Chapter 7: Chemical Names and Formulas
advertisement

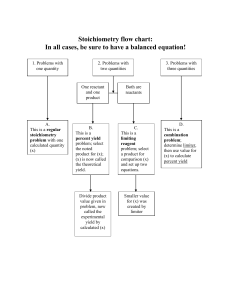
Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 - Stoichiometry Section 9.1 - 9.3 - Stoichiometry Using Chemical Equations to Calculate Moles, Mass, Limiting Reactant and Percent Yield Mole = Avogadro's Number of particles of a substance = unit equivalent to 6.02 x 1023 atoms or molecules = unit equivalent to 12.0 grams of Carbon-12 (molar-mass from the periodic table) Mole ratio = whole-number ratio of moles of substances undergoing reaction found from the coefficients from a balanced equation Molar mass = mass of one mole of a pure substance; the given atomic mass unit, mass number, or gram formula weight from the periodic table Stoichiometry = using a known ratio of moles to calculate an unknown quantity of mass or moles in a chemical reaction 3 steps to convert mass to mass in stoichiometry 1. convert given mass to moles by dividing by the molar mass 2. find mole ratio between unknown and given moles 3. convert unknown moles to mass by multiplying by molar mass Limiting reactant = the reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction; the limiting reactant determines the maximum amount of product Excess reactant = the reactant that is not completely consumed and has left over amounts in a chemical reaction; the excess reactant does not determine the product Actual yield (experimental yield) = the amount produced in the chemical reaction and is measured in the experiment (the given amount) Theoretical yield = the maximum amount of product that is produced from the limiting reactant if there is no percent error or loss of product Percent yield = [Actual yield/Theoretical yield] x 100% Percent error = /100% - Percent yield/ Mrs. Drurey - 1 of 3 - Newton South High School Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 - Stoichiometry Mole Conversion Chart miznerscience.org Mrs. Drurey - 2 of 3 - Newton South High School Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 - Stoichiometry Stoichiometry: Converting from Known Mass to Unknown Mass MASS A MOLE A MOLE B MASS B Step 1: Convert Mass A to Moles A - divide by the molar mass of A to find moles A Step 2: Convert Moles A to Moles B - multiply by the mole ratio from the coefficients from the balanced equation Mole ratio: given moles x (moles looking for) (moles to cancel out) Step 3: Convert Moles B to Mass B - multiply by the molar mass of B to find mass of B Mrs. Drurey - 3 of 3 - Newton South High School