Chapter 3 quiz student copy
advertisement

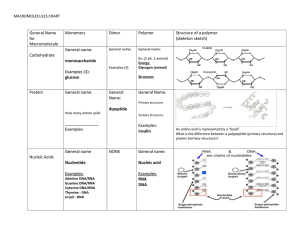
Chapter 3 Quiz: Macromolecules Name: Directions: Select the letter that best answers the question. 1. Which of the following is characteristic of proteins? a. They are insoluble in water. b. They are the structural units of glycogen. c. They possess glycosidic linkages between amino acids. d. Some function as enzymes. e. a, b, and c 2. Molecules with molecular weights greater than 1,000 daltons are usually called a. proteins. b. polymers. c. nucleic acids. d. macromolecules. e. monomers. 3. Which of the following is not a macromolecule? a. RNA b. DNA c. An enzyme d. A protein e. Salt 4. The bonds that form between the monomers in macromolecules are _______ bonds. a. hydrogen b. peptide c. disulfide d. covalent e. ionic 5. You look at the label on a container of shortening and see “hydrogenated vegetable oil.” This means that during processing the number of carbon–carbon double bonds in the oil was decreased. What is the result of decreasing the number of double bonds? a. The oil now has a lower melting point. b. The oil is now a solid at room temperature. c. There are more “kinks” in the fatty acid chains. d. The oil is now a derivative carbohydrate. e. The fatty acid is now a triglyceride. 6. The portion of a phospholipid that contains the phosphorous group has one or more electric charges. That makes this region of the molecule a. hydrophobic. b. hydrophilic. c. nonpolar. d. unsaturated. e. saturated. 7. The monomers that make up polymeric carbohydrates like starch are called a. nucleotides. b. trisaccharides. c. monosaccharides. d. nucleosides. e. fatty acids. 8. A nucleotide contains a pentose, a phosphate, and a(n) a. lipid. b. acid. c. nitrogen-containing base. d. amino acid. e. glycerol. 9. A simple sugar such as ribose with the formula C5H10O5 can be classified as a a. hexose. b. polysaccharide. c. disaccharide. d. pentose. e. lipid. 10. Two important polysaccharides made up of glucose monomers are a. guanine and cytosine. b. RNA and DNA. c. sucrose and lactose. d. cellulose and starch. e. testosterone and cortisone. 11. Which of the following monomer/polymer pairs is not correct? a. Monosaccharide/polysaccharide b. Amino acid/protein c. Triglyceride/lipid d. Nucleotide/DNA e. Nucleotide/RNA 12. Amino acids can be classified by the a. number of monosaccharides they contain. b. number of carbon–carbon double bonds in their fatty acids. c. number of peptide bonds they can form. d. number of disulfide bridges they can form. e. characteristics of their side chains. 13. During the joining of two monomers, which of the following occurs? a. A molecule of water is formed. b. A disulfide bridge is formed. c. A hydrophobic bond is formed. d. A hydrophilic bond is formed. e. An ionic bond is formed. 14. According to the base-pairing rules for nucleic acids, purines always pair with a. deoxyribose sugars. b. uracil. c. pyrimidines. d. adenine. e. guanine. 15. During the separation of two monomers, which of the following occurs? a. A molecule of water is formed. b. A disulfide bridge is formed. c. A molecule of water is used. d. A hydrophilic bond is formed. e. A glucose is used. 16. DNA and RNA contain a. pentoses. b. hexoses. c. fructoses. d. maltoses. e. amyloses. 17. The 20 different common amino acids have different a. amino groups. b. R groups. c. acid groups. d. peptide linkages. e. primary structures. 18. The primary structure of a protein is determined by its a. disulfide bridges. b. a helix structure. c. sequence of amino acids. d. branching. e. three-dimensional structure. 19. When a protein loses its three-dimensional structure and becomes nonfunctional, it is a. permanent. b. reversible. c. denatured. d. hydrolyzed. e. environmentalized. 20. A β pleated sheet organization in a polypeptide chain is an example of _______ structure. a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. quaternary e. coiled 21. The four nitrogenous bases of RNA are abbreviated as a. A, G, C, and T. b. A, G, T, and N. c. G, C, U, and N. d. A, G, U, and T. e. A, G, C, and U. 22. A peptide linkage (peptide bond) holds together two _______ molecules. a. protein b. amino acid c. sugar d. fatty acid e. phospholipid 23. In DNA, A pairs with T and G pairs with C; this is an example of a. complementary base pairing. b. a dehydration reaction. c. a reduction reaction. d. a hydrophobic reaction. e. a purine–purine reaction. 24. The double helix structure of DNA is due to a. complementary base pairings. b. purines bonding with pyrimidines. c. the phosphodiester bonds between deoxyribose and phosphate. d. hydrogen bonding of the two strands. e. ionic bonding of base pairs. 25. Spontaneous generation was disproved by a. Miller. b. Urey. c. Pasteur. d. Allan Hills. e. van der Waal.