AP Bio Ch 17 The Molecular Basis of Disease This chapter is only
advertisement

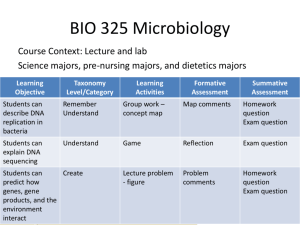
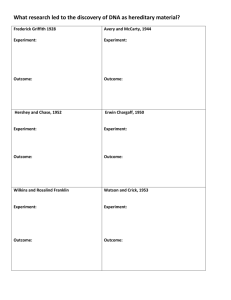
AP Bio Ch 17 The Molecular Basis of Disease This chapter is only 14 pages long and gets into a lot history every biologist needs to know about finding out DNA is the molecule of heredity and how it replicates. p.294 1. Give the proper definition of transformation –this is the term used when a plasmid is put into a bacteria. p.295 2. What kind of microscope got the shot in Figure 16-3? p.296 3.What do the 5’ ( 5 prime) and 3’ refer when talking about DNA? p.297 4.Where did Watson see Rosalind Franklin X-ray crystallography image of DNA? p.298 5. When did Watson and Crick publish their one page paper in Nature? p.299 6. What does the semi-conservative model state? p.300 7. What is an isotope? p.301 8. How often is an error made in DNA replication 9. How many origin of replication sites occur in a eukaryotic chromosome? 10. Where is the replication fork found? 11. What is DNA polymerase? 12. How fast does it work in bacteria? 13. What is a nucleoside? 14. Why are the Triphosphate monomers chemically reactive? 15. What is pyrophosphate? p.302 16. Where does the polymerase add nucleotides? 17. What are Okazaki fragments? p.303 18. What does DNA ligase do? 19. What is a primer? 20. What is primase? AP Bio Ch 17 The Molecular Basis of Disease 21. What is Helicase? 22. What does topo-isomerase do? 23. What does single-stranded binding protein do? p.305 24. Since the replication machine is stationary what is it anchored to? 25. What does extrude mean? 26. What proofreads the DNA after it is made? 27. What does proofreading have to do with cancer? 28. How many DNA repair enzymes are known in E. coli? 29. What is a nuclease? 30. What is a nucleotide excision repair? p.306 31. What causes xeroderma pigmentosum? 32. What are telomeres? 33. What can trigger cell death? p.307 34. What is telomerase? 35. Where is it found? 36. How does shortening of telomerase protect us from cancer?