To accompany Lesson 1.4 of Beginning Statistics. © 2013 Hawkes
advertisement
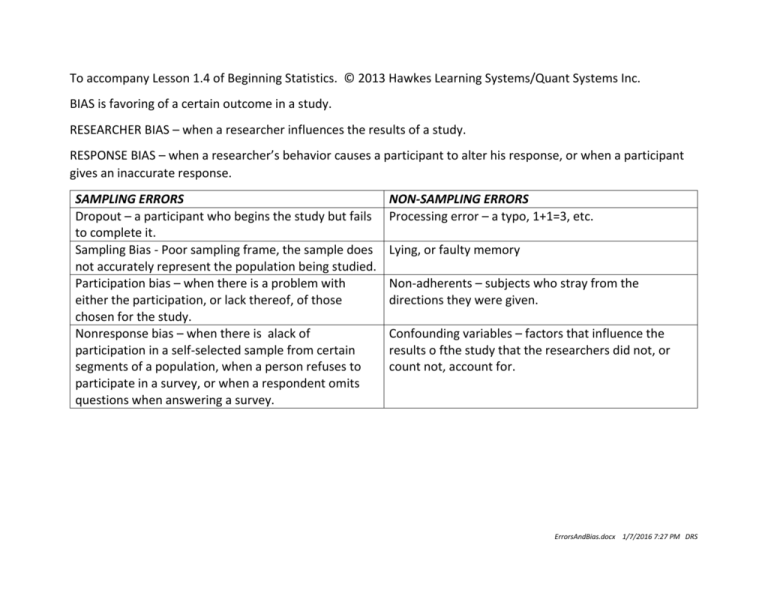
To accompany Lesson 1.4 of Beginning Statistics. © 2013 Hawkes Learning Systems/Quant Systems Inc. BIAS is favoring of a certain outcome in a study. RESEARCHER BIAS – when a researcher influences the results of a study. RESPONSE BIAS – when a researcher’s behavior causes a participant to alter his response, or when a participant gives an inaccurate response. SAMPLING ERRORS Dropout – a participant who begins the study but fails to complete it. Sampling Bias - Poor sampling frame, the sample does not accurately represent the population being studied. Participation bias – when there is a problem with either the participation, or lack thereof, of those chosen for the study. Nonresponse bias – when there is alack of participation in a self-selected sample from certain segments of a population, when a person refuses to participate in a survey, or when a respondent omits questions when answering a survey. NON-SAMPLING ERRORS Processing error – a typo, 1+1=3, etc. Lying, or faulty memory Non-adherents – subjects who stray from the directions they were given. Confounding variables – factors that influence the results o fthe study that the researchers did not, or count not, account for. ErrorsAndBias.docx 1/7/2016 7:27 PM DRS