Photosynthesis: Process by which plants trap the sun's energy and
advertisement

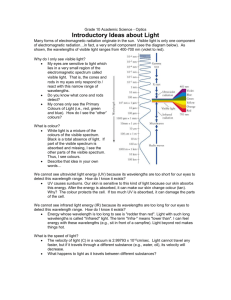
Photosynthesis: Process by which plants trap the sun’s energy and convert it into a useable chemical form (sugar) 6CO2 + 12H2O + Solar irradiation (sunshine)C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6H2O Sun’s energy: -Packaged in particles called Photons -Photons travel in waves Electromagnetic spectrum: the range of wavelengths that photons exhibit with higher energy levels having shorter wavelengths Note: visible light only represents about 40% of the electromagnetic spectrum. Pigments: Molecules that absorb light. Every pigment has a characteristic absorption spectrum: range of the spectrum that it absorbs -the actual color that a pigment appears as is due to which wavelengths of light that particular pigment will not absorb and therefor reflect Chloroplast: The organelles in photosynthesizing cells of plants where photosynthesis occurs -contain chlorophyll: the major photosynthetic pigment in plants which is located in the chloroplast note: other pigments such as carotenoids and xanthophylls are also found in the chloroplasts but in less abundance -many chloroplasts/photosynthesizing cell Structure: -outer and inner membrane -thylakoid membranes: structured in stacks called grana -stroma: fluid component Light Reactions (light dependent reactions): Sunlight activates chlorophyll which in turn splits water molecules releasing oxygen and providing electrons that fuel the electron transport system. Energy carrying molecules are reduced NADP+ NADPH…ADP is phosphorylated ADP +P ATP Calvin cycle (light independent reactions) -CO2 is concerted into sugar using the energy provided by the products of the light reactions (NADPH & ATP)