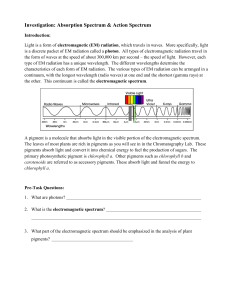
Photosynthesis ● Autotrophs such as plants, algae, and bacteria make organic compounds such as sugar by photosynthesis. ○ Photo.= process in which light energy is converted into chemical energy. ○ 6CO2+6H2O (light)→ C6H12O6 + 6O2 ● Two phases: ○ light dependent reactions (phase 1): light energy absorbed and converted to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) (energy storage molecules) ○ light independent reactions (phase 2): ATP and NADPH energy made in phase 1 are used to make glucose ■ Glucose is a simple sugar and can be used to form more complex molecules such as starch. ■ Products of photo can also be used to make lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Phase 1: Light-Dependent Reactions ● Light is captured by chloroplasts which are mainly found in leaves. ● Chloroplasts are disk shaped and contain 2 compartments: ○ thylakoid: flattened sac-like membranes arranged in stacks; light-dep. reactions occur here ■ each stack is called a grana (sing. granum) ○ stroma: fluid-filled space outside the grana; location of the light independent reactions Pigments ● Thylakoids contain the pigment chlorophyll. ○ Pigments are light absorbing colored molecules. ○ Different pigments absorb different wavelengths of light. ■ Chlorophyll is the main light-absorbing pigment. It is rich in magnesium. It absorbs most wavelengths of light except green light (which it reflects, making it appear green). ■ See Figure 6 page 223. -Ask students to interpret this figure. ○ Two types of chlorophyll: ■ Chloro a: primarily absorbs wavelengths of violet-blue light and red-orange light ■ Chloro b: primarily absorbs blue and red light (accessory pigment) ● Other pigments called accessory pigments. They allow plants to absorb other wavelengths of light on the visible light spectrum. ○ carotenoids: absorb blue and green regions of the spectrum and reflect most light in the red, yellow, and orange regions (they produce the colors of sweet potatoes and carrots) ○ xanthophylls: reflect yellow light ○ anthocyanins: absorb blue-green light and aid chloro a. Reflect reddish, blue, and violet light