Distillation Methods - English for Chemistry & Materials Science
advertisement

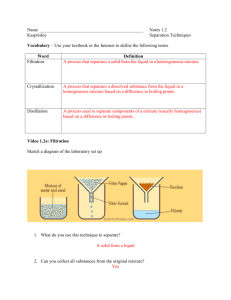
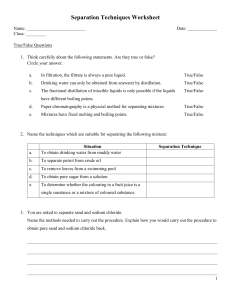
Distillation Methods Distillation is a process that separates the constituents of a mixture. The process is used to fraction crude oil into its various components, each of which has specific uses. Water distillation is used to separate impurities from saline water to make it fit for agricultural and drinking purposes. Air distillation separates the components of air, including nitrogen, oxygen and argon, which are then used for different industrial applications. Molecular, fractional, steam, regular, vacuum, extractive, azeotropic (1), are the most common distillation methods. temperature sensitive liquids can be effectively separated without degradation. The petroleum refining industry uses this distillation to separate the compounds of crude oil. 5. When separation is very difficult because the components of a mixture have almost identical volatilities, improvement can be made by adding a different component which is soluble in the mixture or which forms a constant boiling or azeotropic mixture with one or more of the original ingredients, thus permitting greater ease of separation. An example of this is the addition of benzene to an ethyl alcohol-water mixture in order to produce pure anhydrous ethyl alcohol. ………………………………………………… 1. This process is typically used to separate liquids whose boiling points differ by at least 77 degrees Fahrenheit, and to separate liquids from oils or non-volatile solids. In this process, a mixture is heated at a high temperature to produce vapors, which are then cooled, condensed and collected in a separate container. This method is used in various industries, including the medical and pharmaceutical industries, to remove pathogens from water. 2. This is a process in which a mixture is split into its constituents typically by repeatedly heating, boiling and condensing. It is used to fraction miscible liquids with different boiling points. In this method of distillation, a mixture is heated and converted into vapors, which are then cooled as they pass up a fractionating column. Each component element of the vapor converts back into a liquid at a different level of the column. This distillation method is typically used to separate the components of unrefined petroleum. 3. This process is usually used to separate materials that are temperature sensitive, such as organic and aromatic compounds. Many such compounds decompose at constant high temperatures, making regular distillation nonviable. It proves a more effective method, in which steam or water is added to the mixture to depress the boiling points of its constituent elements. This allows them to evaporate at temperatures lower than those at which they deteriorate. It is typically used to separate organic compounds from water and is widely used in petrochemical plants and petrol refineries. 4. It is a process in which a vacuum is used to extract or separate the components of a mixture at a pressure that is lower than atmospheric pressure. The lowered pressure reduces the boiling point of the mixture, typically a liquid, and its liquid components. At lowered pressure it ensures that 6. In this process, a solvent, which is usually less volatile than any of the substances being separated, is put in the downflowing liquid reflux stream near the top of the column, and is removed from the base. It modifies the vaporization characteristics of the materials to enable them to be parted more easily. 7. This high vacuum process furnishes the lowest temperature believed possible. Unstable substances which can be purified by no other means of can often be treated without harm in the molecular still. I. This process is used for making vitamin A esters, as well as mono and diglycerides of fatty acids which are used widely in the baking and cosmetic industries. By Natasha Gilani , eHow Contributor, updated: September 4, 2010. Glossary: 1.An azeotrope (pronounced /əozi.ətroʊp/ əZEE-ə-trope) is a mixture of two or more liquids in such a ratio that its composition cannot be changed by simple distillation.[1] This occurs because, when an azeotrope is boiled, the resulting vapor has the same ratio of constituents as the original mixture. 2.Volatitlity: a measure of the tendency of a substance to vaporize. It has also been defined as a measure of how readily a substance vaporizes. 3. reflux: technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. Task 1 Define or find a synonym for the terms in bold. Task 2 Name the distillation methods described in each paragraph.