Intermolecular Forces Chemistry Worksheet
advertisement

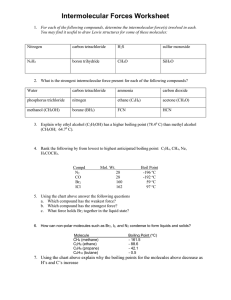
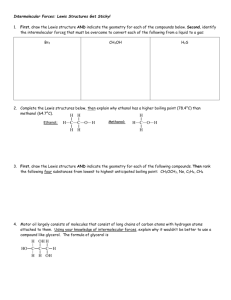
Intermolecular Forces Wkst Chemistry 1) 2) 3) 4) Name: Date: Period: Using your knowledge of molecular structure, identify the main intermolecular force in the following compounds. You may find it useful to draw Lewis structures to find your answer. a) PF3 b) H2CO c) HF What is the strongest intermolecular force present for each of the following compounds? Explain how dipole-dipole forces cause molecules to be attracted to one another. Rank the following compounds from lowest to highest boiling point: calcium carbonate, methane, methanol (CH4O), dimethyl ether (CH3OCH3). 13) water 14) carbon tetrachloride 15) ammonia 16) carbon dioxide 17) phosphorus trichloride 18) nitrogen 19) ethane (C2H6) 20) acetone (CH2O) 21) methanol (CH3OH) 22) borane (BH3) 23) For each of the following compounds indicate which intermolecular force is most important: Explain why nonpolar molecules usually have much lower surface tension than polar ones. For each of the following compounds, determine the main intermolecular force. You may find it useful to draw Lewis structures for some of these molecules: 5) nitrogen 6) carbon tetrachloride 7) H2S 8) sulfur monoxide 9) N2H2 10) boron trihydride 11) CH4O 12) SiH2O a) FCN b) HCN c) C2H6 d) CF2H2 24) Explain why ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) has a higher boiling point (78.40 C) than methyl alcohol (CH3OH; 64.70 C). 25) Rank the following by from lowest to highest anticipated boiling point: C2H4, CH4, Ne, H3COCH3 26) Motor oil largely consists of molecules that consist of long chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms attached to them. Using your knowledge of intermolecular forces, why wouldn’t it be better to use a compound like glycerol. The formula of glycerol is CHOH(CH2OH)2.