the circulatory and blood study guide
advertisement

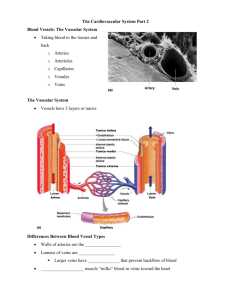
THE CIRCULATORY AND BLOOD STUDY GUIDE 6. The walls of the Heart are made up of Three Layers of Tissue. The outer and inner layers are ____endothelial___ tissue. The middle layer is ___muscular___ tissue called ____myocardium________. 7. The Heart can be thought of as __double _ _pump___ sitting side by side. 8. Our Heart has ______4_______ chambers: A. The upper chambers are the __left__ and __right___ _atria_____. B. The lower chambers are the ___left__ and _right___ __ventricle____. 9. The Right side of the heart pumps from the _heart_____ into the _lungs____. 10. Oxygen poor blood is called __deoxygenated___________. 11. The Left side of the Heart pumps ________oxygen___ Rich Blood from the ___heart__ to the rest of the ____body__________ except the __lungs________. 14. Dividing the Right and Left sides is a common wall called the ___septum__. The __septum___ prevents the mixing of Oxygen-poor and Oxygen-rich Blood. THE RIGHT SIDE OF THE HEART (FROM BODY TO LUNGS, DEOXGENTATED BLOOD) 1. Oxygen-Poor Blood from the body enters the Right side of the Heart through TWO large blood vessels called ____superior/ inferior vena cava_. 2. The _superior______ Vena Cava brings Blood from the UPPER PART OF THE BODY TO THE HEART. 3. The ____inferior__________ Vena Cava brings Blood from the LOWER PART OF THE BODY TO HE HEART. 4. Both VENA CAVA EMPTY INTO THE _____right___ ___atrium______. When the Heart Relaxes (Between Beats), pressure in the circulatory system causes the Atrium to fill with blood. 5. When the Heart CONTRACTS, Blood is squeezed from the RIGHT _____atrium______INTO THE RIGHT __ventricle___________ through flaps of tissue called the ____tricuspid_______ _____valve_________ that prevents blood from flowing back into the Right Atrium called a_heart murmur (backflow through valves). 6. THE GENERAL PURPOSE OF ALL VALVES IN THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM IS TO PREVENT THE __backflow________ OF BLOOD. They also ensure that BLOOD FLOWS IN ONLY _____one________ DIRECTION. 7. THE SPECIFIC PURPOSE OF THE TRICUSPID VALVE IS TO PREVENT ____backflow____ OF BLOOD FROM THE RIGHT _______ventricle______TO THE RIGHT ___atrium____ WHEN THE RIGHT VENTRICLE CONTRACTS. 8. When the Heart CONTRACTS a second time, Blood in the RIGHT VENTRICLE IS SENT THROUGH THE ___pulmonary___ __semilunar valve________ INTO THE _______pulmonary trunk_____. These are the Only Arteries to carry ____deoxygenated__ Blood. At the base of the Pulmonary Arteries is another valve that prevents blood from traveling back into the Right Ventricle. LEFT SIDE 1. Oxygen-Rich Blood leaves the Lungs and Returns to the Heart by way of Blood Vessels called the __pulmonary______ __veins_____. These are the only Veins to carry ____oxygenated___ Blood. 2. Returning Blood enters the LEFT ATRUIM, IT PASSES THROUGH THE ______mitral__ __valve___BICUSPID) INTO THE LEFT VENTRICLE. 3. FROM THE LEFT VENTRICAL, BLOOD IS PUMPED INTO THE ___aortic_________ ARTERY THAT CARRIES IT TO EVERY PART OF THE BODY. THE HEARTBEAT (CARDIAC CYCLE) 1. ____systole______ is the term for CONTRACTION. 2. The term for RELAXATION is _______diastole______. 3. If any of the Valves do not close properly, an extra sound called a __murmur___ may be heard. 4. This Wave begins in a Small Bundle of Cells embedded in the RIGHT ATRUIM CALLED THE ___SA Node_____________. The SA is the Natural ___pasemaker_____ of the Heart. It initiates each Heartbeat and sets the PACE for the HEART RATE. 5. The Heart initiates its own Stimulation from the _____SA____ Node, and Does NOT require Stimulation from the Nervous System. 6. The Autonomic Nervous system does influence Heart Rate. The Sympathetic Nervous System _____increases______ HEART RATE and the Parasympathetic Nervous System __decreases_____ IT. 7. For most of us, at REST our HeartBeats __70__ beats per minute. During Exercise that can increase to as many as 200 beats per minute. BLOOD VESSELS (ARTERIES, VEINS AND CAPILLARIES) 1. After the Blood leaves the Heart, it is pumped through a network of Blood Vessels to different parts of the body. 2. The Blood Vessels that form this network and are part of the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM ARE THE ___arteries_______, ___veins__________, AND ____capilarries________. 3. With the exception of Capillaries and tiny Veins, Blood Vessels have WALLS made of THREE LAYERS OF TISSUE: A. THE INNER LAYER IS ___endothelial_____ TISSUE. B. THE MIDDLE LAYER IS __smooth____MUSCLE TISSUE. C. THE OUTER LAYER IS ___connective______ TISSUE. ATERIES AND ARTERIOLES (SMALL ARTERIES) 1. Arteries carry blood from the _____heart____________ TO _______lungs______________ AND THE REST OF THE BODY. 2. The Walls of Arteries are generally _____more elastic__________ than those of Veins. 3. EXCEPT FOR THE _pulmonary___ ARTERIES, ALL ARTERIES CARRY __oxygen__________-RICH BLOOD. 4. The Artery that carries Oxygen-Rich Blood from the LEFT VENTRICLE to all parts of the body is the __aorta________________. 5. THE AORTA WITH A DIAMETER OF 2.5 cm, IS THE _____largest_____ ARTERY IN THE BODY. 6. THE SMALLEST ARTERIES ARE CALLED_____arterioles__________. CAPILLARIES 1. ARTERIOLES BRANCH INTO NETWORKS OF VERY SMALL BLOOD VESSELES CALLED ______capillaries_________. 2. IT IS IN THE THIN-WALLED (ONE-CELL IN THICKNESS) THAT THE REAL WORK OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM IS DONE. 3. The Walls of the Capillaries consist of only one layer of cells, making it easy for Oxygen and Nutrients to __diffuse____ FROM THE BLOOD INTO THE TISSUE. VEINS 1. THE FLOW OF BLOOD MOVES FROM CAPILLARIES INTO __venuoles___________. 2. Veins form a system that _recieves_____ Blood from every part of the Body and CARRIES it Back to the __heart______________. 3. The smallest Veins are called ____venuoles__________________. 4. LIKE ARTERIES, VEINS ARE LINED WITH ______smooth____ MUSCLE. Vein walls are thinner and less elastic than Arteries. Veins though are _____thin__________________ and are able to stretch out readily. 5. This flexibility reduces the Resistance the flow of blood encounters on its way back to the Heart. 6. Large Veins contain Valves that maintain the one direction flow of Blood. This is important where Blood must flow against the Force of Gravity. 7. The flow of Blood in Veins is help by Contractions of _______skeletal_______ Muscles, especially those in the legs and arms. When muscles contract they squeeze against Veins and help force Blood Toward the Heart. PATHWAYS OF CIRCULATION 1. Blood moves through the body in a continuous pathway, of which there are TWO MAJOR PARTS; THE _____pulmonary______ AND _________systemic_____ CIRCULATION. 2. THE ___Pulmonary___________ CIRCULATION CARRIES BLOOD BETWEEN THE ___heart_______________ AND THE _____lungs_____. THIS CIRCULATION BEGINS AT THE RIGHT _____atrium_________________ AND ENDS AT THE LEFT ____atrium______________. 4. _________Systemic____ ___circulation________ STARTS AT THE LEFT __________atrium__________ AND ENDS AT THE RIGHT ___atirum_______, CARRIES BLOOD TO THE REST OF THE BODY. BLOOD PRESSURE 1. Blood moves through our Circulation System because it is under _____pressure_____________. 2. This Pressure is caused by the ___contracting___________ of the Heart and by Muscles that surround Blood Vessels. 3. A MEASURE OF FORCE THAT BLOOD EXERTS AGAIST A VESSEL WALL IS CALLED ___blood________PRESSURE. 4. Blood Pressure is maintained by TWO WAYS: A.____cardiac output____________________________________________ B. ____resistance_________________________________________ RED BLOOD CELLS (RBC) ERTHROCYTES 1. RBC are the most ___numerous__________ of the Blood Cells. One microliter of blood contains approx. 5 million RBCs. 2. RBC are ____biconcave________, or shaped so that they are narrower in the center than along the edges. 3. RBC are produced from cells in the Bone Marrow, they are gradually filled with _____hemoglobin____________ which forces out the nucleus and other organelles. 4. Mature RBC do not have a Nucleus. 5. __hemoglobin_______is the iron-containing protein that gives RBC the ability to carry Oxygen. Hemoglobin gives the RBC their color. 6. RBC stay in circulation for about 120 days before they are destroyed by special WBC in the liver and spleen. RDC in your body are dying and being replace at a rate of about 2 million per second. WHITE BLOOD CELLS (WBC) LEUKOCYTES 1. Outnumbered by RBC almost 500 to 1. 2. WBC are produced in the ___bone______Marrow, are larger than RBC, almost Colorless, and do not contain Hemoglobin. 3. WBC have a Nucleus and can live for many months or years. 4. THE MAIN FUNCTION OF WBC IS TO _____protect from infection _____. 5. WBC can destroy bacteria and foreign cells by Phagocytosis (engulfed and digested), some produce special proteins called ____antibodies___________, and some release special chemicals that help the body fight off disease and resist infection. 6. Doctors are able to detect the presence of _______infection____ by counting the number of WBC in the blood. DIRECTIONS: Answer the questions below as completely and as thoroughly as possible. Answer the question in essay form (not outline form), using complete sentences. You may use diagrams to supplement your answers, but a diagram alone without appropriate discussion is inadequate. See me if you need Help, Have Problems or Questions or To Check Your Answers. ALL answers should be in your notebook. 1. State the main functions of the circulatory system. 2. Name the three major parts of the circulatory system. 3. Describe the difference between pulmonary circulation and the systemic ciculation. 4. Describe the main parts of the heart. 5. Describe how the two sides of the heart differ in terms of the kind of blood they receive and pump, INCLUDE: Where does the blood come from? How does it enter the heart? How does it exit the heart? Where does it go to? 6. Explain the difference between diastole and systole. 7. How is heart contraction rate controlled? 8. What are the components of Blood, and the function of each component? 9. Compare ateries, veins, and capillaries. In your answer, discuss the types of tissue in them, function, and type of blood generally carried. 11. What are the Three Functions of Blood? 13. Identify the structure that controls the heartbeat, and describe the process by which it regulates the heartbeat.