell. Example: If you spray perfume in the front of the room, the odor will spread to the rest of the room. Example: Oxygen (O2) moving into the cell and CO2 moving out of the cell Draw a picture of diffusion: 2. Osmosis 80 % of the cell is made up of water. Osmosis is the diffusion of WATER into or out of the cell. Why would it be important that a person not drink salt water? Why do plants have a large vacuole? Draw a picture of Osmosis in action ACTIVE TRANSPORT – ENERGY REQUIRED Active transport __________________________ to “carry” a substance/mineral into that cell OR move from a low concentration to a high concentration (across the gradient). Carrier Proteins act like doors to allow molecules to enter and exit cell. Used to carry minerals such as sodium, calcium, and potassium into the cell. Used to eliminate substances out of the cell. A. ENDOCYTOSIS: taking materials into the body by the cell membrane wrapping around the particles B. EXOCYTOSIS: releasing materials into the fluid outside of the cell HOW DO CELLS GET ENERGY? Through a process called Respiration which occurs in the MITOCHONDRIA. TWO TYPES OF RESPIRATION: i. AEROBIC – requires oxygen 1. GLUCOSE (C6H1206) + O2 CO2 + H2O + ATP (ENERGY) ii. ANAEROBIC – does NOT require oxygen (FERMENTATION) 1. Products: CO2 + H2O + ATP (ENERGY) Do plants and plant-like protists complete respiration? ____________ Where do plant-like protists get their food? ________________ PHOTOSYNTHESIS: PHOTOSYNTHESIS : CO2 + H20 SUNLIGHT O2 + glucose (C6H1206) Where, in the cell, does photosynthesis occur? __________________ Types of animal-like protozoans: AMOEBA: Move by using a _____________ or false foot. An extension of the cell membrane, allows it to eat and move. Label: PARAMECIUM: Move by using ___________ or tiny hairs. Label: CLASS: Sporozoan All are Parasites that feed on the cells and body fluids of their host animals Example: plasmodium How does plasmodium work? 1. 2. 3. 4. Infected mosquito bites human Mosquito injects Plasmodium spp. into human Plasmodium spp. travels to liver and reproduces Moves into red blood cells and travels throughout body making human sick with high fevers Types of Plant-Like protists Are __________, can make their own food because they contain _____________. Most live in the water – aquatic. Many algae are considered to be a protist 1. Euglenas: Move by using a __________or whip-like tail. Variety of shapes, have a pouch that holds two flagella, a reddish eyespot, and structures used in making food Label: 2. Diatoms: Enclosed in a two-part glassy shell, water-dwelling organisms, dead diatoms form diatomaceous Earth (coarse powdery material) Important ingredient in car wash and toothpaste 3. Dinoflagellates: Contain cell walls that look like plates of armor, have two cell walls that propel them through the water, can produce sparkles or glow in ocean waves Label: TYPES OF FUNGUS-LIKE PROTISTS SLIME MOLDS: funguslike protists that resemble different organisms throughout their life span. Resemble an amoeba, a fungus with spores and a flagellate.