Periodic Table Worksheet
advertisement
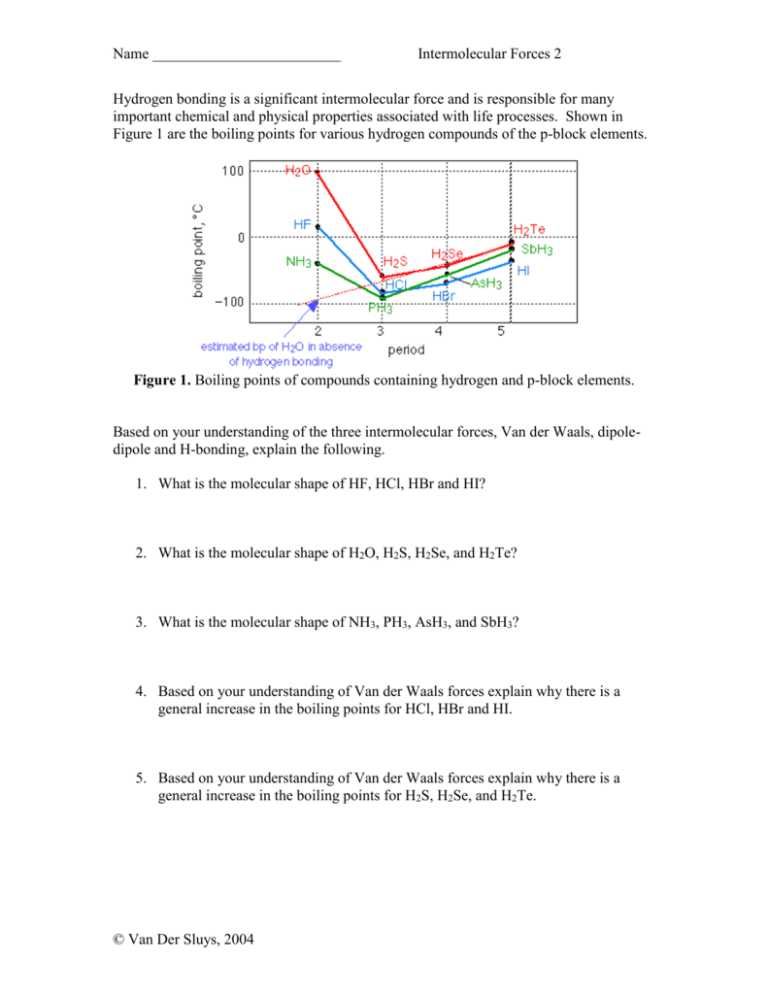
Name _________________________ Intermolecular Forces 2 Hydrogen bonding is a significant intermolecular force and is responsible for many important chemical and physical properties associated with life processes. Shown in Figure 1 are the boiling points for various hydrogen compounds of the p-block elements. Figure 1. Boiling points of compounds containing hydrogen and p-block elements. Based on your understanding of the three intermolecular forces, Van der Waals, dipoledipole and H-bonding, explain the following. 1. What is the molecular shape of HF, HCl, HBr and HI? 2. What is the molecular shape of H2O, H2S, H2Se, and H2Te? 3. What is the molecular shape of NH3, PH3, AsH3, and SbH3? 4. Based on your understanding of Van der Waals forces explain why there is a general increase in the boiling points for HCl, HBr and HI. 5. Based on your understanding of Van der Waals forces explain why there is a general increase in the boiling points for H2S, H2Se, and H2Te. © Van Der Sluys, 2004 Name _________________________ Intermolecular Forces 2 6. Based on your understanding of Van der Waals forces explain why there is a general increase in the boiling points for PH3, AsH3, and SbH3. 7. Why is the boiling point for water so much higher than what would be estimated based on the periodic trend for the other group 16 compounds? 8. Why is the boiling point for ammonia so much higher than what would be estimated based on the periodic trend for the other group 15 compounds? 9. Why is the boiling point for HF so much higher than what would be estimated based on the periodic trend for the other group 17 compounds? 10. What is the ratio of lone pair to covalently bonded hydrogens in water, ammonia and hydrogen fluoride? How does this effect the extent of the hydrogen bonding network that is possible in these molecules? Why is the boiling point of water so much higher than either NH3 or HF? 11. Based on your understanding of dipole-dipole forces, why is the boiling point of HF higher than NH3? 12. Based on your understanding of intermolecular forces and molecular shape, predict the trend in boiling points for the group 14 compounds, CH4, SiH4, GeH4, and SnH4. 13. Based on your understanding of intermolecular forces, predict the trend in boiling points for the Noble gases, Ne, Ar, Kr, and Xe. © Van Der Sluys, 2004 Name _________________________ Intermolecular Forces 2 Answers 1. The shape is linear. 2. The shape is bent. 3. The shape is pyramidal. 4. There are more electrons. 5. There are more electrons. 6. There are more electrons. 7. Due to hydrogen bonding. 8. Due to hydrogen bonding. 9. Due to hydrogen bonding. 10. Due to the 2:2 ratio of nonbonding pairs to hydrogens, creating an extensive hydrogen bonding network, whereas in the other two molecules the hydrogen bonding network is not as extensive due to the formation of only one hydrogen bond per molecule. 11. There is a greater difference in electronegativity between fluorine and hydrogen, resulting in a larger molecular dipole. 12. The shape of all these molecules is tetrahedral and there is no molecular dipole, therefore the strongest intermolecular force is dispersion forces which increase with increasing number of electrons. 13. The strongest intermolecular force is dispersion forces which increase with increasing number of electrons © Van Der Sluys, 2004