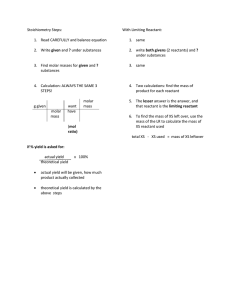
Stoichiometry flow chart
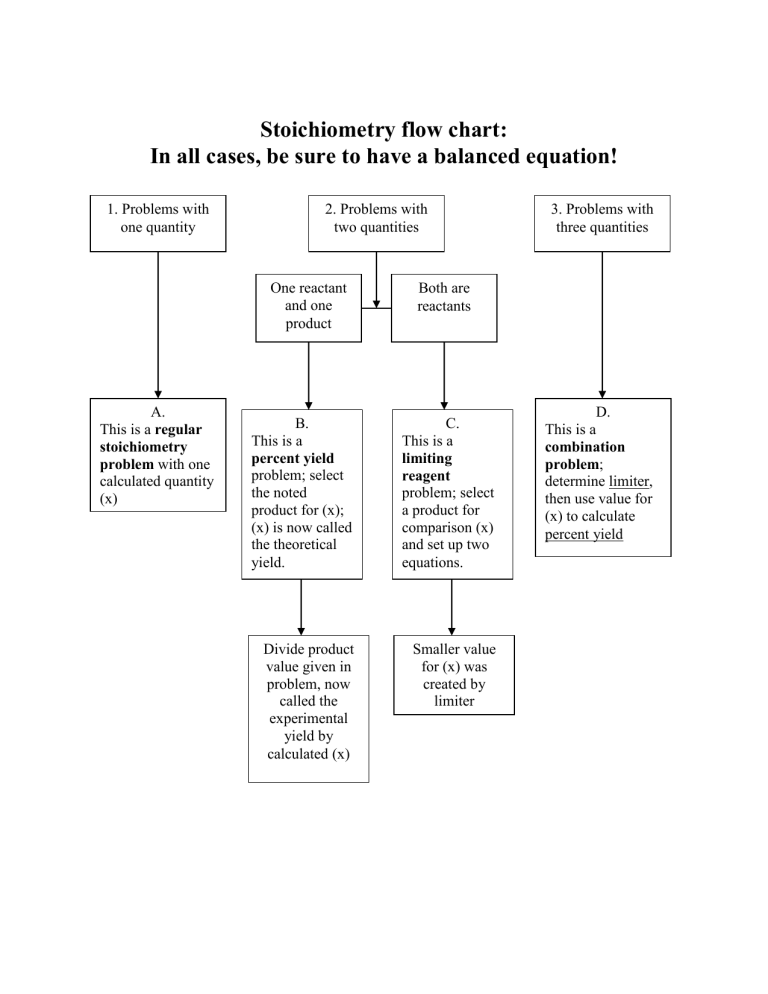
Stoichiometry flow chart:
In all cases, be sure to have a balanced equation!
1. Problems with one quantity
2. Problems with two quantities
3. Problems with three quantities
One reactant and one product
Both are reactants
A.
This is a regular stoichiometry problem with one calculated quantity
(x)
B.
This is a percent yield problem; select the noted product for (x);
(x) is now called the theoretical yield.
C.
This is a limiting reagent problem; select a product for comparison (x) and set up two equations.
This is a
D. combination problem ; determine limiter, then use value for
(x) to calculate percent yield
Divide product value given in problem, now called the experimental yield by calculated (x)
Smaller value for (x) was created by limiter
Measuring Chemical Quantities Checklist
Skill Sets to Master
Counting Atoms in Molecules and Formula Units
Write Chemical Formulas
Determining Molar Mass
Determining Molar Volume of gases @ STP
Mole Conversions on the Mole Road
Determining Percent Composition
Balancing Chemical Equations
Identifying Chemical Reaction Types
Identify LIMITING Reactant and EXCESS Reactant
Observe MOLE RATIOS using a balanced Chem Eqn
Determine Theoretical Yield
Calculate Percent Yield