Science – The Cell
advertisement

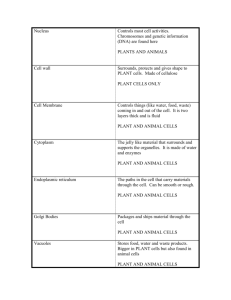
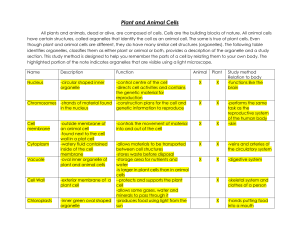
C-5 THE CELL An Ex-CELL-ent Life-building and Life-learning Experience! Team E Science Mrs. P February 2008 NAME: ____________________________________________________________________________ 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRO……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…..3 CALENDAR………………………………………………………………………………………………………4 CELL CARD DIRECTIONS ……………………………………….………………………………..…5 BOX DIRECTIONS and IDEAS………….………………………………………………………6-7 BOX RUBRICS………………………………………………………………………………………………8-9 REVIEW …………………………………..…………………………………………………………………10-12 JOURNAL #12…………………………………………………………………………………………........ 13 CELL CARD MATERIALS……………………………………………………………………14-20 2 INTRODUCTION Since we’ve had the chance to discuss where the universe and life came from as well as the basic “uh-duh’s” of the cell, we can finally get down to work and actually begin to study that building block (a.k.a. box!) that we’ve been talking about. Let’s study THE CELL! The first major questions in our cell unit are: What is the structure and function of the organelles of the cell? What are the differences between plant and animal cells? How are cells organized to make multi-cellular organisms? To accomplish an understanding of the answers to these questions we are going to… Create study cards that illustrate the structure and function of 18 major cell organelles. Create a study card that describes THREE main differences between plant and animal cells. Create a study card that diagrams how cells are organized to make multi-cellular organisms. Build our own building “box” of life models with materials that demonstrate we understand the structure and function of 18 major organelles of the cell. Do a journal that makes us think a little deeper about the structure and function of cells. Practice 2x’s for a quiz! Take a quiz! PLEASE NOTE: The following website will be a special aid in the work we do to accomplish the above tasks. Please explore it on your own…there are games, puzzles, and several interactive links that will help you become ONE WITH THE CELL (which you already kind of are because you’re made of cells!) www.cellsalive.com 3 Calendar of Events DATE ACTIVITY/ASSIGNMENT Thursday 2/7 (1) Intro to Unit, Start ID’ing organelles HW: Study ID’d organelles Friday 2/8 (2) Finish ID’ing organelles HW: Study ID’d organelles Monday 2/11 and Tuesday 2/12 (3,4) Assemble organelle cards, do extra cards (Plant vs. Animal, Multi org.) HW: Study cards, do review quiz I (due WED), final cards (due THURS) Wednesday 2/13 (1) Start planning session for boxes, Review quiz I due/go over HW: Study cards – make sure they are in “hand-in” condition for tomorrow, bring in cell box materials Thursday 2/14 (2) Collect and check cards, begin work on Boxes of Life HW: Study cards, bring in cell box materials Friday 2/15 (3) MR. GILBERT’S MOVIE DAY! Monday 2/25 – Wednesday 2/27 (4-2) Assign review quiz II (due on WED 2/27), Work on boxes (due on WED 2/27) HW: Do review quiz II (due WED), Study cards, bring in cell box materials Thursday 2/28 and Friday 2/29 (3, 4) Work on Journal #12 (due MON 3/3) and list of box organelles explanations typed up (due at END of period) HW: Study cards, do Journal #12 (due MON) Monday 3/3 (1) Review day – go over quiz Journal #12 due (share jnl 12) HW: Study cards for quiz TOMORROW! Tuesday 3/4 (2) Quiz on organelles, plant vs. animal, multi-cell org. organization Wednesday 3/5 And Thursday 3/6 (3,4) Box of Life Presentations! Begin Microscope Work (?) 4 CELL CARD DIRECTIONS STEP ONE. Make 2 general reference cards that will have pictures of the plant and animal cells on one side and the list of corresponding organelles on the other side. Pages 14-15 have the information that you will need to correctly match, cut out, and arrange on each card. These cards will look like the following pictures. FRONT BACK STEP TWO. You will make 18 organelle cards that include the name, appearance, and function of the organelles. Pages 16-20 have the information that you will need to correctly match, cut out, and arrange on each card. Use the interactive cell models on www.cellsalive.com to help you correctly match the organelle pictures and functions. Each card will look like the following pictures. FRONT BACK STEP THREE. You will make 2 “special” info cards. One will outline the three main differences between plant and animal cells. The other will outline how cells are “organized” into multi-cellular organisms. Mrs. P will work directly help you in making these cards these cards. STEP FOUR. USE your cards! Study them! Get a study partner or use them solo! Pages 10-12 of this packet contain some practice pages to help you put to work what you learn from your cards. You will also be given two taken-home practice quizzes to practice with before the actual in-class quiz. 5 Directions and Ideas for your “Building Box of Life” Project There are MANY different things you can use to represent the organelles in your “Building Box of Life.” Most of the items that you could use or make are found in your home! There is no need to go out and buy materials unless there is something special you need or something regular that you just don’t have at home! But remember, you’ve got a partner in this construction project…so between the two of you, someone has got to have the right stuff! 1. Here’s idea for your own play-doh (you can make models of organelles out of it!)… Play-doh recipe: This makes about 850g (30oz) 1 C soda (salt for baking) 1 C flour 1 C corn starch 4 t cream of tarter 2 T oil 1-3/4 C water 2. Here are some ideas for materials for cell parts…but try not to depend upon this list! Think outside of the box (i.e. the “typical way of thinking” box, silly!) 1. Cytoplasm -- play-doh (plain - approx. 260g or 8oz)* 2. Endoplasmic reticulum -- yarn or cooked spaghetti 3. Ribosomes -- pepper 4. Mitochondria -- play-doh (purple - approx. 7g)** 5. Vacuole -- plastic-bubble packing 6. Lysosome -- play-doh (red - approx. 5g) 7. Chloroplasts -- play-doh (green - approx. 10g) 8. Cell wall -- aluminum foil (approx. 12" X 7") 9. Cell membrane -- plastic wrap (approx. 12" X 16") 10. Nucleus -- play-doh (blue - approx. 20g) 11. Nuclear membrane -- plastic wrap (approx. 3"X6") 12. Chromosomes -- pencil shavings 3. Here’s a website that has pictures of student cell models! http://www.edu.pe.ca/gray/class_pages/rcfleming/cells/demos.htm 4. Why not investigate other websites? Or, even talk to your family and friends about ideas? Science is ALL about sharing your thoughts and hypotheses. SO, SHARE! (Most importantly, don’t forget that you HAVE TO share your ideas with your “cellular partner!”) IMPORTANT: Each partner needs to take responsibility for a portion of the project. To ensure this responsibility happens, it is highly suggested that one person builds the plant box and the other builds the animal box. If you have a group of three (or you’re a really enthusiastic group of two), please see Mrs. P for an alternative box project! 6 PLANNING SHEET FOR BUILDING BOX OF LIFE Organelle Cell Membrane Material(s) Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Nucleus Chromosomes/DNA Nucleolus Nuclear Membrane Rough ER Ribosomes Smooth ER Mitochondria Golgi Apparatus Vacuoles Plant Animal Lysosome Peroxisome Centrioles (not plant) Cell Wall (not animal) Chloroplasts (not animal) PARTNER(S): ___________________________________________________________________ Email/Phone#(s): _________________________________________________________________ 7 TEAMWORK RUBRIC PROJECT/LESSON: DATE: TEAM NAME: TEAM MEMBERS: GRADE and REASONING TEAMWORK Rate yourselves AS A GROUP on a scale of 1 (poor) to 5 (excellent). CHARACTERISTIC Half points are allowable. Give a reason or evidence for why you deserve the grade you have assigned to yourselves. COMMUNICATION How well did you communicate knowledge and needs with one another? COOPERATION How well did you work together to get the job done? RESPONSIBILITY Did everyone individually do their share? RESPECT Did everyone value each other’s responses and effort? TOTAL GRADE (out of 20) 8 9 Cell Organelle Summary Review Sheet DIRECTIONS: Use this sheet to organize your thoughts about each organelle’s structure and function! Organelle Picture Location Function Cell Type 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Cytoskeleton 4. Nucleus 5. Chromosomes or DNA 6. Nuclear Membrane 7. Nucleolus 8. Rough ER 9. Ribosomes 10 10. Smooth ER 11. Mitochondria 12. Golgi Body 13. Vacuole 14. Lysosome 15. Peroxisome 16. Centrioles 17. Cell Wall 18. Cholorplast 11 Plant vs. Animal Cells and Multi-cellular Organism Organization Summary Review Sheet DIRECTIONS: Use this sheet to organize your thoughts about the differences between plant and animal cells as well as how multi-cellular organisms are “organized.” Fill in the table with the information behind the THREE major organelles differences that plant cells have compared to animal cells. ORGANELLE Why plants have it and animals cells don’t Fill in the spaces between the arrows to show how cells are organized into multi-cellular organisms. 12 Journal Entry #12 Wrappin’ up The Cell February 2008 DUE ON 3/3 Now that we have explored the organelles of the cell, it is time to think a little deeper and extend some of our new cellular knowledge. This is also a great way to review for the quiz! 1) Identify which organelle or organelles that you learned about would be BEST at helping the cell deal with the following situations. Explain why you selected the organelle(s) that you did. Look to your Cell Study Cards for help! a) A plant cell has been going through the process of photosynthesis. Which organelle would be responsible for capturing the sun energy needed for the plant to make food energy? Which organelle would be responsible for breaking down the excess hydrogen peroxide that gets produced in the cell as a result of photosynthesis? b) The muscle cells in a man’s arms are being used to lift weights at the gym. What organelle would be in charge of creating the energy to make this possible? c) An animal cell is getting ready to divide and make more cells. Which organelle would help to organize and separate the genetic material for each of the cells that are going to be made? d) The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum in a cell is producing lots of protein. It packages it into vesicles that will transport the protein to another part of the cell to be processed. What organelle of the cell will receive the protein for further modifications and packaging? e) A cell needs to repair its cell membrane by replacing some of the lipids and proteins in it. Which organelle would be in charge of processing the materials for making this possible? 2) Create your OWN organelle. Think about all the organelles that you learned about and what they do for the cell. Are any of the life processes not fully covered by the organelles? Is there something special that you would like cells to be able to do? Draw your organelle. Describe where in the cell you can find it. Explain its function and why you thought that it was important that cells have this additional organelle. 3) Research ONE of the following words or topics. Write a short paragraph that explains the meaning of the word or topic you selected and its connection to our recent “learnings” about the cell. CITE WHERE YOU GOT YOUR INFORMATION FROM! Phagocytosis Autolysis How Cells Communicate The Fact that Mitochondria and Chloroplasts contain their very own DNA! The Lipid Bi-layer of the Cell Membrane…Hydrophillic vs. Hydrophobic 13 PLANT CELL ORGANELLES 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 10. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) 11. Mitochondria 3. Cytoskeleton 12. Golgi Body (w/ vesicles) 4. Nucleus 13. Vacuole 5. Chromosomes 14. Lysosome (a vesicle) 6. Nucleolus 15. Peroxisome (a vesicle) 7. Nuclear Membrane 17. Cell Wall 8. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) 9. Ribosomes 18. Chloroplasts ANIMAL CELL ORGANELLES 1. Cell Membrane 9. Ribosomes 2. Cytoplasm 10. 3. Cytoskeleton 11. Mitochondria 4. Nucleus 12. Golgi Body (w/ vesicles) 5. Chromosomes 13. Vacuoles 6. Nucleolus 14. Lysosome 7. Nuclear Membrane 15. Peroxisome 8. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) 16. Centrioles Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) 14 15 13. Vacuoles 14. Lysosome (a vesicle) 15. Peroxisome (a vesicle) 3. Cytoskeleton 16. Centrioles 4. Nucleus 17. Cell Wall 5. Chromosomes 18. Chloroplasts LIST OF ORGANELLES 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Nuclear Membrane 8. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) 9. Ribosomes 10. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) 11. Mitochondria 12. Golgi Body (w/ vesicles) 16 ORGANELLE FUNCTIONS A type of vesicle (storage and transport unit) CHEMICALLY breaks down H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) into H2O and O2 Hydrogen Peroxide is a waste product produced by some cells (e.g. plant cells produce it during “Doorway” for nucleus Controls what goes in and out of nucleus Keeps genetic material (chromosomes) in one location within the cell Made of two layers like the cell membrane Gives cell shape and support Acts as a “doorway” to the cell - allows certain materials in and out through the processes of ACTIVE TRANSPORT (transport that requires energy) and PASSIVE TRANSPORT (i.e. Control center of cell Contains genetic (i.e. hereditary) material of cell (chromosomes) that gives the cell its characteristics and tells the cell what to do PRESENT IN EUKARYOTES ONLY (prokaryotes are single-cellular organisms that photosynthesis and white blood cells produce it to destroy bacteria…notice that the breaking down of hydrogen peroxide is a chemical reaction involves the BREAKING of bonds between atoms!). DIFFUSION – transport of materials w/o energy and OSMOSIS – transport of water w/o energy) have genetic material that is NOT enclosed by a nuclear membrane) Made of lipids (fats) and proteins produced in Smooth ER – consists of TWO layers! PLANT CELLS ONLY! Extra layer of protection around plant cell Gives cell shape with the help of the big water vacuole Made of cellulose (i.e. a polysaccharide) Makes ribosomes Found inside nucleus Transports protein throughout the cell With ribosomes, it helps in making proteins for cell Proteins are molecules that help the cell function and know what to do PLANT CELLS ONLY! Organelle in plant cell that contains a green pigment/substance called chlorophyll Chlorophyll traps sun energy so that the chloroplast can change the light energy into food energy for plant Gives cell shape Helps cell to move Anchors organelles Directs the “traffic” of the cell (e.g. vesicles from Golgi body) Helps the rough ER make protein for the cell Made in the nucleolus 17 Made of DNA (i.e Deoxyribonucleic Acid) DNA contains genetic information that tells the cell how to function and what to do – i.e. the DNA is an “Information booklet” for cell The information within the DNA molecules holds the directions for how to make proteins for the cell; this information is interpreted by the ribosomes and rough ER Made of mostly water (the water part is called the cytosol) Also includes all the organelles Contains the cytoskeleton that holds organelles in place Provides cell with shape and support A type of vesicle (storage and transport unit) Breaks down waste (e.g. old organelles) and bacteria in cell Helps in making and modifying (i.e. changing the form of) lipids and proteins – especially for building and repairing the cell membrane “Powerhouse” of cell – produces the energy that the cell needs to perform all of its functions… it changes glucose (i.e. a molecule that stores the energy the organism obtains from food or sunlight) into ATP (i.e. a molecule that is immediately useable by the cell) Kidney bean-shaped – inside are many folds called cristae that allow for more glucose to be changed into ATP Stores waste, food, and water in both animal and plant cells In a plant cell there is A VERY LARGE version of this organelle in which ONLY water is stored…when it is full of water, it creates turgor pressure against the cell wall and gives plant cell shape ANIMAL CELLS ONLY! Found in the area of the cell called the centrosome Helps organize and separate chromosomes for cell division (i.e. when the cell is going to divide to make more of itself). Contains microtubules that produce the spindles (i.e. threads that organize and separate chromosomes during cell division) Plants cells do not have them, but do have a centrosome (i.e. spindles are still produced, and cell division still happens!) Modifies (i.e. changes the form of), , packages, stores, and ships off materials produced within the cell Modifying and packaging occurs in the “body” Storing and shipping occurs in the vesicles…these vesicles transport the materials throughout the cell 18 19 20