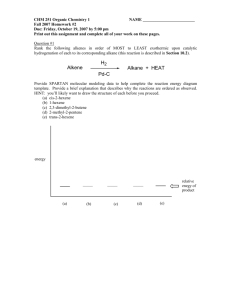
Name:
advertisement

Name: ____________________________ The following Data Table contains a list of compounds that can be classified as acids, bases, or salts. 1. Decide what type of substance each compound is and fill in the appropriate space in the column. Base your answers on the compound’s formula and on the one piece of information supplied about either its pH or its reaction with an indicator. 2. Fill in any remaining blank spaces for that compound. 3. Remember: Phenolphthalein turns colorless in acidic solutions and pink in basic solutions. Litmus turning red indicates an acid and litmus turning blue indicates a base. Compound H3PO4 found in some cola beverages Ca(OH)2 slaked lime used for treating soil CaSO4 used in plaster of Paris H2CO3 produced in human body from metabolism of fats and sugars Na3PO4 used in some water softeners H2S odor of rotten eggs H2SO3 component in acid rain Mg(OH)2 found in milk of magnesia NH4Cl used in batteries and dry cells (NH4)2SO4 nitrogen fertilizer Acid, Base, or Salt Color in Litmus red Color in Phenolphthalein Approximate pH above 7 about 7 clear no effect below 7 red blue about 7 (slightly below) clear Hydrocarbons are compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen. Hydrocarbons called alkanes are the simplest hydrocarbons. These compounds are named by using a prefix that tells the number of carbon atoms they contain and the root –ane. Using the chart below, create the correct structural formulas. Prefix Number of Carbon Atoms meth1 eth2 prop3 but4 pent5 hex6 hept7 oct8 non9 dec10 1. butane 2. methane 3. propane 4. ethane 5. hexane 6. pentane 7. octane 8. Draw a structural formula with 9 carbons. What would the name be? ____________ Count the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms and look at the shapes. Then use the charts in your book to figure out what the following structural formulas are called. Multiple Choice 1. One of the physical properties that all acids share is a. no color c. sour taste b. color d. bitter taste 2. Weak acids do not ionize to a high degree in water, so they produce few a. electrolytes c. hydrogen ions b. hydroxide ions d. carbonates 3. You should never use taste or touch to identify bases because they can be a. corrosive c. sour b. slippery d. antacids 4. Which ion do bases contain? a. OHb. H3O+ c. H+ d. NH4+ 5. Which pH would indicate a strong acidic solution? a. 7 c. 8 b. 2 d. 14 6. A compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen is called a (an) a. isomer c. carbohydrate b. hydrocarbon d. alcohol 7. The simplest aromatic hydrocarbon is a. cyclohexane b. methane c. benzene d. phenol 8. The –OH group is characteristic of an a. organic acid b. aromatic compound c. ester d. alcohol True/False (If false-change the underlined word to make the statement true). 9. Acids are often defined as proton donors. 10. Strong acids are poor electrolytes. 11. Week basis produce small numbers of ions when dissolved in water. 12. A neutral solution has a pH of 10. 13. In neutralization, an acid reacts with a base. 14. Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas are called isotopes. Answer the following with at least two complete sentences. 15. In terms of pH, explain why lemons are more acidic than bananas and why lye is more basic than ammonia. 16. Explain why water is both an acid and a base.