Q2 - Shelby County Schools
advertisement
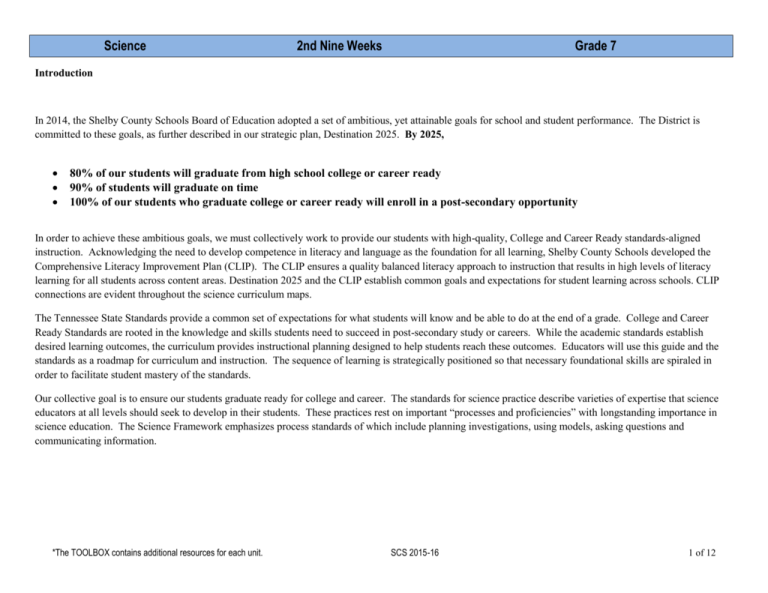
Science 2nd Nine Weeks Grade 7 Introduction In 2014, the Shelby County Schools Board of Education adopted a set of ambitious, yet attainable goals for school and student performance. The District is committed to these goals, as further described in our strategic plan, Destination 2025. By 2025, 80% of our students will graduate from high school college or career ready 90% of students will graduate on time 100% of our students who graduate college or career ready will enroll in a post-secondary opportunity In order to achieve these ambitious goals, we must collectively work to provide our students with high-quality, College and Career Ready standards-aligned instruction. Acknowledging the need to develop competence in literacy and language as the foundation for all learning, Shelby County Schools developed the Comprehensive Literacy Improvement Plan (CLIP). The CLIP ensures a quality balanced literacy approach to instruction that results in high levels of literacy learning for all students across content areas. Destination 2025 and the CLIP establish common goals and expectations for student learning across schools. CLIP connections are evident throughout the science curriculum maps. The Tennessee State Standards provide a common set of expectations for what students will know and be able to do at the end of a grade. College and Career Ready Standards are rooted in the knowledge and skills students need to succeed in post-secondary study or careers. While the academic standards establish desired learning outcomes, the curriculum provides instructional planning designed to help students reach these outcomes. Educators will use this guide and the standards as a roadmap for curriculum and instruction. The sequence of learning is strategically positioned so that necessary foundational skills are spiraled in order to facilitate student mastery of the standards. Our collective goal is to ensure our students graduate ready for college and career. The standards for science practice describe varieties of expertise that science educators at all levels should seek to develop in their students. These practices rest on important “processes and proficiencies” with longstanding importance in science education. The Science Framework emphasizes process standards of which include planning investigations, using models, asking questions and communicating information. *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 1 of 12 Science Construct explanations and design solution Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information Engage in argument 2nd Nine Weeks Grade 7 Ask questions and define problems Patterns Develop and use models Practices in Science Use math, technology, and computational thinking Plan and carry out investigations Stability and change Cross Cutting Concepts Cause and Effect Analyze and interpret data Energy and matter Systems and system models Crosscutting concepts have value because they provide students with connections and intellectual tools that are related across the differing areas of disciplinary content and can enrich their application of practices and their understanding of core ideas. Throughout the year, students should continue to develop proficiency with the eight science practices. Crosscutting concepts can help students better understand core ideas in science and engineering. When students encounter new phenomena, whether in a science lab, field trip, or on their own, they need mental tools to help engage in and come to understand the phenomena from a scientific point of view. Familiarity with crosscutting concepts can provide that perspective. A next step might be to simplify the phenomenon by thinking of it as a system and modeling its components and how they interact. In some cases it would be useful to study how energy and matter flow through the system, or to study how structure affects function (or malfunction). These preliminary studies may suggest explanations for the phenomena, which could be checked by predicting patterns that might emerge if the explanation is correct, and matching those predictions with those observed in the real world. *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 2 of 12 Science 2nd Nine Weeks Grade 7 Science Curriculum Maps This curriculum map is designed to help teachers make effective decisions about what science content to teach so that, our students will reach Destination 2025. To reach our collective student achievement goals, we know that teachers must change their instructional practice in alignment with the three College and Career Ready shifts in instruction for science. To ensure that all student will be taught science content and processes in a comprehensive, consistent, and coherent manner, Science Curriculum Maps are provided. Foundation texts for the maps include Shelby County Schools Framework for Standards Based Curriculum, Science Curriculum Frameworks-K-12 (State of Tennessee Board of Education, and National Science Education Standards). Teachers function most effectively and students learn best within an “aligned” curriculum delivery system. An aligned system begins with a concerted effort to implement the state curriculum frameworks. Many districts have developed curriculum guides built around these frameworks to ensure that what is taught in particular grades and courses is closely linked with student Learning Expectations found in the state standards. Classroom teachers use these locally-generated curriculum guides to plan and implement their individual grade or course Pacing Guides. Expectations for student performance are clear and carefully tied to daily instructional events and classroom assessment practices. In theory, a fully aligned system closes the loop between state standards and student learning. Additionally, a coherent instructional/assessment system offers the potential for heightening student learning as reflected by their performance on state-mandated standardized tests. Our collective goal is to ensure our students graduate ready for college and career. Most of the elements found in the state Curriculum Frameworks were incorporated into the curriculum mapping materials prepared by Shelby County Schools. Additional features were included to add clarity and to offer avenues that could assist teacher in developing grade level lessons. A district-wide, K-12, standards-based curriculum is implemented in science. This curriculum is articulated in the form of individual SCS curriculum maps for each grade and subject. These SCS curriculum maps enable the district to implement a single curriculum that emphasizes specific standards. Since Shelby County has a high rate of mobility among the student population, the SCS curriculum maps ensure that all students receive the same program of high-level instructional content and academic expectations, regardless of which school they attend. The utilization of a district-wide standards-based curricular program ensures that students in SCS are engaged in hands-on inquiry based activities as teachers implement the curriculum maps. *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 3 of 12 Science State Standards 2nd Nine Weeks Embedded Standards Grade 7 Learning Outcomes Adopted Resources* Core Ideas Unit 2.1: Waves, 1 Week GLE 0707.11.5 Compare and contrast the basic parts of a wave. GLE 0707.11.6 Investigate the types and fundamental properties of waves. GLE 0707.Inq.5 Communicate scientific understanding using descriptions, explanations, and models. Compare and contrast the basic parts of a wave. Describe the properties and behavior of waves. Distinguish between longitudinal and transverse waves. Tennessee Holt Science and Technology TE, Chapter 22, Section 1: The Nature of Waves, p. 600-617 CLIP connections Academic vocabulary: amplitude, crest, speed, trough, vibration Glencoe Tennessee Science Grade 7 TWE, Chapter 15, Section 1: What are waves? Section 2: Wave Properties, p. 454 – 463 NGSS Practice 8: Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information. A Glencoe workbook, aligned with State Performance Indicators for 7th grade science, which is designed to assess student mastery. Included are formative assessments, student activities, and more. This is an excellent resource. Literacy Task: Integrate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text with a version of that information expressed visually. Task: Compare and contrast the basic parts of a wave, identify the fundamental features of waves, and the different wave types. Students can build models that represent wave parts, types, and properties. CER template http://www.indps.k12.wi.us/cms_files/resou rces/Notebooking%20ideas_including%20 claim%20evidence%20reasoning.pdf CER Graphic Organizer http://www.cascience.org/csta/pdf/conferen cehandouts/2013/yellenberg_2_c_e_r_gra phicorganizer.pdf *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 4 of 12 Science State Standards 2nd Nine Weeks Embedded Standards Grade 7 Learning Outcomes Adopted Resources* Core Ideas Unit 2.2: Rocks and Minerals, 4 Weeks GLE 0707.7.2 Summarize the basic events that occur during the rock cycle. GLE 0707.7.1 Describe the physical properties of minerals. GLE 0707.Inq.5 Communicate scientific understanding using descriptions, explanations, and models. GLE 0707.Inq.1 Design and conduct open-ended scientific investigations GLE 0707.Inq.4 Recognize possible sources of bias and error, alternative explanations, and questions for further exploration. GLE 0707.Inq.2 Use appropriate tools and techniques to gather, organize, analyze, and interpret data. Observe and compare the properties of sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks. Relate crystal size in igneous rocks to environmental conditions. Describe how the processes of weathering, erosion, and deposition contribute to the formation of sediments, sedimentary rock and landforms. Explain how rocks change as they undergo metamorphosis. Conduct tests to determine the physical properties of selected mineral samples. Justify the identification of an unknown mineral sample by its physical properties. Tennessee Holt Science and Technology TE, Chapter 14, Section 1: The Rock Cycle and Section 2: Igneous Rock and Section 3: Sedimentary Rock, Section 4: Metamorphic Rock, p. 358381 Chapter 13, Section 1: What is a Mineral? Section 2: Identifying Minerals Section 3: The Formation, Mining, and Use of Minerals, p. 344-349. Glencoe Tennessee Science Grade 7 TWE, Chapter 9, Section 3: Metamorphic Rocks and the Rock Cycle, p 284 - 288 and Section 1: Minerals-Earth's Jewels, p 268 - 276 CLIP connections Academic vocabulary: rock cycle, igneous, metamorphic, minerals, sedimentary NGSS Practice 6: Constructing explanations (for science) and designing solutions (for engineering) NGSS Practice 7: Engaging in argument from evidence Literacy Task: Use precise language and domain-specific vocabulary to inform about or explain the topic Literacy Task: Follow precisely a multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks Task: Students can describe how earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading are associated with movements of the earth’s plates. A simple description of sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rock formation (quiz included). http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/ environment_earth_universe/rock_cycle/ac tivity/ *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 5 of 12 Science State Standards 2nd Nine Weeks Embedded Standards Grade 7 Learning Outcomes Adopted Resources* Core Ideas Unit 2.3: Plate Tectonics, 3 Weeks GLE 0707.7.4 Explain how earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading are associated with movements of the earth’s major plates. GLE 0707.7.3 Analyze the characteristics of the earth’s layers and the location of the major plates. GLE 0707.Inq.4 Recognize possible sources of bias and error, alternative explanations, and questions for further exploration. Relate wave movement in a spring to earthquake waves. GLE 0607.Inq.5 Communicate scientific understanding using descriptions, explanations, and models. Identify and describe the layers of the earth. GLE 0707.T/E.1 Explore how technology responds to social, political, and economic needs. GLE 0707.T/E.2 Evaluate a protocol to determine if the engineering design process was successfully applied. Tennessee Holt Science and Technology TE, Chapter 15, Plate Tectonics p. 390-415. Describe how scientists study the structure of the earth’s interior. Explain how plate boundaries result in earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading. Analyze the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes around the world. Hypothesize about the reasons for patterns in the location of earthquakes and volcanoes. Use the engineering design process to determine the characteristics of earthquakeproof structures. Chapter 16, Section 1: What are Earthquakes? p 424-441 Chapter 17, Section 1: Volcanic Eruptions and Section 3: Causes of Volcanic Eruptions, p. 424-467 Glencoe Tennessee Science Grade 7 TWE, Chapter 11, Section 1: Earthquakes and Section 2: Volcanoes and Section 3: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Plate Tectonics, p 328-349 Chapter 10, Section 1: Continental Drift and Section 2: Seafloor Spreading and Section 3: Theory of Plate Tectonics, p.300-317 A Glencoe workbook, aligned with State Performance Indicators for 7th grade science, which is designed to assess student mastery. Included are formative assessments, student activities, and more. This is an excellent resource. *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 CLIP connections Academic Vocabulary: earth layers, earthquake, plate, volcano, crust, mantle, tectonic plate, continental drift NGSS Practice 3: Planning and carrying out investigations. NGSS Practice 4: Analyzing and interpreting data. Literacy Task: Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the argument presented. Literacy Task: Follow precisely a multistep procedure when carrying out experiments, taking measurements, or performing technical tasks. Literacy Task: Analyze the structure an author uses to organize a text, including how the major sections contribute to the whole and to an understanding of the topic. An assortment of lesson plans, labs, and student activities on plate tectonics. http://science.lotsoflessons.com/platetecto nics.html 6 of 12 Science State Standards 2nd Nine Weeks Embedded Standards Grade 7 Learning Outcomes Adopted Resources* Core Ideas Unit 2.4: Natural Resources, 1 Week GLE 0707.7.5 Differentiate between renewable and nonrenewable resources in terms of their use by man. GLE 0707.7.6 Evaluate how human activities affect the earth’s land, oceans, and atmosphere. GLE 0707.Inq.5 Communicate scientific understanding using descriptions, explanations, and models. GLE 0707.T/E.3 Compare the intended benefits with the unintended consequences of a new technology. Differentiate between renewable and nonrenewable resources in terms of their use by man. Evaluate how human activities affect the earth’s land, oceans, and atmosphere. Tennessee Holt Science and Technology TE, Chapter 18, Section 1: Natural Resources and Section 2, Fossil Fuels and Section 3 The Three R's of Conservation, p. 476-497 CLIP connections Academic vocabulary: natural resource, non-renewable resource, renewable resource, recycling Glencoe Tennessee Science Grade 7 TWE, Chapter 12, Section 1: Resources and Section 2 Pollution, p. 360-376 NGSS Practice 4: Analyzing and interpreting data A Glencoe workbook, aligned with State Performance Indicators for 7th grade science, which is designed to assess student mastery. Included are formative assessments, student activities, and more. This is an excellent resource. Mathematics Task: Analyze proportional relationships and use them to solve realworld and mathematical problems Predict how human behaviors affect cycles. Evaluate the impact of specific technologies on the environment. Variety of activities to increase students’ ability to determine the impact of man's use of renewable and nonrenewable resources on future supplies. http://www.internet4classrooms.com/grade _level_help/earth_science_renewable_and _nonrenewable_seventh_7th_grade_scien ce.htm *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 7 of 12 Science 2nd Nine Weeks Grade 7 TOOLBOX Unit 2.1: Waves, 1 Week Plans Students learn about wave movement and properties (wavelength, frequency, amplitude and speed) and record their notes on a handout. They then label wave parts on a worksheet diagram (crest, trough and wavelength) and use the diagram to determine wave frequency. http://www.teachengineering.org/view_lesson.php?url=collection/clem_/lessons/clem_waves_lessons/clem_waves_lesson02.xml Properties of Waves Lesson Plan: Making waves visible, students will be able to identify that there are various types of waves with properties that are similar and different, identify properties of waves, and create models that demonstrate relationships. http://betterlesson.com/lesson/633219/properties-of-waves-making-waves-visible?grade=&subject=2&from=bl_explore-1_waves_all_all_mtlesson_633219_title Background for Teachers Student Activities Bite-Size Physics is an awesome resource for understanding wave types and characteristics. Demonstrations requiring minimum resources are provided. http://www.bitesizephysics.com/energywaveslesso.html Additional background information on the nature and properties of waves. http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves A tutorial on the general properties of waves, which includes visual effects for the students. http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/aqa/waves/generalwavesact.shtml Students can manipulate waves in this web-based simulation in order to determine the properties and behavior of a wave on a string. http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/wave-on-a-string Students can graph water waves at different frequencies and amplitudes using a simulation at: http://www.classzone.com/books/ml_science_share/vis_sim/wslm05_pg18_graph/wslm05_pg18_graph.html Hands on Activity - Make Some Waves (student worksheet included): http://www.teachengineering.org/view_activity.php?url=collection/cub_/activities/cub_soundandlight/cub_soundandlight_lesson1_activity1.xml Other Resources An online wave properties quiz. http://glencoe.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0078617766/student_view0/chapter1/section2/self-check_quiz-eng_.html Pink Palace Museum Field Trips Labs: Sound Science *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 8 of 12 Science 2nd Nine Weeks Grade 7 TOOLBOX Unit 2.2: Rocks and Minerals, 4 Weeks Plans Background for Teachers Lesson plans on Rocks and Minerals: http://www.rocksandminerals4u.com/lesson_plans.html Fun Rocks and Minerals Facts: http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/sciencefacts/earth/rocksandminerals.html Additional Background Information on Rocks and minerals: http://www.archaeology.ncdcr.gov/ncarch/GeoArcheo/RocksA.htm Use Poetry To Teach About Minerals: A study discussing the incorporation of writing to teach about the different types of minerals. Student work examples are provided. http://www.nagt.org/files/nagt/jge/abstracts/Rule_v52n1p10.pdf Student Activities 12 Links to Scholastic Study Jam Interactive Science Activities: http://www.scholastic.com/teachers/activity/rocks-minerals-and-landforms-12-studyjamsinteractive-science-activities Learn about rocks, minerals & soils as you complete a variety of interesting experiments with this fun, interactive activity. Rocks, minerals and soils have different characteristics that set them apart from others. Find out about the properties of rocks such as slate, marble, chalk, granite and pumice. Which rocks split? Can you find a rock that floats? Answer these and other scientific questions with this cool science game. http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/gamesactivities/rockssoils.html Rocks & Minerals: A variety of student labs and activities with worksheets included (The Science Spot). http://sciencespot.net/Pages/classearth.html Interactive Rock Cycle: reviews types of rocks and the processes of the rock cycle with students. http://www.learner.org/interactives/rockcycle/index.html A variety of rock cycle animations from Interactive Sites for Education. Assists with differentiating instruction, as animations are appropriate for various grade levels. http://interactivesites.weebly.com/rocks-and-minerals.html ReadWorks passage and comprehension questions on rocks and minerals: https://www.readworks.org/sites/default/files/passages/860_hard_minerals.pdf A variety of activities, animations, and quizzes geared towards increasing the students understanding of the major processes that drive the rock. http://www.internet4classrooms.com/grade_level_help/earth_science_rock_cycle_processes_seventh_7th_grade_science.htm Scaffolding activities for teaching students both the types of rocks and the rock cycle. https://quizlet.com/10905786/the-rock-cycle-flash-cards/original Rock Cycle Quiz: Assesses student understanding of the conditions required for rock to change from one type to another. *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 9 of 12 Science 2nd Nine Weeks Grade 7 TOOLBOX http://www.quia.com/quiz/1195085.html Rock Cycle Project Choice Board (with rubric). http://fourthgradeteam2012-2013.cmswiki.wikispaces.net/file/view/TheRockCycleProjectChoiceBoardandRubricFreebie.pdf Characteristic Properties of Minerals Quiz: http://www.quia.com/quiz/2895643.html Other Resources This is a mini-project requiring students to research a particular mineral, create an advertisement for its common uses, and describe its characteristic properties: http://www.sciencespot.net/Media/mghtymin.pdf The American Association for the Advancement of Science - This is a list of key ideas related to Weathering Erosion, and Deposition. For each key idea, you will find a list of sub-ideas, a list of items, results from the AAAS field-testing, and a list of student misconceptions. Questions items provided can be used to assess student understanding. http://assessment.aaas.org/topics/WE#/ An interactive rock cycle tutorial allowing students to see the various routes igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks take through the rock cycle. http://www.phschool.com/atschool/phsciexp/active_art/rock_cycle/ Rock Cycle Simulation Lab: http://www.lewistonpublicschools.org/~nsousa/Mrs._Sousa/Rock_Cycle_and_Geologic_Time_files/Rock%20Cycle%20Crayon%20lab.pdf Pink Palace Museum Field Trips Exhibits: Geology Labs: Rocks & Minerals Pink Palace Museum Outreach Suitcase Exhibits: (free) Rocks & Minerals Unit 2.3: Plate Tectonics, 3 Weeks Plans Background for Teachers Lesson Plan on Plate Tectonics with multimedia resources: http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/ess05.sci.ess.earthsys.lp_platetectonics/plate-tectonics/ Khan Academy Video - Plate Tectonics: Evidence of plate movement. http://www.khanacademy.org/science/cosmology-and-astronomy/earth-historytopic/plate-techtonics/v/plate-tectonics----evidence-of-plate-movement *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 10 of 12 Science 2nd Nine Weeks Grade 7 TOOLBOX Khan Academy Video - Structures of the Earth. http://www.khanacademy.org/science/cosmology-and-astronomy/earth-history-topic/platetechtonics/v/structure-of-the-earth Plate Tectonic Unit Review. http://plate-tectonics.org/plate-tectonics/plate-tectonics-lesson-plans.html Student Activities This is a Layers of the Earth foldable illustrating the mantles’ convection currents. A color-coded key is included. http://mjksciteachingideas.com/pdf/EarthFoldable.pdf A great introductory activity on plate tectonics for students. http://www.amnh.org/explore/curriculum-collections/dinosaurs-ancient-fossils-newdiscoveries/plate-tectonics-puzzle An excellent resource for students to research convergent, divergent, and transform boundary movement (especially when used with a cloze activity). Illustrations are included. http://www.cotf.edu/ete/modules/msese/earthsysflr/plates1.html ReadWorks passage and comprehension questions on Plate Tectonics: https://www.readworks.org/sites/default/files/passages/610_our_changing_earth_plate_tectonics_and_large_scale_system_interactions.pdf A game that assesses student understanding of earth’s layers. May be used in a whole or small group setting. (Rags to Riches format.) http://www.quia.com/rr/38064.html Other Resources The American Association for the Advancement of Science - This is a list of key ideas related to Plate Tectonics. For each key idea, you will find a list of subideas, a list of items, results from the AAAS field-testing, and a list of student misconceptions. Question items provided can be used to assess student understanding. http://assessment.aaas.org/topics/PT#/ A kid’s geography website with four quizzes (earth’s structure, volcanoes, earthquakes, and plate tectonics). Great for independent or collaborative instructional time. http://www.geography4kids.com/activities.html Pink Palace Museum Field Trips Exhibits: Geology, Nature Unleashed (Feb 6 – May 1, 2016) Nature Unleashed was developed by the Field Museum in Chicago. This link takes you to their website. Pink Palace Museum Outreach Suitcase Exhibits: (free) Earthquakes Unit 2.4: Natural Resources, 1 Week Unit Plan on Natural Resources, which contains handouts, graphic organizers, discussion questions and background information for teachers. *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 11 of 12 Science 2nd Nine Weeks Grade 7 TOOLBOX Plans http://www.calrecycle.ca.gov/Education/curriculum/ctl/K3Module/Unit1/Lesson1.pdf A PowerPoint lesson about renewable and nonrenewable resources, ending with a check for understanding. http://view.officeapps.live.com/op/view.aspx?src=http%3A%2F%2Feducation.jlab.org%2Fjsat%2Fpowerpoint%2F0708_renewable_nonrenewable.ppt Background for Teachers Student Activities This website uses a chart to list renewable and non-renewable resources. It identifies natural resource origins and the advantages and disadvantages of consuming them. http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/geography/energy_resources/energy_rev1.shtml An interactive website from Manchester University focusing on energy and the environment. Provides an overview of natural resources and how they are refined and used by consumers. An excellent introduction to natural resources. http://www.childrensuniversity.manchester.ac.uk/interactives/science/energy/renewable/ Renewable or Not? Students learn the difference between renewable and non-renewable resources and discover why sustainable use of natural resources is important. http://www.msichicago.org/fileadmin/Education/learninglabs/lab_downloads/RE_renewable_or_not.pdf Other Resources Teach students about Earth's resources with TeacherVision lessons on energy, power, and electricity (renewable and non-renewable resources). Lessons include math and science connections (calculating the cost of electricity) as well as conservation tips to improve energy efficiency and help save money. These resources are appropriate for elementary, intermediate, and high school students. http://www.teachervision.fen.com/energy-resources/teacherresources/55943.html Want to learn more about recycling and reducing waste? Click on this site's colorful maps and illustrations to explore a virtual town and pick up a few tips from the locals. http://www.epa.gov/recyclecity/ A variety of short video clips illustrating energy consumption. Can be used to spark student conversation. http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=conserving+energy+video+clip&FORM=VIRE1&adlt=strict Lichterman Nature Center Field Trips Exhibits: Buckman Water Science Trail *The TOOLBOX contains additional resources for each unit. SCS 2015-16 12 of 12