Correlation of Glencoe Tennessee Science Grade 7
advertisement
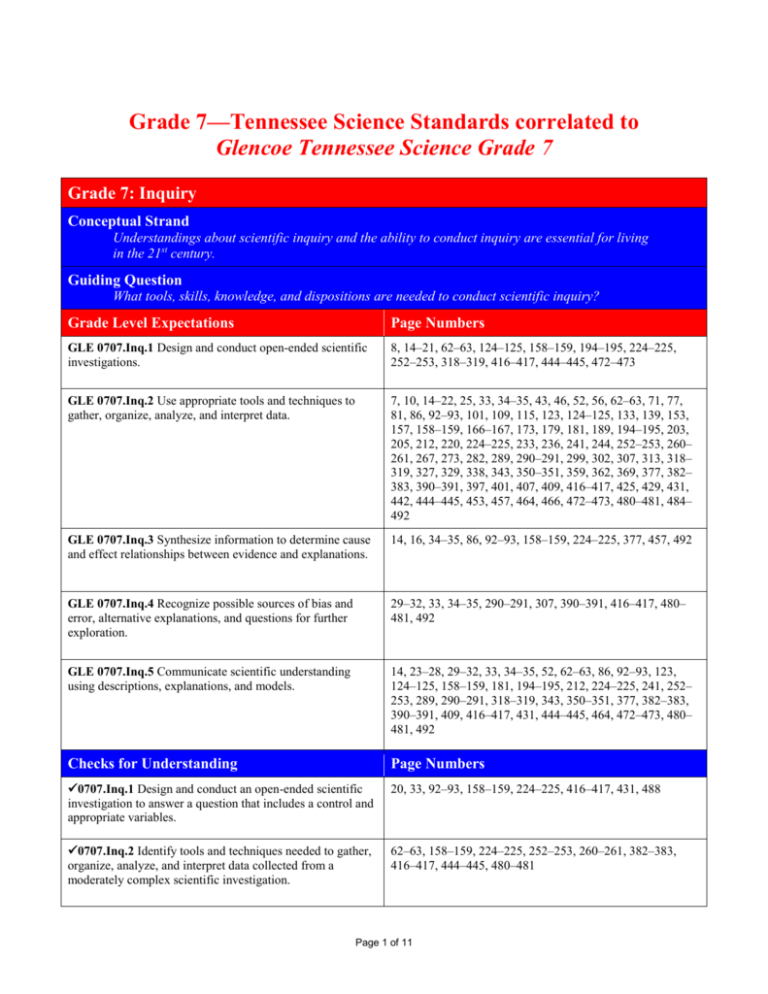
Grade 7—Tennessee Science Standards correlated to Glencoe Tennessee Science Grade 7 Grade 7: Inquiry Conceptual Strand Understandings about scientific inquiry and the ability to conduct inquiry are essential for living in the 21st century. Guiding Question What tools, skills, knowledge, and dispositions are needed to conduct scientific inquiry? Grade Level Expectations Page Numbers GLE 0707.Inq.1 Design and conduct open-ended scientific investigations. 8, 14–21, 62–63, 124–125, 158–159, 194–195, 224–225, 252–253, 318–319, 416–417, 444–445, 472–473 GLE 0707.Inq.2 Use appropriate tools and techniques to gather, organize, analyze, and interpret data. 7, 10, 14–22, 25, 33, 34–35, 43, 46, 52, 56, 62–63, 71, 77, 81, 86, 92–93, 101, 109, 115, 123, 124–125, 133, 139, 153, 157, 158–159, 166–167, 173, 179, 181, 189, 194–195, 203, 205, 212, 220, 224–225, 233, 236, 241, 244, 252–253, 260– 261, 267, 273, 282, 289, 290–291, 299, 302, 307, 313, 318– 319, 327, 329, 338, 343, 350–351, 359, 362, 369, 377, 382– 383, 390–391, 397, 401, 407, 409, 416–417, 425, 429, 431, 442, 444–445, 453, 457, 464, 466, 472–473, 480–481, 484– 492 GLE 0707.Inq.3 Synthesize information to determine cause and effect relationships between evidence and explanations. 14, 16, 34–35, 86, 92–93, 158–159, 224–225, 377, 457, 492 GLE 0707.Inq.4 Recognize possible sources of bias and error, alternative explanations, and questions for further exploration. 29–32, 33, 34–35, 290–291, 307, 390–391, 416–417, 480– 481, 492 GLE 0707.Inq.5 Communicate scientific understanding using descriptions, explanations, and models. 14, 23–28, 29–32, 33, 34–35, 52, 62–63, 86, 92–93, 123, 124–125, 158–159, 181, 194–195, 212, 224–225, 241, 252– 253, 289, 290–291, 318–319, 343, 350–351, 377, 382–383, 390–391, 409, 416–417, 431, 444–445, 464, 472–473, 480– 481, 492 Checks for Understanding Page Numbers 0707.Inq.1 Design and conduct an open-ended scientific investigation to answer a question that includes a control and appropriate variables. 20, 33, 92–93, 158–159, 224–225, 416–417, 431, 488 0707.Inq.2 Identify tools and techniques needed to gather, organize, analyze, and interpret data collected from a moderately complex scientific investigation. 62–63, 158–159, 224–225, 252–253, 260–261, 382–383, 416–417, 444–445, 480–481 Page 1 of 11 0707.Inq.3 Use evidence from a dataset to determine cause and effect relationships that explain a phenomenon. 34–35, 86, 92–93, 158–159, 224–225, 377 0707.Inq.4 Review an experimental design to determine possible sources of bias or error, state alternative explanations, and identify questions for further investigation. 33, 34–35, 290–291, 307, 390–391, 416–417, 480–481, 492 0707.Inq.5 Design a method to explain the results of an investigation using descriptions, explanations, or models. 14, 23–28, 29–32, 33, 34–35, 52, 62–63, 86, 92–93, 123, 124–125, 158–159, 181, 194–195, 212, 224–225, 241, 252– 253, 289, 290–291, 318–319, 343, 350–351, 377, 382–383, 390–391, 409, 416–417, 431, 444–445, 464, 472–473, 480– 481, 492 State Performance Indicators Page Numbers SPI 0707.Inq.1 Design a simple experimental procedure with an identified control and appropriate variables. 20, 33, 224–225, 416–417, 431, 488 SPI 0707.Inq.2 Select tools and procedures needed to conduct a moderately complex experiment. 62–63, 158–159, 224–225, 252–253, 260–261, 382–383, 416–417, 444–445, 480–481 SPI 0707.Inq.3 Interpret and translate data into a table, graph, or diagram. 34–35, 157, 158–159, 212, 224–225, 289, 377. 444–445 SPI 0707.Inq.4 Draw a conclusion that establishes a cause and effect relationship supported by evidence. 14, 16, 34–35, 86, 92–93, 158–159, 224–225, 377, 457, 492 SPI 0707.Inq.5 Identify a faulty interpretation of data that is due to bias or experimental error. 33, 34–35, 416–417, 480–481 Grade 7: Technology & Engineering Conceptual Strand Society benefits when engineers apply scientific discoveries to design materials and processes that develop into enabling technologies. Guiding Question How do science concepts, engineering skills, and applications of technology improve the quality of life? Grade Level Expectations Page Numbers GLE 0707.T/E.1 Explore how technology responds to social, political, and economic needs. 13, 53, 56, 64, 126, 210, 226, 245, 249, 251, 394, 446 Page 2 of 11 GLE 0707.T/E.2 Know that the engineering design process involves an ongoing series of events that incorporate design constraints, model building, testing, evaluating, modifying, and retesting. 151, 166–167, 260–261, 480–481 GLE 0707.T/E.3 Compare the intended benefits with the unintended consequences of a new technology. 418 GLE 0707.T/E.4 Describe and explain adaptive and assistive bioengineered products. 36, 446 See ONLINE STUDENT CENTER under textbook resources for adaptive and assistive products. http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078901359/student_view0/additional_inform ation_for_adaptive_and_assistive_technology.html Checks for Understanding Page Numbers 0707.T/E.1 Use appropriate tools to test for strength, hardness, and flexibility of materials. 272, 273, 290–291 0707.T/E.2 Apply the engineering design process to construct a prototype that meets certain specifications. 166–167, 382–383, 444–445, 480–481 0707.T/E.3 Explore how the unintended consequences of new technologies can impact society. 226, 249–251 0707.T/E.4 Research bioengineering technologies that advance health and contribute to improvements in our daily lives. 90, 191, 226, 249, 251, 254, 446 State Performance Indicators Page Numbers SPI 0707.T/E.1 Identify the tools and procedures needed to test the design features of a prototype. 382–383, 480–481 SPI 0707.T/E.2 Evaluate a protocol to determine if the engineering design process was successfully applied. 166–167, 382–383, 480–481 SPI 0707.T/E.3 Distinguish between the intended benefits and the unintended consequences of a new technology. 226, 249–251, 418 SPI 0707.T/E.4 Differentiate between adaptive and assistive bioengineered products (e.g., food, biofuels, medicines, integrated pest management). 226, 446 Page 3 of 11 Grade 7 : Standard 1 – Cells Conceptual Strand 1 All living things are made of cells that perform functions necessary for life. Guiding Question 1 How are plant and animals cells organized to carry on the processes of life? Grade Level Expectations Page Numbers GLE 0707.1.1 Make observations and describe the structure and function of organelles found in plant and animal cells. 44–49, 51–53, 65–69, 80, 82–85, 88–89, 95–96, 102–104, 108, 111, 113–118, 128–132, 134, 137, 144–145, 156, 208, 230 GLE 0707.1.2 Summarize how the different levels of organization are integrated within living systems. 51, 66–69, 113–118, 134–137, 144–145, 156, 208, 230 GLE 0707.1.3 Describe the function of different organ systems and how collectively they enable complex multicellular organisms to survive. 11, 44, 69, 113–118, 137, 144–147, 154, 156, 162–165 GLE 0707.1.4 Illustrate how cell division occurs in sequential stages to maintain the chromosome number of a species. 174–177, 180–187, 198–200 GLE 0707.1.5 Observe and explain how materials move through simple diffusion. 71, 80–86, 96–98, 196 Checks for Understanding Page Numbers 0707.1.1 Examine and describe plant and animal cells using compound microscopes. 52–53, 56–57, 66–67, 181 0707.1.2 Identify the function of the major plant and animal cellular organelles. 44–49, 51, 66, 99, 103, 107, 134 0707.1.3 Make a Venn diagram to compare the structures and functions of an animal cell with a city or school. Content: 44–51 Rubric for Venn diagram: Performance Assessment in the Science Classroom, p. 165 0707.1.4 Build a 3-D model of a cell. 67, 166–167 Page 4 of 11 0707.1.5 Construct a poster that illustrates the hierarchy among cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. 67 0707.1.6 Describe the function of different organ systems. 113–118, 138–140, 144, 147, 154, 156, 162–165 0707.1.7 Explain how different organ systems interact to enable complex multicellular organisms to survive. 113–118, 138–140, 144, 147, 154, 156, 162–165 0707.1.8 Apply the idea of the division of labor to explain why living things are organized into cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. 51 0707.1.9 Model the movement of chromosomes during plant cell division. 179, 181 0707.1.10 Design a demonstration that illustrates how materials move across a semi-permeable membrane by simple diffusion. 71, 86, 97 State Performance Indicators Page Numbers SPI 0707.1.1 Identify and describe the function of the major plant and animal cell organelles. 44–49, 51–52, 66, 80, 84–85, 99, 104, 134 SPI 0707.1.2 Interpret a chart to explain the integrated relationships that exist among cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. 67 SPI 0707.1.3 Explain the basic functions of a major organ system. 44, 113–118, 138–140, 144, 147, 154, 156, 162–165 SPI 0707.1.4 Sequence a series of diagrams that depict chromosome movement during plant cell division. 179, 181 SPI 0707.1.5 Explain how materials move through simple diffusion. 71, 80–86, 96–98, 196 Grade 7 : Standard 3 – Flow of Matter and Energy Conceptual Strand 3 Matter and energy flow through the biosphere. Page 5 of 11 Guiding Question 3 What scientific information explains how matter and energy flow through the biosphere? Grade Level Expectations Page Numbers GLE 0707.3.1 Distinguish between the basic features of photosynthesis and respiration. 48, 87–93, 95–96, 99 GLE 0707.3.2 Investigate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between living things and the environment. 48, 87–93, 99, 103–104 Checks for Understanding Page Numbers 0707.3.1 Associate the fundamental processes of photosynthesis and respiration with appropriate cell structures. 48, 88–89, 99 0707.3.2 Examine and identify the chloroplasts in a leaf cell. 48 0707.3.3 Identify the materials used by plants to make food. 48, 87–88, 99 0707.3.4 Create a chart that compares the reactants and products of photosynthesis and respiration. 95 0707.3.5 Model the pathways of water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide through a plant. Content: 87–91 Rubric for models: Performance Assessment in the Science Classroom, p. 121 0707.3.6 Describe the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide between living things and the environment. 48, 81, 88–93, 97, 99 0707.3.7 Describe structures that animals use to obtain oxygen. 48, 117 State Performance Indicators Page Numbers SPI 0707.3.1 Compare the chemical compounds that make up the reactants and products of photosynthesis and respiration. 87, 91–92, 96–99 SPI 0707.3.2 Interpret a diagram to explain how oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between living things and the environment. 91, 97 Grade 7 : Standard 4 – Heredity Page 6 of 11 Conceptual Strand 4 Plants and animals reproduce and transmit hereditary information between generations. Guiding Question 4 What are the principal mechanisms by which living things reproduce and transmit information between parents and offspring? Grade Level Expectations Page Numbers GLE 0707.4.1 Compare and contrast the fundamental features of sexual and asexual reproduction. 137–138, 172, 174, 176–180, 182–183, 187, 197–198, 201, 204–205, 207–208, 211, 213–215, 228, 230 GLE 0707.4.2 Demonstrate an understanding of sexual reproduction in flowering plants. 131, 204–207, 213, 217–221, 228–231 GLE 0707.4.3 Explain the relationship among genes, chromosomes, and inherited traits. 175, 178, 188, 190, 192–195, 198–199, 201, 234, 240, 242– 248, 256–259 GLE 0707.4.4 Predict the probable appearance of offspring based on the genetic characteristics of the parents. 234–248, 257 Checks for Understanding Page Numbers 0707.4.1 Classify organisms according to whether they reproduce sexually or asexually. 137–139, 179–180, 182–183, 198–202, 204–211, 213–219, 228–231 0707.4.2 Label and explain the function of the reproductive parts of a flower. 217–219, 223, 228–229, 231 0707.4.3 Describe various methods of plant pollination. 209–211, 213–219, 228–231 0707.4.4 Investigate the relationship among DNA, genes, and chromosomes. 193, 198–201, 256–257 0707.4.5 Explain the differences between dominant and recessive traits. 195, 236, 238–241, 246–247, 256–259 0707.4.6 Use a Punnett square to predict the genotypes of offspring resulting from a monohybrid cross. 239–241, 243, 256–259 State Performance Indicators Page Numbers Page 7 of 11 SPI 0707.4.1 Classify methods of reproduction as sexual or asexual. 137–138, 172, 174, 176–180, 182–183, 187, 197–198, 201, 204–205, 207–208, 211, 213–215, 228, 230 SPI 0707.4.2 Match flower parts with their reproductive functions. 131, 204–207, 213, 217–221, 228–231 SPI 0707.4.3 Describe the relationship among genes, chromosomes, and inherited traits. 175, 178, 188, 190, 192–195, 198–199, 201, 234, 240, 242– 248, 256–259 SPI 0707.4.4 Interpret a Punnett square to predict possible genetic combinations passed from parents to offspring during sexual reproduction. 239–241, 243, 256–259 Grade 7 : Standard 7 – The Earth Conceptual Strand 7 Major geologic events that occur over eons or brief moments in time continually shape and reshape the surface of the Earth, resulting in continuous global change. Guiding Question 7 How is the earth affected by long-term and short term geological cycles and the influence of man? Grade Level Expectations Page Numbers GLE 0707.7.1 Describe the physical properties of minerals. 269–272, 276, 290–291 GLE 0707.7.2 Summarize the basic events that occur during the rock cycle. 287–288 GLE 0707.7.3 Analyze the characteristics of the earth’s layers and the location of the major plates. 308–311, 314, 315, 318–319, 345, 344–349 GLE 0707.7.4 Explain how earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading are associated with movements of the earth’s major plates. 304–307, 308–313, 315–320, 328–329, 337, 344–349 GLE 0707.7.5 Differentiate between renewable and nonrenewable resources in terms of their use by man. 360–367 GLE 0707.7.6 Evaluate how human activities affect the earth’s land, oceans, and atmosphere. 50, 110, 121, 158–159, 264, 368–377, 394 Checks for Understanding Page Numbers Page 8 of 11 0707.7.1 Organize and explain information about the properties of minerals and their uses. 269–273, 290–292 0707.7.2 Label a diagram that depicts the major processes of the rock cycle. 289 0707.7.3 Distinguish among sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks and relate these to a simple diagram of the rock cycle. 267, 277–288 0707.7.4 Recognize that the earth’s layers have different thickness, states of matter, densities, and chemical makeup. 277–287, 304, 306, 308, 313–315 0707.7.5 Analyze the relationship between plate movements and areas of earthquake activity. 328–330, 344, 347–352 0707.7.6 Analyze the relationship between plate movements and mountain building. 314, 315 0707.7.7 Analyze the relationship between plate movements, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading. 304–307, 337–339, 342–346, 349 0707.7.8 Determine the impact of man’s use of renewable and nonrenewable resources on future supplies. 363, 378–383, 390–391, 394 0707.7.9 Evaluate how human activities affect the condition of the earth’s land, water, and atmosphere. 110, 121, 158–159, 264, 369, 372, 377, 384, 394 State Performance Indicators Page Numbers SPI 0707.7.1 Use a table of physical properties to classify minerals. 290–291, 528–529 SPI 0707.7.2 Label a diagram that depicts the three different rock types. 267, 293 SPI 0707.7.3 Identify the major processes that drive the rock cycle. 284, 287–288 SPI 0707.7.4 Differentiate among the characteristics of the earth’s three layers. 348, 349 SPI 0707.7.5 Recognize that lithospheric plates on the scale of continents and oceans continually move at rates of centimeters per year. 265, 300–303, 413 Page 9 of 11 SPI 0707.7.6 Describe the relationship between plate movements and earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading. 263, 265, 304–311, 319, 328–329, 337, 339, 342–347, 349 SPI 0707.7.7 Analyze and evaluate the impact of man’s use of earth’s land, water, and atmospheric resources. 76, 110, 121, 158–159, 369, 370–372, 375–377, 394 Grade 7 : Standard 11 – Motion Conceptual Strand 11 Objects move in ways that can be observed, described, predicted, and measured. Guiding Question 11 What causes objects to move differently under different circumstances? Grade Level Expectations Page Numbers GLE 0707.11.1 Identify six types of simple machines. 432–433, 435–443 GLE 0707.11.2 Apply the equation for work in experiments with simple machines to determine the amount of force needed to do work. 426, 428–430, 480–481 GLE 0707.11.3 Distinguish between speed and velocity. 399, 401 GLE 0707.11.4 Investigate how Newton’s laws of motion explain an object’s movement. 410–417 GLE 0707.11.5 Compare and contrast the basic parts of a wave. 454–458, 459–464 GLE 0707.11.6 Investigate the types and fundamental properties of waves. 454–458, 459–464, 471–474 Checks for Understanding Page Numbers 0707.11.1 Compare the six types of simple machines. 437–443 0707.11.2 Complete an investigation to determine how machines reduce the amount of force needed to do work. 425, 442, 444–445, 480–481 Page 10 of 11 0707.11.3 Summarize the difference between the speed and 399, 401 velocity based on the distance and amount of time traveled. 0707.11.4 Recognize how a net force impacts an object’s motion. 397, 404 0707.11.5 Create a graphic organizer to illustrate and describe the basic parts of a wave. 475 0707.11.6 Compare how transverse and longitudinal waves 456, 457, 464 are produced and transmitted. State Performance Indicators Page Numbers SPI 0707.11.1 Differentiate between the six simple machines. 437–443 SPI 0707.11.2 Determine the amount of force needed to do work using different simple machines. 432–438, 440, 480–481 SPI 0707.11.3 Apply proper equations to solve basic problems pertaining to distance, time, speed, and velocity. 398–401 SPI 0707.11.4 Identify and explain how Newton’s laws of motion relate to the movement of objects. 410–417 SPI 0707.11.5 Compare and contrast the different parts of a wave. 454–458, 459–463 SPI 0707.11.6 Differentiate between transverse and longitudinal waves in terms of how they are produced and transmitted. 456, 457, 464 Page 11 of 11