Chapter 13 & 14 Jigsaw Topics
advertisement

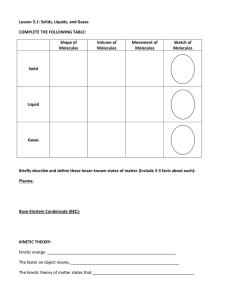
Name:________________________________ Per:___ Kinetic-Molecular Theory and Gases Jigsaw Topics – Focus Questions (for Conceptual Chemistry) Overall Unit theme/understanding: According to the Kinetic-Molecular Theory, the state of matter of a substance depends on the kinetic energy of its particles and strength of attraction between the particles. 1. Kinetic Energy and Temperature: pg 55-56, 403, 418 Define kinetic energy. Define temperature. What is temperature really measuring? Explain what determines the kinetic energy of a gas sample. If the gases in Figure 13-3 were all at the same temperature, would their motion be identical? Why or why not? 2. Kinetic Molecular Theory applied to gasses: pg 420-423 What are the postulates of the Kinetic-Molecular Theory? What are the behaviors that result from each postulate? (how do gases move/interact with each other?) How do chemists know that gases are in constant motion? 3. Boyle’s Laws: pg 431-433 Give the equation for Boyle’s Law. Explain the relationship between temperature and volume of a gas. Provide a specific, everyday example of when Boyle’s Law could be observed. 4. Charles’ Law: pg: 434-437 Give the equation for Charles’ Law. Explain the relationship between pressure and volume of a gas. Provide a specific, everyday example of when Charles’s Law could be observed. 5. Measuring Gases: pg 424 - 430 What are the measurable properties of a gas? What units is each measured in? What instruments and/or methods are used to measure each property? What is STP (in oC and atm) and why is it important to consider when we are measuring gas properties? 6. Ideal Gas Law: 441-443 Explain the formula for the ideal gas law. What does each letter represent? If V and T are held constant, and more gas molecules (n) are added, what happens to the pressure? Why? If n and V are held constant, and temperature increases, what happens to the pressure? Why? If n and T and held constant, and volume is decreased, what happens to the pressure? Why? Explain the significance of this equation for the properties of all gases.