Unit I Study Guide - Jones College Prep

AP Psychology: Unit I Study Guide Ms. McClory
History and Approaches to Psychology and Methods of Research Ch. 1 and 2
Directions: As you read and take notes, be sure that you cover all of the following information. If it is not in your text, be sure to ask in class.
People to Know
Wilhelm Wundt
Sigmund Freud
Terms to Know
Empiricism
Introspection
William James
John Watson
B. F. Skinner
Functionalism
Hypothesis
Theory
Operational Definition
Hindsight bias
Applied research
Basic research
Validity
Reliability
Sampling
Population
Random selection
Stratified sampling
Confounding variables
Assignment
Random assignment
Experimenter bias
Double blind procedure
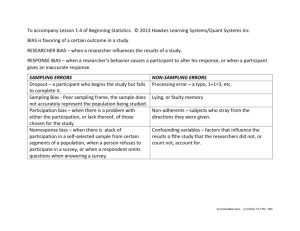
Participant Bias
Hawthorn effect
Scatter plot
Normal curve
Key Concepts
Subfields of Psychology
What are the main areas that psychologists focus upon
History
Be able to describe how the field developed
Know the people and their theories
Approaches
Behaviorism
Humanism
Biopsychology (or neuroscience)
Evolutionary (or Darwinian)
Psychoanalytic
Cognitive
Socio-cultural
Research
Goals of psychological research
Methods of research (what they are, when to use, etc.)
Use of correlational studies
Difference b/t correlation and causation
Use for experiments
Experimental Design (variables, groups, sampling)
Statistical Analysis
Difference b/t descriptive and inferential statistics
Measures of central tendency
Measures of variability
Correlation
Statistical Significance
Ethical Guidelines for Research