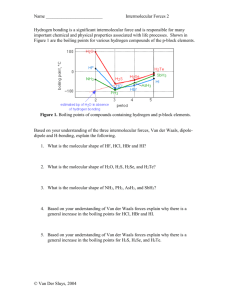
Name - Hopkinton School District
advertisement

Name: ______________________ 90. Why is the boiling temperature of water out of line with the hydrogen compounds of the other group VI hydrogen compounds? 91. For hydrogen bonding to occur, hydrogen must be attached to what other elements? 92. Explain why there is no hydrogen bonding in CH4, even though there are 4 hydrogens. 93. The formula for ethanol is CH3CH2OH. Would you expect ethanol to exhibit hydrogen bonding? If so, circle the hydrogen(s) that would be involved. 94. What holds one helix to the other helix in a DNA molecule? 100. Explain why network solids usually contain either carbon or silicon. 101. Explain why diamond is such a strong material. 102. If you were to examine a salt crystal under a microscope you would observe that the crystals look like little cubes. Suggest a reason for this. 103. Explain why ionic crystals tend to shatter along planes or faces, whereas when glass shatters you get all types of different shaped shards. 104. Explain why metals are malleable. 105. Explain why metals are good electrical conductors. 106. What type of solid is formed by molecules attracted to each other with dipole-dipole attractions? 110. What forces hold non-polar molecules together? 111. Explain why the boiling temperature of the noble gases increases as you go down the family. 112. Oil contains a large mixture of different molecular weight hydrocarbons. In all refineries, the oil is first separated by fractional distillation, which separates the components by their boiling temperatures. Suggest a reason why methane, CH4, has a low boiling temperature whereas octane, C8H18, has a higher boiling temperature and wax, C25H52, has the highest of the three. 113. If you have two equivalent weight molecular compounds and the only real difference separating them was the fact that one was polar and the other was non-polar, what different physical properties would you expect to see? 114. Identify the most important types of inter-particle forces present in the solids of each of the following substances: a. BaSO4 b. H2S c. Xe The warrior princess d. C2H6 e. RbI f. P4 g. H2O h. CaCO3 i. Teflon, CF3(CF2CF2)nCF3 j. CO2 k. NH3 l. PH3 m. Polyethylene, CH3(CH2)nCH3 115. In each of the following groups of substances, pick the one that has the given property. Justify your answer: a. Highest boiling temperature, HCl, Ar, or F2 b. Highest freezing temp: H2O, NaCl, or HF c. Lowest vapor pressure at room temp: F2, Br2, or I2 d. Lowest freezing temp: N2, CO, or CO2 e. Lowest boiling temp: CH4, CH3CH3, or CH3CH2CH3 116. Identify the type of solid (network, ionic, metallic or molecular/atomic) each of the following would form: a. C as diamond b. CO2 c. P4 d. Pd e. Br2 f. Cu g. CuNO3 h. Kr i. H2O 117. In unit 2, you found the heat involved in melting wax, C25H52, and the heat of combustion of wax. Explain, using the types of forces involved, why the Heat of Combustion is much larger than the Heat of Fusion.