E3 Academy Unit Power Standards
advertisement

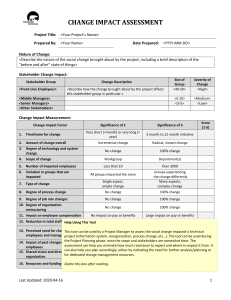
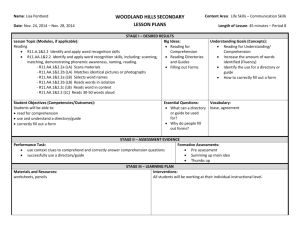
E3 Academy Unit Power Standards Task and Guidance: Using the Dysart Curriculum Tool or the Arizona State Standards , your team will identify several DUSD Power Standards or AZ Performance Objectives that you will explore as possible learning outcomes for your problem-based curricular unit. Choose standards/objectives that encompass multiple curricular areas, and that are rich enough to develop a unit of study around. Choose standards that you will cover in the second semester as this unit will be delivered during that time. Reading: 3rd grade— Reading Process: R03-S1C1 R03-S1C3 R03-S1C3 R03-S1C3 R03-S1C3 R03-S1C3 R03-S1C4 R03-S1C4 R03-S1C4 R03-S1C5 R03-S1C5 R03-S1C6 - Print Concepts (PO1, PO2) Decoding Words with Phonics (PO3) Decoding Words with Phonics (PO4) Decoding Words with Phonics (PO5) Decoding Words with Phonics (PO6) Decoding Words with Phonics (PO1, PO2) Vocabulary (PO1, PO2) Vocabulary (PO3) Vocabulary (PO5) Fluency(PO1) Fluency(PO2) Comprehension Strategies (PO1, PO2, PO3) Comprehending Literary Text: R03-S2C1 - Elements of Literature (PO1, PO2, PO3, PO4, PO5, PO6, PO7) R03-S2C2 - Historical and Cultural Aspects of Literature (PO1) Comprehending Informational Text: R03-S3C1 - Expository Text (PO1, PO2, PO3, PO4) R03-S3C2 - Functional Text (PO1, PO2, PO3, PO4) R03-S3C3 - Persuasive Text (PO1, PO2) 4th grade— Reading Process: R04-S1C4 R04-S1C4 R04-S1C4 R04-S1C5 R04-S1C6 R04-S1C6 R04-S1C6 - Vocabulary (PO1, PO2) Vocabulary (PO3) Vocabulary (PO6) Fluency(PO1) Apply Strategies to Comprehend Text (P01, 02) Apply Strategies to Comprehend Text (P04, 06) Apply Strategies to Comprehend Text (PO 5) Comprehending Literary Text: R04-S2C1 R04-S2C1 R04-S2C1 R04-S2C1 R04-S2C1 - Elements Elements Elements Elements Elements of of of of of Literature Literature Literature Literature Literature (PO1, PO2) (PO 6) (PO 7) (PO 8) (PO 9) R04-S2C1 - Elements of Literature (PO 10) Comprehending Informational Text: R04-S3C1 R04-S3C1 R04-S3C1 R04-S3C1 R04-S3C2 R04-S3C3 - Expository Text (PO4, PO6) Expository Text (PO 1) Expository Text (PO 2) Expository Text (PO 7) Informational Text (PO1, PO2) Persuasive Text (PO1, PO2) - Use new vocabulary in relevant contexts (PO1, PO2, PO4) Use new vocabulary in relevant contexts (PO5) Use new vocabulary in relevant contexts (PO6) Fluency(PO1) Apply Strategies to Comprehend Text (P04, 06) Apply Strategies to Comprehend Text (P01, 02) Apply Strategies to Comprehend Text (PO 5) 5th grade— Reading Process: R05-S1C4 R05-S1C4 R05-S1C4 R05-S1C5 R05-S1C6 R05-S1C6 R05-S1C6 Comprehending Literary Text: R05-S2C1 R05-S2C1 R05-S2C1 R05-S2C1 - Elements Elements Elements Elements of of of of Literature Literature Literature Literature (PO (PO (PO (PO 1) 5) 6) 9) Comprehending Informational Text: R05-S3C1 R05-S3C1 R05-S3C1 R05-S3C1 R05-S3C2 R05-S3C3 - Expository Text (PO 1) Expository Text (PO 2) Expository Text (PO4, PO6) Expository Text (PO 3) Informational Text (PO1, PO2) Persuasive Text (PO1, PO2) 6th grade— Reading Process: R06-S1C4 - Acquire and use new vocabulary in relevant contexts (PO1-PO4) R06-S1C5 - Read fluently (PO1) R06-S1C6 - Employ strategies to comprehend text ( PO1-PO7) Comprehending Literary Text: R06-S2C1 - Identify, analyze, and apply knowledge of the structures and elements of literature ( PO1-PO2, PO5-PO7) R06-S2C2 - Recognize and apply knowledge of the historical and cultural aspects of American, British, and World literature (PO1-PO2) Comprehending Informational Text: R06-S3C1 - Identify, analyze, and apply knowledge of the purpose, structures, and elements of expository text (PO1-PO2, PO4-PO5, PO7) R06-S3C2 - Identify, analyze, and apply knowledge of the purpose, structures, clarity, and relevancy of functional text (PO1-PO3) R06-S3C3 - Explain basic elements of argument in text and their relationship to the authors purpose and use of persuasive strategies (PO 1-3) 7th grade— Reading Process: R07-S1C4 - Vocabulary(PO1-PO4) R07-S1C5 - Reading Fluency (PO1) R07-S1C6 - Comprehension (PO1-7) Comprehending Literary Text: R07-S2C1 - Elements of Literature (PO1-PO7) R07-S2C2 - Historical and Cultural Aspects of Literature (PO1-PO2) Comprehending Informational Text: R07-S3C1 - Expository Text (PO1-PO2, PO4-PO5, PO7, PO9-PO12) R07-S3C2 - Functional Text (PO1-PO3) R07-S3C3 - Persuasive Text (PO1-PO3) Math: 3rd grade— Data Analysis, Probability, and Discrete Mathematics: M03-S2C1 - Understand, organize, and interpret data (PO2, PO3, PO4) M03-S2C2 - Understand and apply probability concepts (PO2) M03-S2C3 - Discrete Mathematics (PO1) Patterns, Algebra, and Functions: M03-S3C1 - Patterns (PO2) 4th grade— Data Analysis, Probability, and Discrete Mathematics: M04-S2C1 - Solve contextual problems using graphs, charts, and tables (PO7) M04-S2C1 - Data Analysis (PO5) M04-S2C2 - Name the possible outcomes for a probability experiment. (PO1) Patterns, Algebra, and Functions: M04-S3C3 - Evaluate expressions involving the four basic operations by substituting given whole numbers for the variable (PO1) 5th grade— Data Analysis, Probability, and Discrete Mathematics: M05-S2C1 - Identify the mode and mean of given data.(PO5) M05-S2C1 - Solve contextual problems using graphs, charts, and tables.(PO8) M05-S2C1 - Data Analysis (PO5) M05-S2C2 - Make predictions from the results of a student-generated experiments using objects.(PO6) M05-S2C3 - Find all possible combinations when 1 item is selected from each of 2 sets of different items, using a systematic approach.(PO1) Patterns, Algebra, and Functions: M05-S3C1 - Extend and solve grade level appropriate iterative patterns (PO2, PO3) 6th grade— Data Analysis, Probability, and Discrete Mathematics: M06-S2C1 M06-S2C2 M06-S2C3 M06-S2C4 - Data Analysis and Displays (PO 2 - PO 8) Probability (PO1 - PO7) Systematic Listing and Counting(PO 2) Vertex-Edge Graphs(PO 1) Patterns, Algebra, and Functions: M06-S3C1 - Number Patterns(PO 1) 7th grade— Data Analysis, Probability, and Discrete Mathematics: M07-S2C1 M07-S2C1 M07-S2C2 M07-S2C3 - Data Displays (PO 3, PO 4, PO 5, PO 7, PO 8, PO 9) Measures of Central Tendency (PO 6, PO 7, PO 8) Probability (PO 1, PO 2, PO 4, PO 5, PO 6, PO 7) Systematic Listing and Counting(PO 2) Patterns, Algebra, and Functions: M07-S3C2 - Functions and Relationships (PO1) Writing: 3rd grade— Writing Process: Prewriting: W03-S1C1- Prewriting includes using strategies to generate, plan, and organize ideas for specific purposes. (PO1-PO7) Drafting: W03-S1C2- Drafting incorporates prewriting activities to create a first draft containing necessary elements for a specific purpose (PO1-PO2) Revision: W03-S1C3-Revising includes evaluating and refining the rough draft for clarity and effectiveness. (Ask: Does this draft say what you want it to say?) (PO1-PO8) Editing: W03-S1C4-Editing includes proofreading and correcting the draft for conventions (PO1-PO4). Publishing: W03-S1C5-Format and present a final product for the intended audience (PO1-PO4). Writing Elements: Ideas and Content: W03-S2C1-Writing is clear and focused, holding the reader’s attention throughout. Main ideas stand out and are developed by strong support and rich details. Purpose is accomplished (PO1-PO4). Organization: W03-S2C2- Organization addresses the structure of the writing and integrates the central meaning and patterns that hold the piece together (PO1-PO6), Voice: W03-S2C3- Voice will vary according to the type of writing, but should be appropriately formal or casual, distant or personal, depending on the audience and purpose (PO1-PO2). Word Choice: W03-S2C4- Word choice reflects the writer’s use of specific words and phrases to convey the intended message and employs a variety of words that are functional and appropriate to the audience and purpose (PO1-PO4). Sentence Fluency: W03-S2C5-Fluency addresses the rhythm and flow of language. Sentences are strong and varied in structure and length (PO1-PO3). Conventions: W03-S2C6- Conventions addresses the mechanics of writing, including capitalization, punctuation, spelling, grammar and usage, and paragraph breaks (PO1-PO12). Writing Applications: Expository Writing: W03-S3C2- Expository writing includes non-fiction writing that describes, explains, informs, or summarizes ideas and content. The writing supports a thesis based on research, observation, and/or experience (PO1-PO3). Functional Writing: W03-S3C3-Functional writing provides specific directions or information related to real-world tasks. This includes letters, memos, schedules, directories, signs, manuals, forms, recipes, and technical pieces for specific content areas (PO1-PO3). Persuasive Writing: W03-S3C4- Persuasive writing is used for the purpose of influencing the reader. The author presents an issue and expresses an opinion in order to convince an audience to agree with the opinion or to take a particular action (PO1). Literary Response: W03-S3C5- Literary response is the writer’s reaction to a literary selection. The response includes the writer’s interpretation, analysis, opinion, and/or feelings about the piece of literature and selected elements within it (PO1PO3). Research: W03-S3C6- Research writing is a process in which the writer identifies a topic or question to be answered. The writer locates and evaluates information about the topic or question, and then organizes, summarizes, and synthesizes the information into a finished product (PO1-PO3). 4th grade— Writing Process: Prewriting: W04-S1C1- Prewriting includes using strategies to generate, plan, and organize ideas for specific purposes. (PO1-PO7) Drafting: W04-S1C2- Drafting incorporates prewriting activities to create a first draft containing necessary elements for a specific purpose (PO1-PO2) Revision: W04-S1C3-Revising includes evaluating and refining the rough draft for clarity and effectiveness. (Ask: Does this draft say what you want it to say?) (PO1-PO8) Editing: W04-S1C4-Editing includes proofreading and correcting the draft for conventions (PO1-PO4). Publishing: W04-S1C5-Format and present a final product for the intended audience (PO1-PO4). Writing Elements: Ideas and Content: W04-S2C1-Writing is clear and focused, holding the reader’s attention throughout. Main ideas stand out and are developed by strong support and rich details. Purpose is accomplished (PO1-PO4). Organization: W04-S2C2- Organization addresses the structure of the writing and integrates the central meaning and patterns that hold the piece together (PO1-PO6), Voice: W04-S2C3- Voice will vary according to the type of writing, but should be appropriately formal or casual, distant or personal, depending on the audience and purpose (PO1-PO2). Word Choice: W04-S2C4- Word choice reflects the writer’s use of specific words and phrases to convey the intended message and employs a variety of words that are functional and appropriate to the audience and purpose (PO1-PO4). Sentence Fluency: W04-S2C5-Fluency addresses the rhythm and flow of language. Sentences are strong and varied in structure and length (PO1-PO4). Conventions: W04-S2C6- Conventions addresses the mechanics of writing, including capitalization, punctuation, spelling, grammar and usage, and paragraph breaks (PO1-PO13). Writing Applications: Expository Writing: W04-S3C2- Expository writing includes non-fiction writing that describes, explains, informs, or summarizes ideas and content. The writing supports a thesis based on research, observation, and/or experience (PO1-PO3). Functional Writing: W04-S3C3-Functional writing provides specific directions or information related to real-world tasks. This includes letters, memos, schedules, directories, signs, manuals, forms, recipes, and technical pieces for specific content areas (PO1-PO3). Persuasive Writing: W04-S3C4- Persuasive writing is used for the purpose of influencing the reader. The author presents an issue and expresses an opinion in order to convince an audience to agree with the opinion or to take a particular action (PO1). Literary Response: W04-S3C5- Literary response is the writer’s reaction to a literary selection. The response includes the writer’s interpretation, analysis, opinion, and/or feelings about the piece of literature and selected elements within it (PO1PO3). Research: W04-S3C6- Research writing is a process in which the writer identifies a topic or question to be answered. The writer locates and evaluates information about the topic or question, and then organizes, summarizes, and synthesizes the information into a finished product (PO1-PO3). 5th grade— Writing Process: Prewriting: W05-S1C1- Prewriting includes using strategies to generate, plan, and organize ideas for specific purposes. (PO1-PO7) Drafting: W05-S1C2- Drafting incorporates prewriting activities to create a first draft containing necessary elements for a specific purpose (PO1-PO2) Revision: W05-S1C3-Revising includes evaluating and refining the rough draft for clarity and effectiveness. (Ask: Does this draft say what you want it to say?) (PO1-PO8) Editing: W05-S1C4-Editing includes proofreading and correcting the draft for conventions (PO1-PO4). Publishing: W05-S1C5-Format and present a final product for the intended audience (PO1-PO4). Writing Elements: Ideas and Content: W05-S2C1-Writing is clear and focused, holding the reader’s attention throughout. Main ideas stand out and are developed by strong support and rich details. Purpose is accomplished (PO1-PO4). Organization: W05-S2C2- Organization addresses the structure of the writing and integrates the central meaning and patterns that hold the piece together (PO1-PO6), Voice: W05-S2C3- Voice will vary according to the type of writing, but should be appropriately formal or casual, distant or personal, depending on the audience and purpose (PO1-PO3). Word Choice: W05-S2C4- Word choice reflects the writer’s use of specific words and phrases to convey the intended message and employs a variety of words that are functional and appropriate to the audience and purpose (PO1-PO4). Sentence Fluency: W05-S2C5-Fluency addresses the rhythm and flow of language. Sentences are strong and varied in structure and length (PO1-PO4). Conventions: W05-S2C6- Conventions addresses the mechanics of writing, including capitalization, punctuation, spelling, grammar and usage, and paragraph breaks (PO1-PO13). Writing Applications: Expository Writing: W05-S3C2- Expository writing includes non-fiction writing that describes, explains, informs, or summarizes ideas and content. The writing supports a thesis based on research, observation, and/or experience (PO1-PO3). Functional Writing: W05-S3C3-Functional writing provides specific directions or information related to real-world tasks. This includes letters, memos, schedules, directories, signs, manuals, forms, recipes, and technical pieces for specific content areas (PO1-PO3). Persuasive Writing: W05-S3C4- Persuasive writing is used for the purpose of influencing the reader. The author presents an issue and expresses an opinion in order to convince an audience to agree with the opinion or to take a particular action (PO1). Literary Response: W05-S3C5- Literary response is the writer’s reaction to a literary selection. The response includes the writer’s interpretation, analysis, opinion, and/or feelings about the piece of literature and selected elements within it (PO1PO3). Research: W05-S3C6- Research writing is a process in which the writer identifies a topic or question to be answered. The writer locates and evaluates information about the topic or question, and then organizes, summarizes, and synthesizes the information into a finished product (PO1-PO3). 6th grade— Writing Process: Prewriting: W06-S1C1- Prewriting includes using strategies to generate, plan, and organize ideas for specific purposes. (PO1-PO7) Drafting: W06-S1C2- Drafting incorporates prewriting activities to create a first draft containing necessary elements for a specific purpose (PO1-PO2) Revision: W06-S1C3-Revising includes evaluating and refining the rough draft for clarity and effectiveness. (Ask: Does this draft say what you want it to say?) (PO1-PO8) Editing: W06-S1C4-Editing includes proofreading and correcting the draft for conventions (PO1-PO4). Publishing: W06-S1C5-Format and present a final product for the intended audience (PO1-PO4). Writing Elements: Ideas and Content: W06-S2C1-Writing is clear and focused, holding the reader’s attention throughout. Main ideas stand out and are developed by strong support and rich details. Purpose is accomplished (PO1-PO4). Organization: W06-S2C2- Organization addresses the structure of the writing and integrates the central meaning and patterns that hold the piece together (PO1-PO6), Voice: W06-S2C3- Voice will vary according to the type of writing, but should be appropriately formal or casual, distant or personal, depending on the audience and purpose (PO1-PO4). Word Choice: W06-S2C4- Word choice reflects the writer’s use of specific words and phrases to convey the intended message and employs a variety of words that are functional and appropriate to the audience and purpose (PO1-PO4). Sentence Fluency: W06-S2C5-Fluency addresses the rhythm and flow of language. Sentences are strong and varied in structure and length (PO1-PO4). Conventions: W06-S2C6- Conventions addresses the mechanics of writing, including capitalization, punctuation, spelling, grammar and usage, and paragraph breaks (PO1-PO13). Writing Applications: Expository Writing: W06-S3C2- Expository writing includes non-fiction writing that describes, explains, informs, or summarizes ideas and content. The writing supports a thesis based on research, observation, and/or experience (PO1-PO3). Functional Writing: W06-S3C3-Functional writing provides specific directions or information related to real-world tasks. This includes letters, memos, schedules, directories, signs, manuals, forms, recipes, and technical pieces for specific content areas (PO1-PO4). Persuasive Writing: W06-S3C4- Persuasive writing is used for the purpose of influencing the reader. The author presents an issue and expresses an opinion in order to convince an audience to agree with the opinion or to take a particular action (PO1). Literary Response: W06-S3C5- Literary response is the writer’s reaction to a literary selection. The response includes the writer’s interpretation, analysis, opinion, and/or feelings about the piece of literature and selected elements within it (PO1). Research: W06-S3C6- Research writing is a process in which the writer identifies a topic or question to be answered. The writer locates and evaluates information about the topic or question, and then organizes, summarizes, and synthesizes the information into a finished product (PO1-PO2). 7th grade— Writing Process: Prewriting: W07-S1C1- Prewriting includes using strategies to generate, plan, and organize ideas for specific purposes. (PO1-PO7) Drafting: W07-S1C2- Drafting incorporates prewriting activities to create a first draft containing necessary elements for a specific purpose (PO1-PO2) Revision: W07-S1C3-Revising includes evaluating and refining the rough draft for clarity and effectiveness. (Ask: Does this draft say what you want it to say?) (PO1-PO8) Editing: W07-S1C4-Editing includes proofreading and correcting the draft for conventions (PO1-PO4). Publishing: W07-S1C5-Format and present a final product for the intended audience (PO1-PO4). Writing Elements: Ideas and Content: W07-S2C1-Writing is clear and focused, holding the reader’s attention throughout. Main ideas stand out and are developed by strong support and rich details. Purpose is accomplished (PO1-PO4). Organization: W07-S2C2- Organization addresses the structure of the writing and integrates the central meaning and patterns that hold the piece together (PO1-PO6), Voice: W07-S2C3- Voice will vary according to the type of writing, but should be appropriately formal or casual, distant or personal, depending on the audience and purpose (PO1-PO4). Word Choice: W07-S2C4- Word choice reflects the writer’s use of specific words and phrases to convey the intended message and employs a variety of words that are functional and appropriate to the audience and purpose (PO1-PO4). Sentence Fluency: W07-S2C5-Fluency addresses the rhythm and flow of language. Sentences are strong and varied in structure and length (PO1-PO4). Conventions: W07-S2C6- Conventions addresses the mechanics of writing, including capitalization, punctuation, spelling, grammar and usage, and paragraph breaks (PO1-PO13). Writing Applications: Expository Writing: W07-S3C2- Expository writing includes non-fiction writing that describes, explains, informs, or summarizes ideas and content. The writing supports a thesis based on research, observation, and/or experience (PO1-PO3). Functional Writing: W07-S3C3-Functional writing provides specific directions or information related to real-world tasks. This includes letters, memos, schedules, directories, signs, manuals, forms, recipes, and technical pieces for specific content areas (PO1-PO4). Persuasive Writing: W07-S3C4- Persuasive writing is used for the purpose of influencing the reader. The author presents an issue and expresses an opinion in order to convince an audience to agree with the opinion or to take a particular action (PO1). Literary Response: W07-S3C5- Literary response is the writer’s reaction to a literary selection. The response includes the writer’s interpretation, analysis, opinion, and/or feelings about the piece of literature and selected elements within it (PO1). Research: W07-S3C6- Research writing is a process in which the writer identifies a topic or question to be answered. The writer locates and evaluates information about the topic or question, and then organizes, summarizes, and synthesizes the information into a finished product (PO1-PO2).