7th Science Modern Living
advertisement
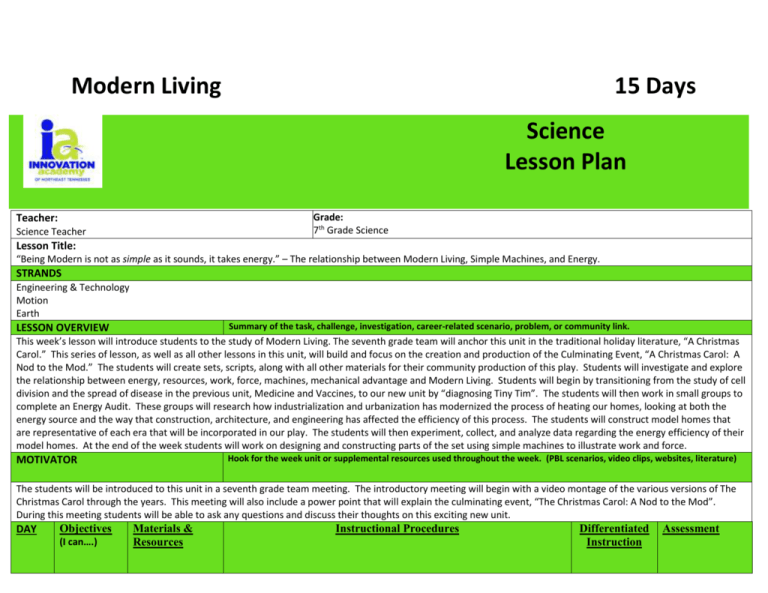
Modern Living 15 Days Science Lesson Plan Grade: 7th Grade Science Teacher: Science Teacher Lesson Title: “Being Modern is not as simple as it sounds, it takes energy.” – The relationship between Modern Living, Simple Machines, and Energy. STRANDS Engineering & Technology Motion Earth Summary of the task, challenge, investigation, career-related scenario, problem, or community link. LESSON OVERVIEW This week’s lesson will introduce students to the study of Modern Living. The seventh grade team will anchor this unit in the traditional holiday literature, “A Christmas Carol.” This series of lesson, as well as all other lessons in this unit, will build and focus on the creation and production of the Culminating Event, “A Christmas Carol: A Nod to the Mod.” The students will create sets, scripts, along with all other materials for their community production of this play. Students will investigate and explore the relationship between energy, resources, work, force, machines, mechanical advantage and Modern Living. Students will begin by transitioning from the study of cell division and the spread of disease in the previous unit, Medicine and Vaccines, to our new unit by “diagnosing Tiny Tim”. The students will then work in small groups to complete an Energy Audit. These groups will research how industrialization and urbanization has modernized the process of heating our homes, looking at both the energy source and the way that construction, architecture, and engineering has affected the efficiency of this process. The students will construct model homes that are representative of each era that will be incorporated in our play. The students will then experiment, collect, and analyze data regarding the energy efficiency of their model homes. At the end of the week students will work on designing and constructing parts of the set using simple machines to illustrate work and force. Hook for the week unit or supplemental resources used throughout the week. (PBL scenarios, video clips, websites, literature) MOTIVATOR The students will be introduced to this unit in a seventh grade team meeting. The introductory meeting will begin with a video montage of the various versions of The Christmas Carol through the years. This meeting will also include a power point that will explain the culminating event, “The Christmas Carol: A Nod to the Mod”. During this meeting students will be able to ask any questions and discuss their thoughts on this exciting new unit. DAY Objectives (I can….) Materials & Resources Instructional Procedures Differentiated Instruction Assessment 1 I CAN demonstrat e my understandi ng of work and energy I CAN use previous knowledge along with research to determine the most likely medical diagnosis. KWL Chart Diagnosing Tiny Tim PDF containing directions iPad Essential Questions: How can modern medicine be used to treat and prevent disease? What are simple machines and how are they used? 1. Bell Work - Students will fill out the K and W of a KWL chart on the topic “work and energy.” 2. Direct Instruction - Students will receive instruction on their “Diagnosing Tiny Tim” assignment and ask questions about their task 3. Group Practice: - Diagnosing Tiny Tim a) Students will research four possible conditions that Tiny Tim could have suffered from: Tuberculosis, Renal Tubular Acidosis, Polio, and Rickets. b) Students will work in pairs to create an informational foldable about the four possible medical conditions and a diagnosis letter to the Cratchit family that will include a treatment plan for Tiny Tim. 4. Individual Practice: - When students complete Tiny Tim’s diagnosis assignment, they will research energy and work to prepare for their study of energy, work, force, simple machines, and mechanical efficiency. 5. Summary: - Exit ticket Students will fill out the “L” portion of their KWL chart using the information gathered from their research. Homework—Students were assigned Frayer Models for the following vocabulary terms: Simple Machines, Mechanical Efficiency, Longitudinal Waves, Transverse Waves, and Velocity. Adapted from: Goodman Theatre Education http://education.goodmantheatre.org/resources/a-christmas-carol/lessonplan-diagnosing-tiny-tim/ Remediation Formative assessment Prompting on KWL chart will KWL and provide research information on Heterogeneous what students’ grouping previous knowledge and Extension what they Heterogeneous learned from grouping their research. Peer tutoring Summative Assessment Summative assessment at the end of the unit will cover waves, forces, energy, mechanical efficiency, and simple machines. 2 I CAN explain the relationsh ip between force, distance, and work. I CAN correctly calculate work. I CAN explain the difference in mechanic al advantage and mechanic al efficiency. I CAN provide examples of how machines are used for constructi on. iPad Forces PPT “Forces” ppt “Work” ppt “Waves” ppt Concept map E Essential Questions: What is the relationship between force, distance, and work? How do simple machines make work easier? Provide examples of what type of simple machines we can use to construct the set of our play. How do you differentiate between mechanical advantage and mechanical efficiency? 1. Bell Work: - Students will respond to the lesson’s essential questions in the form of an entrance ticket. - The students will respond to the following questions to recap the material from the student teaches: a) What is the relationship between work and power? b) How do you calculate work? c) What is mechanical advantage? d) How do you differentiate between mechanical advantage and mechanical efficiency? - Students will have five minutes to complete the task. 2. Direct Instruction: - Simple Machines and Mechanical Efficiency Review - Forces and Work Review - Waves Review - Students will take notes in their Science Notebooks - Students will ask questions and discuss the concepts presented in the notes. 3. Individual Practice: - Students will practice calculating work and power. - Students will practice calculating mechanical efficiency and mechanical advantage. - Students will research various ways in which modern technology has increased the efficiency of machinery. - The class will discuss the answers and methods for solving the practice problems. 4. Summary: - The students will answer the following questions as an exit ticket a) How do you differentiate between mechanical advantage and mechanical efficiency? Remediation Prompting on bell work and exit ticket Teacher guidance during independent practice Extension Additional questions during individual practice. Formative Assessment Students’ answers to the essential questions will assess what they learned from student teaches and what needs to be the focus of today’s review. Teacher will view students as they are completing calculations to determine which areas may need to be reviewed. Summative Assessment Summative assessment at the end of the unit will cover waves, forces, energy, mechanical efficiency, and simple machines. b) How are simple machines utilized in the process of construction? c) How are work and force related? d) What is the difference in a longitudinal and transverse wave? I CAN explain how modern technolog y has increased the efficiency of machines. 3 Refer to Unit Plan for Days 3-15 “A Christmas Carol: A Nod to the Mod” Identify what you want to teach. Reference State, Common Core, ACT College Readiness Standards and/or State Competencies. STANDARDS Embedded Technology & Engineering Conceptual Strand Society benefits when engineers apply scientific discoveries to design materials and processes that develop into enabling technologies. Guiding Question How do science concepts, engineering skills, and applications of technology improve the quality of life? Grade Level Expectations: GLE 0707.T/E.1 Explore how technology responds to social, political, and economic needs. GLE 0707.T/E.2 GLE 0707.T/E.3 GLE 0707.T/E.4 Know that the engineering design process involves an ongoing series of events that incorporate design constraints, model building, testing, evaluating, modifying, and retesting. Compare the intended benefits with the unintended consequences of a new technology. Describe and explain adaptive and assistive bioengineered products. Checks for Understanding 0707.T/E.1 0707.T/E.2 0707.T/E.3 0707.T/E.4 0707.T/E.5 Use appropriate tools to test for strength, hardness, and flexibility of materials. Apply the engineering design process to construct a prototype that meets certain specifications. Explore how the unintended consequences of new technologies can impact society. Research bioengineering technologies that advance health and contribute to improvements in our daily lives. Develop an adaptive design and test its effectiveness. State Performance Indicators SPI 0707.T/E.1 SPI 0707.T/E.2 SPI 0707.T/E.3 SPI 0707.T/E.4 Identify the tools and procedures needed to test the design features of a prototype. Evaluate a protocol to determine if the engineering design process was successfully applied. Distinguish between the intended benefits and the unintended consequences of a new technology. Differentiate between adaptive and assistive engineered products (e.g., food, biofuels, medicines, integrated pest management). Standard 7 – The Earth Conceptual Strand 7 Major geologic events that occur over eons or brief moments in time continually shape and reshape the surface of the Earth, resulting in continuous global change. Guiding Question 7 How is the earth affected by long-term and short term geological cycles and the influence of man? Grade Level Expectations: GLE 0707.7.5 GLE 0707.7.6 Differentiate between renewable and nonrenewable resources in terms of their use by man. Evaluate how human activities affect the earth’s land, oceans, and atmosphere. Checks for Understanding 0707.7.8 0707.7.9 Determine the impact of man’s use of renewable and nonrenewable resources on future supplies. Evaluate how human activities affect the condition of the earth’s land, water, and atmosphere. State Performance Indicators SPI 0707.7.7 Analyze and evaluate the impact of man’s use of earth’s land, water, and atmospheric resources. Standard 11 - Motion Conceptual Strand 11 Objects move in ways that can be observed, described, predicted, and measured. Guiding Question 11 What causes objects to move differently under different circumstances? Grade Level Expectations: GLE 0707.11.1 GLE 0707.11.2 GLE 0707.11.3 GLE 0707.11.4 Identify six types of simple machines. Apply the equation for work in experiments with simple machines to determine the amount of force needed to do work. Distinguish between speed and velocity. Investigate how Newton’s laws of motion explain an object’s movement. Checks for Understanding 0707.11.1 0707.11.2 0707.11.3 0707.11.4 Compare the six types of simple machines. Compete an investigation to determine how machines reduce the amount of force needed to do work. Summarize the difference between the speed and velocity based on the distance and amount of time traveled. Recognize how a net force impacts an object’s motion. State Performance Indicators SPI 0707.11.1 SPI 0707.11.2 SPI 0707.11.3 SPI 0707.11.4 Differentiate between the six simple machines. Determine the amount of force needed to do work using different simple machines. Apply proper equations to solve basic problems pertaining to distance, time, speed, and velocity. Identify and explain how Newton’s laws of motion relate to the movement of objects.