Comparative Systems Worksheet
advertisement

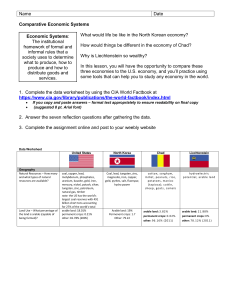
Name Date Comparative Economic Systems Economic Systems: The institutional framework of formal and informal rules that a society uses to determine what to produce, how to produce and how to distribute goods and services. What would life be like in the North Korean economy? How would things be different in the economy of Chad? Why is Liechtenstein so wealthy? In this lesson, you will have the opportunity to compare these three economies to the U.S. economy, and you’ll practice using some tools that can help you to study any economy in the world. 1. Complete the data worksheet by using the CIA World Factbook at https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html If you copy and paste answers – format text appropriately to ensure readability on final copy (suggested 8 pt. Arial font) 2. Answer the seven reflection questions after gathering the data. 3. Complete the assignment online and post to your weebly website Data Worksheet Geography Natural Resources – How many and what types of natural resources are available? Land Use – What percentage of the land is arable (capable of being farmed)? United States North Korea Chad Liechtenstein coal, copper, lead, molybdenum, phosphates, uranium, bauxite, gold, iron, mercury, nickel, potash, silver, tungsten, zinc, petroleum, natural gas, timber note: the US has the world's largest coal reserves with 491 billion short tons accounting for 27% of the world's total arable land: 18.01% permanent crops: 0.21% other: 81.78% (2005) Coal, lead, tungsten, zinc, magnesite, iron, copper, gold, pyrites, salt, fluorspar, hydro power cotton, s orghum, millet, pea nuts, rice, pota toes, man ioc (ta pioca ); cattle, sheep, goa ts, camels hydroelect ric poten tia l, a rab le la nd Arable land: 19% Permenent crops: 1.7 Other: 79.22 arable land: 3.82% permanent crops: 0.02% other: 96 .16% (201 1) arable land: 21.88% permanent crops: 0% other: 78 .12% (201 1) Name People Life Expectancy at Birth – How long are children born today expected to live? Date total population: 78.11 years country comparison to the world: 49 male: 75.65 years female: 80.69 years (2009 est.) Total: 69.51 Total Fertility Rate – How many children does each woman have, on average? 2.05 children born/woman (2009 est.) country comparison to the world: 126 1.99 Literacy Rate – What % of people over the age of 15 can read and write? definition: age 15 and over can read and write total population: 99% male: 99% female: 99% (2003 est.) Government Government Type –How are leaders elected? Government Spending as Percent of GDP (Budget Expenditures Divided by GDP). Find in Economy section Military Spending as a Percentage of GDP. Find in Military section Economy Economy Overview – What are the most serious economic problems facing each of these four nations? Summarize from Economic Overview GDP Per Capita – What is the value of goods and services produced per person? Population Below Poverty Line – How many people live in poverty? GDP Composition by Sector – What % of GDP is industry and services? 50 total population: 81.59 yea rs country comparison to the world: 1 2 male: 79.45 years female: 84.29 yea rs (2013 est. ) 4.8 ch ildren born/w oman (2013 est. ) 1.69 ch ildren born/w oman (2013 est. ) country comparison to the world: 1 7 1 Age 15 and over 100% can read and write 15 and over- 35.4% of total population 100% Constitution-based federal republic; strong democratic tradition Communist one man dictatorship Republic-vote? GDP (PPP): $14.26 trillion (2009 est.) Budget: revenues: $1.914 trillion expenditures: $3.615 trillion (2009 est.) 40 billion $21 billion (20 12 est. ) country comparison to the world: 1 2 9 $19.99 billion (2011 est. ) $19.89 billion (2010 est. ) $3.2 billion (2009) NA 5% (2012 es t.) country comparison to the world: 6 4 0.5% (2011 es t.) 13% (2010 es t.) No military- national police North Korea has a struggling economy, shortages of crops and fuel, they receive much aid from China. 11 billion in debt with Russia. Kim Jong working on economy. Chad's p rima rily agricultural econ omy will con tin ue to be boos ted b y major foreign d irect inves tment projects in the oil sect or tha t began in 2000 . Highly industrialized, free enterprise economy, second highest capita income in the world. 20% tax rate $2,000 (2012 es t.) $89,400 (2009 es t.) country comparison to the country comparison to the world: 1 9 4 $1,900 (2011 es t.) $1,900 (2010 es t.) world: 2 $90,600 (2008 es t.) $89,700 (2007 es t.) $3.615 trillion / $14.26 trillion = .25 (25%) 4.06% of GDP (2005 est.) country comparison to the world: 28 Long-term problems include inadequate investment in economic infrastructure, rapidly rising medical and pension costs of an aging population, sizable trade and budget deficits, and stagnation of family income in the lower economic groups. $46,400 (2009 est.) country comparison to the world: 11 12% (2004 est.) agriculture: 1.2% industry: 21.9% services: 76.9% (2009 est.) $1800 NA Agriculture: 23.3 Industry: 42.9 Services: 33.8 80% agriculture: 47.1% industry: 9.2% services: 43.7% (20 12 est. ) Hereditary constitutional monarchy country comparison to the world: 1 7 9 $3.216 billion (2008) $3.159 billion (2007 NA agriculture: 8% industry: 37% services: 55% (2009 ) Name Date Labor Force by Occupation – What % of workers is in agriculture? farming, forestry, and fishing: 0.7% Agriculture: 35% Industry: 65% 4.293 Million Industries – What are the primary industries? leading industrial power in the world, highly diversified and technologically advanced; petroleum, steel, motor vehicles, aerospace, telecommunications, chemicals, electronics, food processing, consumer goods, lumber, mining military p roducts; machin e b uilding, electric power, chemicals; min ing (coal, iron ore, limes tone, magnesite, graphite, copper, zinc, lead, and precious metals), meta llu rgy; tex tiles, food proces sing; tourism oil, cotton textiles, meatpa cking, b rew ing, natron (s od ium carb ona te), s oap, cigarettes, cons truction ma teria ls Are the industries primarily producing for consumer or government consumption? Determine this by assessing the industries and their consumers – answer not found at CIA WorldFactBook Mostly producing for the consumer (private citizens) Government consumption because since they are a communist gov’t nothing goes through to the people without going through the gov’t The people produce for themselves a lot. It’s sounds like they are getting away from traditional living and going into Agriculture Products – What are the primary agricultural goods produced? wheat, corn, other grains, fruits, vegetables, cotton; beef, pork, poultry, dairy products; fish; forest products rice, corn, p ota toes, soyb ean s, pu ls es; cattle, p igs, p ork, eggs cotton, s orghum, millet, pea nuts, rice, pota toes, man ioc (ta pioca ); cattle, sheep, goa ts, camels wheat, ba rley, corn, pota toes; livestock, dairy products Industrial Production Growth Rate -5.5% (2009 est.) country comparison to the world: 110 4.11 trillion kWh (2008 est.) country comparison to the world: 1 NA 10.6% NA 20.45 billion kWh 95 million na 150 million (2008) country comparison to the world: 2 231 million (2008) country comparison to the world: 2 1.18 million 31, 200 19600 total: 226,427 km country comparison to the world: 1 total: 6,465,799 km country comparison to the world: 1 paved: 4,209,835 km (includes 75,040 km of expressways) unpaved: 2,255,964 km (2007) 5,242 Electricity Production Communications Telephones – Main Lines in Use Internet Users Transportation Railways Roadways (Paved and Unpaved Highways Airports with Paved Runways Reflection: total: 5,174 NA agriculture: 0.8% industry: 39. 4% services: 59.9% (20 10) electronics, metal manufactu ring, den ta l prod ucts, ceramics, pharmaceu ticals, food prod ucts, precision ins truments, tou rism, optica l ins trumen ts 23,000 NA 9 km total: 25,554 km total: 40,000 km total: 380 km country comparison to the country comparison to the country comparison to the world: 1 0 1 paved: 724 km unpaved: 24,830 km (2006) world: 8 8 note: con sis ts of 25,000 km of na tiona l a nd regiona l road s an d 15,000 km of local road s; 206 km of urb an road s a re paved (2011) world: 2 0 1 paved: 380 km (2010 ) 39 Na na Name Date 1. How can the presence or absence of natural resources and arable land affect a nation’s economy, regardless of the type of economic system? Well, if a country has a natural resource it can create jobs for people, because you need someone to extract it and since its already existing in that country they don’t have to pay anything for it, just the price of managing and extracting it then from there out its all profit. 2. How can life expectancy and literacy rates affect the quality of labor in the economy? If you have educated and literate workers there is a way less chance of injury on the job site and you can have people work for longer periods of there life because they have longer life expectancy. 3. How can fertility rates affect the use of scarce resources? With more and more kids being brought into the world they need stuff as well as everyone else so that resource is being used that much more. 4. How can GDP per capita and poverty rates indicate standards of living in each system? If the GDP per capita is high and the poverty rates are low you can indicate a good healthy standard of living where people have proper health care and housing for all. If the GDP per capita is low and poverty rates are high you can indicate that the people there are rather poor and this could lead to lack of health care and sick people thus a low life expectancy. 5. How can the size of the industrial/service sector and the agriculture employment rate indicate the level of industrialization? The size of the industrial/service sector and the agriculture can indicate how industrialized a country is. 6. How can electricity, communication, and transportation facilities indicate the potential for industrial growth? If a country has a sufficient electricity, sources of communication and transportation facilities then they have maximum potential for industrial growth. 7. Considering the lack of natural resources, the labor problems, and the lack of capital and little industrialization of developing countries, how can developing countries develop? (Hint: Look at Economy - Overview for Chad). Name Date Developing countries such as Chad can continue to gain profit on their oil sales, then continue to develop their gov’t then set up programs to get people the health care they need and put people back into work there and out of poverty. 8. Now that you have studied the economic characteristics of these three countries, define the terms market-oriented, command, and developing economy in your own words. For each term, describe the specific characteristics of the countries you studied that would help to support your definition. The US and Liechtenstein are developed countries with developed economies. Liechtenstein claimed to be a market oriented economy and the US is a mixed economy. Chad is a developing country they are just getting oil fields extracted and starting to make their economy sufficient.