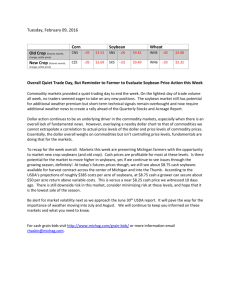
factors effecting commodities market
advertisement

CHAPTER-I INTTRODUCTION 1 COMMODITIES MARKET INTRODUCTION: Commodities Futures’ trading…! in India have a long history. The first commodity futures market appeared in 1875. But the new standardized form of trading in the Indian capital market is an attractive package for all the people who earn money through speculation by trading into FUTURES. It is a well-known fact and should be remembered that the trading in commodities through futures’ exchanges is merely, “Old wine in a new bottle”. The trading in commodities was started with the first transaction that took place between two individuals. We can relate this to the ancient method of trading i.e., BARTER SYSTEM. This method faced the initial hiccups due to the problems like: store of value, medium of exchange, deferred payment, measure of wealth etc.. This led to the invention of MONEY. As the market started to expand, the problem of scarcity piled up. The farmers/traders then felt the need to protect themselves against the fluctuations in the price for their produce. In the ancient times, the commodities traded were – the Agricultural Produce, which was exposed to higher risk i.e., the natural calamities and had to face the price uncertainty. It was certain that during the scarcity, the farmer realized higher prices and during the oversupply he had to loose his profitability. On the other hand, the trader had to pay higher price during the scarcity and vice versa. It was at this time that both joined hands and entered into a contract for the trade i.e., delivery of the produce after the harvest, for a price decided earlier. By this both had reduced the future uncertainty. One stone still remained unturned- ‘surety of honoring the contract on part from either of the parties’. This problem was settled in the year 1848, when a group of traders in CHICAGO came forward to standardize the trading. They initiated the concept of “toarrive” contract and permitted the farmers to lock in the price upfront and deliver the grain at a contracted date later. This trading was carried on a platform called CHICAGO 2 BOARD OF TRADE, one of the most popular commodities trading exchanges’ today. It was this time that the trading in commodity futures’ picked up and never looked back. Although in the 19th century only agricultural produce was traded as a futures contract, but now, the commodities of global or at least domestic importance are being traded over the commodity futures’ exchanges. This form of trading has proved useful as a device for HEDGING and SPECULATION. The commodities that are traded today are: Agro-Based Commodities… Wheat, Corn, Cotton, Oils, Oilseeds etc.. Soft Commodities…………….. Coffee, Cocoa, Sugar etc Livestock………………………. Live Cattle, Pork Bellies etc Energy………………………….. Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Gasoline etc Precious Metals……………….. Gold, Silver, Platinum etc Other Metals…………………… Nickel, Aluminum, Copper etc NEED AND IMPORTENCE OF STUDY One of the single best things you can do to further your education in trading commodities is to keep thorough records of your trades. Maintaining good records requires discipline, just like good trading. Unfortunately, many commodity traders don’t take the time to track their trading history, which can offer a wealth of information to improve their odds of success Most professional traders, and those who consistently make money from trading commodities, keep diligent records of their trading activity. The same cannot be said for the masses that consistently lose at trading commodities. Losing commodity traders are either too lazy to keep records or they can’t stomach to look at their miserable results. You have to be able to face your problems and start working on some solutions if you want to be a successful commodities trader. If you can’t look at your mistakes and put in the work necessary to learn from them, you probably shouldn’t be trading commodities. 3 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY To study about major exchanges trading in Indian commodity market. To study about participants in Indian derivative market. To understand the basics of commodity market and to discover the Emerging prospects (Gold, Copper And Silver) In the Indian commodity market. To empathize trading and settlement mechanism for commodities ( Gold, Copper And Silver ) In Indian stock exchange. To know how exactly the commodities are traded through the trading Desks and what happens in the market. To identify the working procedure of the commodity trading practices in India. To identify the perception of investors in commodities market. Study aims at understanding the governance for commodity Derivatives exchanges, traders, investors and other participants. 4 SCOPE OF THE STUDY The study mainly focuses on Indian commodity market, its history and latest developments in the country in commodities market (Gold, Copper And Silver). The study also keeps a birds-eye view on global commodity market and its development. The study vastly covered the aspects of commodity trading (Gold, Copper And Silver), clearing and Settlement mechanisms in Indian commodity exchanges. The scope of the study is limited to Indian commodity market A network of 2500 business locations spread over 500 cities across India facilitates the smooth acquisition and servicing of a large customer base. Most of our offices are connected with the corporate office in Mumbai with cutting edge networking technology. The group helps service more than a million customers, over a variety of mediums viz. online, we cannot study all the data in the organization. 5 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY The present study is conducted to provide information to the company regarding the investor perception towards commodity market. SOURCES OF DATA Primary data Data was collected in systematic manner by meeting the existing investors in commodity market & other individuals. Primary and secondary data were utilized for the purpose of the study by the researcher. The research is aimed to obtain the data mainly through primary sources. Survey method has been used to obtain information. Secondary data Secondary data was collected from companies and from commodities (Gold, Copper And Silver) trading websites. TYPE OF RESEARCH Based on the objectives of the study, the descriptive research method is used . Descriptive study is taken up when the researcher is interested in knowing the investor perception in commodities market. The conclusions are arrived at from the collected data. Statistical tools were used to analyze the data collected from the survey. Survey method A survey was conducted amongst the investors in Hyderabad and Secunderabad. The researcher personally met the investors, interviewed them and got their questionnaires filled. 6 Instrument Design In order to obtain information the researcher prepared a structured questionnaire. The researcher prepared a single questionnaire according to the need of the data from the respondent. Pre-Testing Of Questionnaire The researcher to remove questions that are of vague and ambiguity in the nature conducted the pre-testing. The samples of 10 respondents were selected and the questionnaire was pre-tested and the researcher made necessary modifications. Coding and Tabulation After the survey was conducted, the data had to be converted in to statistical or numerical form so that inference could be drawn about the sample collected. For this, every option of every question was coded into alphabets (i.e; they would be represented in alphabets). The alphabets were used to denote the option and no ranking order was used. The coded data was entered into the data sheet. Frequencies were found out for each option and thus giving us the percentage of the option usage, etc. 7 LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY The survey was confirmed to the surroundings of twin cities Hyderabad & Secundrabad. The size of sample was only 50. The investor’s response could have been biased. Time of 6 weeks was constraint for the study. Brokers can only transact futures trades if they are registered with the CFTC and the NFA. Only certain types of commodities (Gold, Copper And Silver) can be the basis for futures trading. CHAPTER-II INDUSTRY PROFILE & 8 COMPANY PROFILE INDUSTRY PROFILE 9 INDIAN FINANCIAL SERVICE SECTOR “Financial stability is crucial for sustained economic growth but this cannot be achieved without strong financial systems “.(Financial stability institute). The far-reaching changes in the Indian economy since liberalization in the early 1990s have had a deep impact on Indian financial sector. The financial has gone through a complex and sometimes painful process of restructuring capitalizing on new opportunities as well as responding to new challenges. During the last decade, there has been a broadening and deepening of financial markets. Several new instruments and products have been introduced. Existing sectors have been opened to new private players. This has given a strong impetus to the development and modernization of the financial sector. New players have adopted international best practices and modern technology to offer a more sophisticated range of financial services to corporate and retail customers. Until the early nineties, corporate financial management in India was a relatively drab and placid activity. There were not many important financial decisions to be made for the simple reason that firms were given very little freedom in the choice of key financial policies. The government regulated the price at which firms could issue equity, the rate of interest which they could offer on their bonds, and the debt equity ratio that was permissible in different industries. Moreover, most of the debt and a significant part of the equity was provided by public sector institutions. Working capital management was even more constrained with detailed regulations on how much inventory the firms could carry or how much credit they could give to their customers. Working capital was financed almost entirely by banks at interest rate laid down by the central bank. The idea that the interest rate should be related to the creditworthiness of the borrower was still heretical. Even the quantum of working capital finance was related more to the credit need of the borrower then to creditworthiness on the principle that bank credit should be used only for productive purposes. 10 THE ROLE OF THE FINANCIAL SERVICE SECTOR IN EXPANDING ECONOMIC OPPORTUNITY Financial services are fundamental to economic growth and development. Banking, saving and investment, insurance, and debt and equity financing help private citizens save money, guard against uncertainty, and build credit, while enabling businesses to start up, expand, increase efficiency, and complete in local and international markets. For the poor, these services reduce vulnerability and enable people to manage the assets available to them in ways that generates income and option-ultimately creating paths out of poverty. The financial service sector is largest in the world in terms of earnings, comprised of a wide range of businesses including merchant banks, credit card companies, stock brokerages, and insurances companies, other companies. This report focuses primarily on large domestic and multination’s commercial banks. These large firms have the expertise, reputation, and geographic reach to have significant direct impact and through engagement and example, to change the way entire markets operate. They are using increasingly deliberate strategies to expand economic opportunity through business models that serve poor individuals and SMEs as clients. They are also developing initiatives to build human and institutional capacity and using their experience and influence to shape policy frameworks in the regions in which they work. Despite their potential, to date impact of large commercial banks on expanding economic opportunity has remained limited in developing world, were a vicious cycle of insufficient information, inappropriate products, inadequate infrastructure, and inflexible regulatory environments has kept costs, and therefore prices high, limiting companies markets to clients within the top tiers of the economic pyramid. 11 Mission, members, and offices US operation SIFMA brings together the shared interests of more than 650 securities firms, banks, and asset managers. SIFMA's mission is to promote effective and efficient regulation, facilitate more open, competitive, and efficient global capital markets, champion investor education, retirement preparedness, and savings, and ensure the public’s trust in the securities industry and financial markets. SIFMA represents its members’ interests in the U.S. and in Hong Kong. It has offices in New York and Washington, D.C., and its associated firm, the Asia Securities Industry & Financial Markets Association (ASIFMA), is based in Hong Kong. In June 2009, SIFMA began a campaign to combat the “populist overreaction” against Wall Street’s role in the global financial crisis. It hired two aides who had worked for Henry Paulson when he was Treasury Secretary, to help cleanse Wall Street’s image in the eyes of average Americans. The effort is aimed at policymakers and the media worldwide, and designed to beat back public skepticism over Wall Street’s commitment to change. SIFMA is paying $85,000 a month for polling, lobbying, and public relations to counter the "lynch mob", according to an internal SIFMA memo. In internal memos about confidential meetings with top financial executives, SIFMA said that the securities industry "must be perceived as part of the solution, which will allow it to better defend against populist overreaction." In January 2010, SIFMA announced that it had hired the law firm Sidley Austin to consider filing a lawsuit challenging the Obama administration's banking levy. But an attorney familiar with the matter said: "I suspect SIFMA got out ahead of its key members." One person with a large bank said SIFMA had not consulted the bank about its position, and that it was "wildly premature" to pursue legal action. In October, 2010, CEO Tim Ryan announced the organization's opposition in the residential real estate market to a "system wide moratorium on all foreclosures," reacting to problems and pullbacks in the market by a number of SIFMA members, saying a 12 moratorium "would be catastrophic." Financial writer Felix Salmon drew attention to the position, terming it "unhelpful," detailing it as "bizarre" and "sad, ... an inchoate and unhelpful blast of opposition ... [without] constructive solutions" proposed. Political giving and lobbying "SIFMA's political action committees gave more than $1 million during the 2006 election season, putting the organization in the top 25 of all PACs. Its combined $8.5 million in spending on federal lobbying last year placed it in the top 30. The financial-services industry is the biggest corporate player in national politics. Only organized labor donates more money to candidates for federal offices." European operation SIFMA also has offices in London, though it announced in May 2009 that it would shed its European operation. The European High Yield Association (EHYA) in London is a trade association representing participants in the European high yield market. Members include banks, investors, issuers, law firms, accounting firms, financial sponsors, and other participants in the European high yield market. The European Securitisation Forum (ESF) promotes the efficient growth and continued development of securitisation throughout Europe. It advocates the positions, represents the interests, and serves the needs of its members—European securitisation market participants. Groups SIFMA has three product and customer-based groups that focus on the U.S.: Capital Markets, Private Client, and Asset Management. The Capital Markets Group focuses on the primary and secondary markets for equity and fixed income securities. Its customer focus is issuers, underwriters, traders, and institutional investors. The Private Client Group focuses on investment products sold to private clients, as well as individual investor education. The Asset Management Group focuses on investment products about 13 which asset managers provide investment advice or investment management services, and on institutional investors and hedge funds. Senior management T. Timothy Ryan, Jr., is SIFMA's CEO & President. He took the position after pulling his name from consideration for a Treasury Department international policy advisor position in April 2007, after problems were noted concerning Ryan's financial portfolio, and he refused to take certain steps demanded by the Treasury Department's ethic lawyers. SIFMA's other senior management consists of Kenneth E. Bentsen (EVP, Public Policy and Advocacy), Ileane F. Rosenthal (EVP, Global Communications & Member Engagement), Randy Snook (EVP), and Ira Hammerman (Senior Managing Director & General Counsel). In August 2008, SIFMA hired Michael Paese, former Deputy Staff Director of the Committee on Financial Services of the House of Representatives, as EVP, Global Advocacy; eight months later Paese left SIFMA to become director of government affairs at Goldman Sachs. Scott DeFife, who had reported to Paese, left SIFMA in December 2009. After the 2006 merger which created SIFMA, the organization had a co-CEO structure, with the SIA's Marc E. Lackritz and BMA's Micah S. Green filling the positions. As a 2007 report summarized it, "Lackritz [then 60] ha[d] been a friend, colleague and mentor of Green's [then 49] for two decades." However, with slower-than-hoped-for integration of the merged organization's operations, and with questions about the handling of executive loans by BMA, Green resigned abruptly that year and Lackritz assumed the role of sole CEO. Nine months later, Lackritz retired and T. Timothy Ryan was named CEO. 14 Board of directors SIFMA's Chairman of the Board is Blythe Masters (Head of Global Commodities, JPMorgan Chase), and Vice Chair is Bernard Beal (CEO of M.R. Beal & Company). Other directors include Samir Assaf (HSBC Bank plc), Shigesuki Kashiwagi (Nomura Holdings America Inc.) and Sallie Krawcheck (former Chairman & CEO, Citi Global Wealth Management), among others. Peter Madoff, brother of fraudster and "money manager" Bernard L. Madoff, and chief compliance officer and senior managing director of the Madoff investment advisor and broker dealer businesses, stepped down from the SIFMA Board of Directors in December 2008. His resignation came amid growing criticism of the Madoff firm’s links to Washington, and how those relationships may have contributed to the $50 billion Madoff fraud. The Madoff family had long-standing ties to SIFMA. Bernard Madoff sat on the board of directors of the Securities Industry Association, which merged with the Bond Market Association in 2006 to form SIFMA. Peter Madoff served two terms as a member of SIFMA’s Board of Directors. Over the years 2000-08, the two Madoff brothers personally gave $56,000 to political action committees controlled by SIFMA or its predecessor organizations in addition to dues paid to SIFMA by their firm, and tens of thousands of dollars more to sponsor SIFMA industry meetings. In addition, Bernard Madoff's niece Shana Madoff, who served as a compliance attorney at the Madoff firm, was active on the Executive Committee of SIFMA's Compliance & Legal Division, but resigned her SIFMA position shortly after her uncle's arrest. 15 Finances In 2007 SIFMA had $105 million in both revenues and expenses. SIFMA's highest-paid officers that year were Donald Kittel (then CFO), $2.1 million, Marc Lackritz (then President & CEO), $1.5 million, and Randolph Snook (SMD), $1.1 million. SIFMA's highest-paid officer in 2008 was its new President & CEO Tim Ryan (at approximately $2 million, for January-October). Ryan had been hired to replace Lackritz in January 2008, at a 43% ($600,000) higher level of compensation, for less than a full year. In related news, ironically, Ryan wrote in a USA Today editorial in August 2009 that compensation practices at financial services firms should align with long-term, not short-term, performance. SIFMA's top three highest paid officers in the fiscal year ending 31 October 2009 were CEO Tim Ryan at $2.43 million, Executive Vice President Randolph Snook at $1.04 million and General Counsel Ira Hammerman at $777,000. SIFMA received total revenue that year of $75 million, had total expenses of $82 million, and finished the year with a fund balance of $40 million 16 COMPANY PROFILE 17 COMPANY PROFILE Religare is an emerging markets financial services group with a presence across Asia, Africa, Middle East, Europe, and the Americas. In India, Religare’s largest market, the group offers a wide array of products and services including broking, insurance, asset management, lending solutions, investment banking and wealth management. With 10,000-plus employees across multiple geographies, Religare serves over a million clients, including corporate and institutions, high net worth families and individuals, and retail investors.Vision "To be the leading emerging markets financial services group driven by innovation, delivering superior value for all stakeholders globally". Religare is established in the January 30th 1984. It is one of the leading integrated financial services institutions of India, backed by a blue chip promoter pedigree and a proven track record. Religare’s businesses are broadly clubbed across 3 key verticals, the retail, institutional and the wealth spectrum, catering to a diverse and wide base of clients spread across the length and breadth of the country. Structurally, all business is operated through various subsidiaries held through the holding company Religare Enterprises Limited. The company offers a diverse bouquet of services and through it’s consolidated network reach, Religare is present in more than 1300 locations across more than 400 cities and towns. As part of its recent initiatives the group has also started expanding globally. Religare has also successfully partnered with Aegon, one of the global leaders to launch Life Insurance, Mutual Fund and Pension products in India and with Macquarie Bank, for a wealth management joint venture. The vision of the company is to build Religare as a globally trusted brand in the financial services domain and present it as the ‘Investment Gateway of India’. All employees of 18 the group relentlessly strive to provide financial care, driven by the core values of diligence and transparency Mission - To provide financial care driven by the core values of diligence & transparency Brand Essence – the Company Core essence is diligence and ethical and dynamic processes for wealth creation drive it. Brand Identity Religare is a Latin word that translates as 'to bind together'. This name has been chosen to reflect the integrated nature of the financial services the company offers. The name is intended to unite and bring together the phenomenon of money and wealth to co-exist and serve the interest of individuals and institutions, alike. Symbol The Religare name is paired with the symbol of a four-leaf clover. The four-leaf clover is used to define the rare quality of good fortune that is the aim of every financial plan. It has traditionally been considered good fortune to find a single four leaf clover considering that statistically one may need to search through over 10,000 three-leaf clovers to even find one four leaf clover. The first leaf of the clover represents Hope. The aspirations to succeed. The dream of becoming. Of new possibilities. It is the beginning of every step and the foundation on which a person reaches for the stars. The second leaf of the clover represents Trust. The ability to place one’s own faith in another. To have a relationship as partners in a team. To accomplish a given goal with the balance that brings satisfaction to all, not in the binding, but in the bond that is built. The third leaf of the clover represents Care. The secret ingredient that is the cement in every relationship. The truth of feeling that underlines sincerity and the 19 triumph of diligence in every aspect. From it springs true warmth of service and the ability to adapt to evolving environments with consideration to all. The fourth and final leaf of the clover represents Good Fortune. Signifying that rare ability to meld opportunity and planning with circumstance to generate those often looked for remunerative moments of success. Hope. Trust. Care. Good Fortune. All elements perfectly combine in the emblematic and rare, four-leaf clover to visually symbolize the values that bind together and form the core of the Religare vision. Top Management Team Mr. Sunil Godhwani - CEO & Managing Director, Religare Enterprises Limited Mr. Shachindra Nath - Group Chief Operating Officer, Religare Enterprises Limited Mr. Anil Saxena- Group Chief Finance Officer, Religare Enterprises Limited Board of Directors - Religare Enterprises Limited Mr. Malvinder Mohan Singh - Chairman (Non Executive) Mr. Sunil Godhwani - CEO & Managing Director Mr. Shivinder Mohan Singh - Non Executive Director Mr. Harpal Singh - Non Executive Director Mr.Deepak Ramchand Sabnani - Independent Director Mr.Padam Bahl - Independent Director Mr. Baldev Singh Johal - Independent Director Mr. R. K. Shetty - Alternate to Mr. J. W. Balani Capt.G.P.S.Bhalla - Alternate to Mr. Deepak Sabnani 20 Awards & Accolades Religare Finvest Limited has been awarded the Finnoviti 2012 award in the “Innovation in Process” category. Religare Securities Limited has been awarded the "Best Investor Education & Category Enhancement – Currency Broker" at the Bloomberg UTV Financial Leadership Awards. Religare Commodities Limited has been awarded the "Best Commodity Broker" at the Bloomberg UTV Financial Leadership Awards. Religare Broking TVC (archery creative) won Silver Abby in the Sound and Design craft category at Goafest 2011. Religare Capital Markets Limited has been awarded the coveted Starmine award for the 'Best Brokerage Research House'. Religare Commodities Ltd has been awarded the 'The Best Commodity Broker of the year' at the Bloomberg UTV's financial Leadership awards. Religare Enterprises Ltd presented the the Best Retail Marketing Campaign of the Year 2010 at Asia Retail Congress. Religare Enterprises Ltd received the coveted Master Brand Award for 2010 and Best Marketing Campaign of the year at World Brand Congress 2010. RELIGARE SPECTUM 1. Retail spectrum Equity Trading Commodities Trading Online Investment Portal Personal Financial Services Personal Credit 21 2. Wealth Spectrum Wealth Advisory Portfolio Management Services Arts Initiative Priority Client Equity Services 3. Institutional Spectrum Institutional Broking Services Investment Banking Corporate Finance Insurance Advisory RETAIL SPECTRUM Equity Trading Trading in Equities with Religare truly empowers you for your investment needs. A highly process driven, diligent approach backed by powerful Research & Analytics and one of the “best in class” dealing rooms ensures that you have a superlative experience. Further, Religare also has one of the largest retail networks, with its presence in more than 1,217 locations across more than 392 towns & cities. This means, you can walk into any of these branches and connect toreligare’shighly skilled and dedicated relationship managers to get the best services. You could also choose to enjoy the freedom to execute your own trades through Religare’s online mechanism 22 Commodities Trading Religare Commodities Limited (RCL) was initiated to spearhead Exchange based Commodity Trading. As a member of NCDEX, MCX and NMCE, RCL is a trade facilitator providing the platform to trade in commodities. Grounded in the Religare philosophy, highly skilled and dedicated professionals strive to offer the client best investment solutions across the country. Online Investment Investing online will never be the same again withreligare’s360 degree portal www.religareonline.com Now you can not just invest online in Equities, IPOs, Mutual Funds, Commodities and much more but, also get TRADE REWARDS each time you invest. Personal Financial Services Religare has recently entered into personal financial advisory services. It caters to the financial needs of individuals by advising them on various financial plans. Religare’s Personal financial advisors, also called financial planners or financial consultants, use their knowledge of investments, tax laws, and insurance to recommend financial options to individuals in accordance with the individual’s short-term and long-term goals. Some of the issues that planners address are general investments, retirement and tax planning. Product offerings Mutual Funds Insurance - Life & Non - Life Bonds Deposits IPO’s Small Savings Instruments 23 PHILOSOPHY Define… Refine…. Achieve At Religare The Company believes “Our clients are people, not accounts” hence successful investment management relationship begins with a clear understanding of each client’s specific needs, concerns and long term objectives. Religare’s investment philosophy applies a disciplined approach to building a customized strategy designed to meet your individual financial goals and tolerance for risk. PROCESS The Religare Edge Pan India foot print Dedicated team of trained and skilled advisors Strong pedigree driven by diligent processes and ethical business practices Wide & varied platter of products & services to choose from Backed by strong & Credible research 24 Their Process WEALTH SPECTRUM Wealth Management @ Religare To provide investment advisory and execution services To work hand in hand with clients to identify and analyze their long-term goals, risk tolerance and existing asset base To Utilize Religare’s full-suite platform with an open architecture along with a fully focused client centric approach to offer customized solutions for clients Supported by dedicated team of highly skilled and qualified wealth managers and research professionals. Critical Steps in Religare’s Client Centric Operating Process Risk Profiling Research & Asset Allocation Product Recommendations Review & Rebalancing 25 International Advisory Funds Management Services (AFMS) - A new horizon for international investments Religare’s wealth clients is an opportunity to invest in international financial instruments (currently limited to the US). Equities, Mutual Funds and Debts are some the key instruments available and the clients have the option to choose from various asset allocation modules. Portfolio Management Service Religare offers PMS to address varying investment preferences. As a focused service, PMS pays attention to details, and portfolios are customized to suit the unique requirements of investors. Religare PMS currently extends five portfolio management schemes - Panther, Tortoise, Elephant, Caterpillar and Leo. Each scheme is designed keeping in mind the varying tastes, objectives and risk tolerance of Religare’s investors Investment Philosophy We believe that Religare’s investors are better served by a disciplined investment approach, which combines an understanding of the goals and objectives of the investor with a fine tuned strategy backed by research. Stock specific selection procedure based on fundamental research for making sound investment decisions. Focus on minimizing investment risk by following rigorous valuation disciplines. Capital preservation. Selling discipline and use of Derivatives to control volatility. Overall to enhance absolute return for investors. 26 Schemes Panther The Panther portfolio aims to achieve higher returns by taking aggressive positions across sectors and market capitalization. It is suitable for the “High Risk High Return” investor with a strategy to invest across sectors and take advantage of various market conditions. Tortoise The Tortoise portfolio aims to achieve growth in the portfolio value over a period of time by way of careful and judicious investment in fundamentally sound companies having good prospects. The scheme is suitable for the “Medium Risk Medium Return” investor with a strategy to invest in companies, which have consistency in earnings, growth and financial performance. Elephant The Elephant portfolio aims to generate steady returns over a longer period by investing in Securities selected only from BSE 100 and NSE 100 index. This plan is suitable for the “Low Risk Low Return” investor with a strategy to invest in blue chip companies, as these companies have steady performance and reduce liquidity risk in the market. Caterpillar The Caterpillar portfolio aims to achieve capital appreciation over a long period of time by investing in a diversified portfolio. This scheme is suitable for investors with a highrisk appetite. The investment strategy would be to invest in scrips which are poised to get a re-rating either because of change in business, potential fancy for a particular sector in the coming years/months, business diversification leading to a better operating performance, stocks in their early stages of an upturn or for those which are in sectors currently ignored by the market. 27 Leo Leo is aimed at retail customers and structured to provide medium to long-term capital appreciation by investing in stocks across the market capitalization range. This scheme is a mix of moderate and aggressive investment strategies. Its aim is to have a balanced portfolio comprising selected investments from both Tortoise and Panther. Exposure to Derivatives is taken within permissible regulatory limits. The Religare Edge We serve you with a diligent, transparent & process driven approach and ensure that your money gets the care it deserves. PMS brought to you by Religare with its solid reputation of an ethical and scientific approach to financial management. While The Company offers you the services of a Dedicated Relationship Manager who is at your service 24x7, The Company do not depend on individual expertise alone. For you, this means lower risk, higher dependability and unhindered continuity. Moreover, you are not limited by a particular individual’s investment style. The company ensures that a part of the broking at Religare Portfolio Management Services is through external broking houses. This means that your portfolio is not churned needlessly. Using more broking firms gives us access to a larger number of reports and analysis, enabling us to make better, more informed decisions. Furthermore, your portfolio is customized to suit your investment objectives. Religare Portfolio Management Services gives you daily updates on your investment. You can pinpoint where your money is being invested, 24x7, instead of waiting till the end of the month to keep track. No charge till you profit*.So sure are The company of religare’s approach to Portfolio Management that The company do not charge you for Religare’s services, until your investments start showing profit. With customized investment options Religare Portfolio Management Services invites you to invest across five broad portfolios to suit your investment needs 28 Institutional Broking Services The mission of this division is to institutionalize and implement a process driven approach to cater to the needs of leading corporate houses and institutions. The division would like to be seen as a one-stop investment gateway and knowledge repository for its clients servicing their unique and sophisticated needs. The division is structured as a separate SBU and is housed out of Mumbai, manned by a small yet fleet footed and extremely skilled group of top-notch professionals drawn from the best in the industry. The key highlights of Religare’s service platter are: Highly skilled, dedicated dealing, research and sales teams Dealing capabilities on the NSE, BSE and in the cash and derivatives segment In-depth, detailed and insightful coverage of more than 60 stocks across diverse sectors. The sectors covered are FMCG, Hotels, Media, Pharma, Auto, Cement, Steel pipes, Logistics, Telecom, Construction and much more. Company’s Current clientele includes some major domestic mutual funds, insurance companies, banks and FII’s We provide innovative, integrated and best-fit solutions to Religare’s corporate customers. It is Religare’s continuous endeavor to provide value enhancement through diverse financial solutions on an on-going basis, through offerings like corporate debt, private equity, IPO, ECB, FCCB, GDR/ADR etc. Religare's Investment Banking Division offers the following services: Corporate Finance It focuses on finding partners for Religare’s clients, who not only help in adding value, but also improve the future valuation of the organization. The company specializes in structured financing and in providing advisory services related to financial planning, modeling and advising on financial requirements. 29 Placement of Debt Syndication of Domestic Loan / Foreign Currency Loan Securitisation Debt Swap & Loan Restructuring Short Term Corporate Debt Working Capital (Cash Credit & Short term Loan) Capital Market Instruments Overseas Acquisition Placement of Equity (Private Equity) Both for listed and unlisted companies Merchant Banking IPO/FPO/RIGHTS Mergers & Acquisitions Corporate Advisory Services ADR/GDR/FCCB Buy Back Of Shares 30 Service Offerings Research Services We at Religare believe in providing independent research for clients to make investment decisions, with strict emphasis on self-regulation, avoiding possible conflict of interest in objectivity. Varied research reports are prepared on different categories of Equities like Fundamental research Technical research Daily reports Intraday trading tech calls Intraday Derivative call Directional F&O calls 31 Structured products Index Arbitrage – Arbitraging between Index (NIFTY) Futures and its constituents (Underlying Stock Futures) Volatility Trading – Arbitrage between volatilities i.e. between implied volatility of Options and forecasted volatility of underlying stock futures. Financial Data Historically, we conducted business as separate companies. Their business was carried on by Fortis. Securities Limited, Fortis Comdex Limited and Fortis Finvest Limited, some of which were subsidiaries of certain of our Promoter Group companies. In order to integrate our financial services operations under the Religare name, the Company acquired a controlling stake in Fortis Securities Limited, Fortis Comdex Limited and Fortis Finvest Limited and subsequently, acquired a 100% stake in these entities and in Religare Insurance Broking Limited and Religare Venture Capital Private Limited. These entities are now our Company’s subsidiaries. For further details regarding our acquisitions and subsidiaries, see the sectionistory and Certain Corporate Matters” We have set forth in this Draft Red Herring Prospectus the following financial statements: · Stand-alone financial statements of Religare Enterprises Limited for Fiscal 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006 and 2007 prepared in accordance with Indian GAAP and restated in accordance with SEBI Guidelines; 32 · Stand-alone financial statements of Religare Securities Limited for Fiscal 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006 and 2007 prepared in accordance with Indian GAAP and restated in accordance with SEBI Guidelines; · Stand-alone financial statements of Religare Finvest Limited for Fiscal 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006 and 2007 prepared in accordance with Indian GAAP and restated in accordance with SEBI Guidelines; · Stand-alone financial statements of Religare Commodities Limited for Fiscal 2004, 2005, 2006 and 2007 prepared in accordance with Indian GAAP and restated in accordance with SEBI Guidelines; · Stand-alone financial statements of Religare Insurance Broking Limited for Fiscal 2006 and 2007, Prepared in accordance with Indian GAAP and restated in accordance with SEBI Guidelines. Currency of Presentation All references to “Rupees” or “Rs.” or “INR” are to Indian Rupees, the official currency of the Republic of India. All references to “$”, “US$”, “USD”, “U.S. $”, “U.S. Dollar(s)” or “U.S. Dollar(s)” are to United States Dollars, the official currency of the United States of America. This Draft Red Herring Prospectus contains translations of certain U.S. Dollar and other currency amounts into Indian Rupees (and certain Indian Rupee amounts into U.S. Dollars and other currency amounts). These have been presented solely to comply with the requirements of Clause 6.9.7.1 of the SEBI 33 Guidelines. These translations should not be construed as a representation that such Indian Rupee or U.S.Dollar or other amounts could have been, or could be, converted into Indian Rupees, at any particular rate, or at all. Unless otherwise specified, all currency translations provided herein have been made based on the exchange rates specified at www.oanda.com, a currency web site. Industry and Market Data Unless stated otherwise, industry data used throughout this Draft Red Herring Prospectus has been obtained from industry publications. Industry publications generally state that the information contained in those publications has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable but that their accuracy and completeness are not guaranteed and their reliability cannot be assured. Although the Company believes that the industry data used in this Draft Red Herring Prospectus is reliable, it has not been verified by any independent source. Further, the extent to which the market data presented in this Draft Red Herring Prospectus is meaningful depends on the reader’s familiarity with and understanding of the methodologies used in compiling such data and methodologies and assumptions may vary widely among different industry sources. INTERNAL RISK FACTORS 1. There are certain criminal proceedings against one of our Promoters and Directors. Mr. Malvinder Mohan Singh, our Promoter and Director, is involved in a criminal proceeding wherein a Mr. Tarsem Lal has claimed that Mr. Singh and others have dishonestly received Rs. 0.40 million from him. The High Court of Punjab and Haryana has stayed the proceedings before the concerned judicial authority. The defendants have filed a petition in the High Court of Punjab and Haryana to quash the complaint. The matter is currently pending. For further details, see the section Titled “Outstanding Litigation and Material Developments” beginning on page 377. 34 2. We have been in the past and may in the future be barred by securities regulators from dealing in the securities of certain Indian companies. From time to time, we are subject to SEBI investigations or other regulatory scrutiny in connection with our securities broking business. Typically, our equity broking business involves trading on national stock exchanges. Our clients use our terminals to trade on these stock exchanges and may engage in activities that result in price manipulation of the securities in which they trade. While we believe that our business is conducted in accordance with applicable regulations and market conduct norms, we cannot control every trading activity of our clients apart from implementing the prescribed “Know Your Client” norms. Share price manipulation by our clients may result in the SEBI or other regulatory authority commencing investigations or imposing sanctions on us. On January 17, 2007, the SEBI barred us along with five other day-traders from dealing in the securities of Nissan Copper Limited (“Nissan Copper”). This prohibition has been imposed on us as an interim measure pending SEBI investigations into allegations that we and other entities may have Manipulated Nissan Copper’s share price following its listing on the BSE and the NSE in December 2006. SEBI has not currently concluded that we and other barred day-traders have manipulated Nissan Copper’s share price but the role played by each of us in trading Nissan’s shares will be examined during the investigation. In the matter of Ind Tra Deco Limited, the SEBI observed a sharp increase in price and trading volume in the scrip of Ind Tra Deco Limited and issued an interim order, dated October 5, 2005, restraining RSL (along with other stockbrokers) and the promoters and directors of Ind Tra Deco Limited from buying, selling or dealing in the securities of Ind Tra Deco Limited, directly or indirectly, from October 5, 2005 until the receipt of further orders. Subsequently, the SEBI confirmed its interim order on June 20, 2006. The SEBI in the matters of IFSL Limited, Mega Corporation Limited, Karuna Cables Limited and Millennium Cybertech Limited, issued orders restraining RSL, among other stock brokers, from buying, selling or dealing in the shares of the companies mentioned 35 above, directly or indirectly, on behalf of certain promoters, directors and clients specified by the SEBI from the date of the respective orders until the receipt of further orders. SEBI is also investigating trading in the shares of Vijay Textile Limited, and has directed RSL to explain its reasons for entering into transactions. In these shares on behalf of certain clients, which allegedly resulted in artificial increases in the Vijay Textiles’ share price? The SEBI has also directed RSL to provide reasons for having undertaken certain transactions on behalf of its clients. The BSE, the NSE and the NSCCL have, in the period from April 2004 till date, issued various letters and show cause notices against RSL. An aggregate penalty/ fine of approximately Rs. 3.15 million has been imposed upon RSL in these matters. In addition, the National Securities Depositories Limited has levied penalties aggregating to Rs. 0.11 million on RSL. We intend to cooperate fully with all SEBI, stock exchange and other regulatory investigations and respond promptly to any notices. The outcome of any such investigations cannot be predicted and could result in our being censured, fined, deregistered, suspended or disqualified from dealing in the securities market, including as an underwriter or an asset management company. Any such action would restrict our trading activities and growth plans, severely impair our equity brokerage business, harm our reputation and materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. For details regarding other legal proceedings to which we are a party, see the section titled “Outstanding Litigation and Material Developments”. SUMMARY OF OUR BUSINESS, STRENGTHS AND STRATEGY We are a financial services company in India, offering a wide range of financial products and services targeted at retail investors, high net worth individuals and corporate and institutional clients. We are promoted by the promotes of Ranbaxy Laboratories Limited. We operate from six regional offices and 25 sub-regional offices and have a presence in 330 cities and towns controlling 979 locations managed by us and our Business Associates all over India, as well as a representative office in London. While the majority 36 of our offices provide the full complement of our services, we also have dedicated offices for our investment banking, institutional brokerage, portfolio management services and priority client services. Religare Enterprises Limited is the holding company for our subsidiaries. Our principal subsidiaries include: Retail Spectrum covers equity brokerage services, commodity brokerage services, personal financial services (financial planning for the retail investor, including the distribution of mutual funds, savings products, life insurance and initial public offerings (“IPOs”) and personal credit (personal loans services (“PLS”) and loans against shares (“LAS”). Historically, the services offered in this spectrum have been the most substantial part of our business. Our Retail Spectrum services in India are being offered through a network of 979 business locations spread across 330 cities and towns and also through our online platform, www.religareonline.com,which is being developed as an integrated portal to offer financial and other services. Our business locations include intermediaries, or our “Business Associates”, who deliver a standard quality of service offering on the basis of a pre-determined revenue sharing ratio for the business generated through them. Our Retail Spectrum focuses on clients who keep less than Rs. 2.5 million on a continuing basis, in the form of either equity trading account margin, mutual fund investment, portfolio management investments or insurance premiums paid up. We have also increased our local commodity locations (or “mandis”) to 42 as of March 31, 2007 in order to expand our retail commodity brokerage services. Wealth Spectrum Covers products and services which are geared to service high net worth individuals and Provide wealth advisory services (on an asset allocation model), PMS (discretionary equity investments), priority client equity services (non-discretionary equity trading services), art initiatives (an art fund which we intend shortly to launch as an investment diversification product) and international equity investment advisory services. We have 37 entered into an exclusive arrangement with Wall Street Electronics, Inc., a New York broker dealer, to give Indian clients access through us to U.S. markets. Our Wealth Spectrum focuses on clients who keep at least Rs. 2.5 million on a continuing basis or more in the form of equity trading account margins, mutual fund investments, portfolio management investment or insurance premiums paid up. Institutional Spectrum Covers products and services which cater under one service offering to corporate and institutional clients, including domestic mutual funds, FIIs, banks and corporate customers. The Institutional Spectrum provides services to the institutional investor community through institutional brokerage and RISK FACTOR · This is a public issue of 11,364,152 Equity Shares for cash at a price of Rs. per Equity Share including a share premium of Rs. per Equity Share aggregating to Rs. million. The Issue would constitute 15% of the post Issue paid-up capital of our Company. Our Company is exploring the possibility of a Pre-IPO Placement. If the Pre-IPO Placement is completed, the number of Equity Shares issued pursuant to the Pre-IPO Placement, will be reduced from the Issue, subject to a minimum Issue size of 10% of the post-Issue share capital. · In terms of Rule 19 (2) (b) of the SCRR, this being an issue for less than 25% of the post–Issue capital, the Issue is being made through the 100% Book Building Process wherein at least 60% of the Issue will be allocated on a proportionate basis to Qualified Institutional Buyers (“QIBs”), out of which 5% shall be available for allocation on a proportionate basis to Mutual Funds only. The remainder shall be available for allocation on a proportionate basis to QIBs and Mutual Funds, subject to valid Bids being received from them at or above the Issue Price. If at least 60% of the Issue cannot be allocated to QIBs, then the entire application money will be refunded forthwith. 38 Further, up to 10% of the Issue will be available for allocation on a proportionate basis to Non-Institutional Bidders and up to 30% of the Issue will be available for allocation on a proportionate basis to Retail Individual Bidders, subject to valid Bids being received at or above the Issue Price. · Under-subscription, if any, in the Non-Institutional Portion and Retail Individual Portion would be met with spill over from other categories at the sole discretion of our Company in consultation with the BRLMs. For more information, see the section titled “Issue Procedure - Basis of Allotment” beginning on page 444. · The average cost of acquisition of equity shares (on ‘first in first out’ basis) by each of our Promoters, Mr. Malvinder Mohan Singh and Mr. Shivinder Mohan Singh is Rs. 17.33. For detail see the section titled “Capital Structure” beginning on page 24. The average cost of acquisition of Equity Shares by our Promoters has been calculated by taking the average of the amounts paid by them to acquire the Equity Shares currently held by them. · The net worth of our Company, on a consolidated basis, is Rs. 3,209.88 million as at March 31, 2007, respectively, as per restated consolidated financial statements of our Company under Indian GAAP in the section titled “Financial Statements” beginning on page 132. · The net asset value/book value per Equity Share of Rs. 10 each was Rs. 49.85 as at March 31, 2007, as per restated consolidated financial statements of our Company included in this Draft Red Herring Prospectus. For further information, see the section titled “Capital Structure” beginning on page 24. · Our Promoters, Directors and key managerial personnel are interested in our Company to the extent of remuneration and the Equity Shares held by them or their relatives and associates or held by the companies, firms and trusts in which they are interested as directors, member, partner and/or trustee and to the extent of the benefits arising out of such shareholding, if any, in our Company. For further details, see the sections titled “Capital Structure”, “Our Promoters and Promoter Group” and “Our Management” beginning on pages 24, 105 and 92, respectively. 39 · Other ventures promoted by our Promoters are interested to the extent of their shareholding in our Company. For details, see the section titled “Capital Structure” · Certain of our Promoter Group entities are engaged in similar businesses as ours, resulting in a conflict of interest with respect to our business strategies. For further details, see the sections titled “Risk Factors” and “Our Promoters and Promoter Group” beginning on pages xii and 105, respectively. · Except as disclosed in the section titled “Capital Structure” beginning on page 24, we have not issued any Equity Shares for consideration other than cash. Industry Industry : Group : ISIN No : Finance - General Religare INE621H01010 BSE Code : NSE Code : Market Lot : 532915 RELIGARE Book Closure : Market Cap : Face 1 Value : 11/08/2010 Rs. 6,558.77 Cr. Rs. 10.00 Registered & Corporate Office Registrar & Share Transfer Agent D3, P3B, District Centre, Saket, New Delhi, D3, P3B, District Centre, Saket, Delhi - 110017 New Delhi, Delhi - 110017 Tel : +91 11 39125000 Tel : +91 11 39125000 Fax : +91 11 39126050 Fax : +91 11 39126050 Email : info@religare.in Email : info@religare.in Website: www.religare.in 40 CHAPTER-III LITERATURE REVIEW 41 INTRODUCTION Until 1990, the Gold Control Act forbade the private holding of gold bars in India. There was physical investment in smuggled ten tola bars, but it was limited and often amounted to keeping a few bars ready to be made into jewellery for a family wedding. Gold investment essentially was in 22 carat jewellery. Reserve Bank of India Since 1990, investment in small bars, both imported ten tolas and locally-made small bars, which have proliferated from local refineries, has increased substantially. GFMS estimate that investment has exceeded 100 tonnes (3.2 million oz) in some years, although it is hard to segregate true investment from stocks held by the 16,000 or more gold dealers spread across India. Certainly gold has been used to conceal wealth, especially during the mid-1990s, when the local rupee price increased steadily. It was also augmented in 1998 when over 40 tonnes (1.3 million oz) of gold from bonds originally issued by the Reserve Bank of India were restituted to the public. In the cities, however, gold is having to compete with the stock market, investment in internet industries, and a wide range of consumer goods. In the rural areas 22 carat jewellery remains the basic investment. The Gold Deposit Scheme The government announced a new initiative in its 1999/2000 budget to tap the hoard of private gold in India by permitting commercial banks to take gold deposits of bars, coins or jewellery against payment of interest. Interest levels can be set by each bank, and deposits must be for three to seven years. Interest and any capital gains on the gold will be exempt from tax. The banks can lend the gold to local fabricators or sell it in the 42 Indian market or to local banks. However, the depositor has to declare the origin of the gold, so that metal bought illegally to hide wealth cannot be deposited. The State Bank of India was the first to accept deposits. To date, the amount of gold collected under this scheme (less than 10 tonnes or 0.32 million oz) has fallen well short of the 100 tonnes (3.2 million oz) that was mentioned when it was launched. The introduction of a modern gold market in India: 1990 Abolition of the long-standing Gold Control Act, which had forbidden the holding of 'primary' or bar gold except by authorised dealers and goldsmiths and sought to limit jewellery holdings of families. Imports were then permitted in three stages. 1992 Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) on a visit to India were each allowed to bring in up to 5 kilos (160.7 oz) on payment of a small duty of six per cent. This allocation was raised to 10 kilos in 1997. 1994 Gold dealers could bid for a Special Import Licence (SIL) which was issued for a variety of luxury imports. 1997 Open General Licence (OGL) was introduced, paving the way for substantial direct imports by local banks from the international market, thus partly eliminating the regional supplies from Dubai, Singapore and Hong Kong. The OGL system has also largely eclipsed imports by NRIs and SILs. Additionally, significant temporary imports are permitted under an Export Replenishment scheme for jewellery manufacturers working for export in designated special zones. In 2001 unofficial imports fell because of a reduction in import duties, pushing down the 43 local premium and making smuggling less profitable. Ten tola bars are still the preferred form of gold in India, accounting for 95% of imports. Precious Metal bulls will tell you to buy the dips. This means, wait for the price to temporarily deflate, and then purchase your position. It is a way to maximize dollars for gold and silver purchased while maintaining a steady buying program in that metal. The same concept could be used for any fund or stock, as well. This morning I woke to find gold and silver had tumbled. This doesn't surprise me anymore because gold and silver have become hotter markets, and there will be more speculation in them. As I wrote in Mr. Market Speaks: Flight to Safety, the market is slowing moving away from long term debt, looking for safety of principal and inflation protection. Gold and silver markets have benefited from this movement. Gold has steadily been moving relatively sideways the last two days, as seen in the following Kitco chart. But also notice the sharp drop off on Jan 20th at approximately 8am. Silver looked exactly the same. The sharp downward move happened about the same time. So I took a look at a 5 minute gold chart and found a 15 minute sharp drop, which I circled in red. I have written before about how sharp, quick movements in liquid markets don't signal normal price action. Even on bad news, liquid markets take time to react and respond because they are traded by people. And people take time to make decisions on the overall balance of the news in a given market in a given time frame. So I decided to take a look at what the news was in the precious metals market. CNBC didn't have much. 44 On gold, Bloomberg Businessweek had a piece on everyone getting out of gold. Definitely bearish. The Street agreed with that assessment, commenting that interest rate hikes in Brazil and buying of US Dollars weakened gold demand domestically. But the article also notes that China continues to buy gold in Brazil. The Wall Street Journal reports gold weakness on improving economic conditions. Bloomberg had a piece about silver profit taking potentially lowering silver 20%. Definitely bearish and timely. I also found an article from FMX Connect on silver, discussing reasons for silver contango yesterday. The two main reasons FMX outlines for this movement in silver would either be an interest rate move (none) or metals delivery issues. If metals delivery issues, then this is bullish for silver (and potentially gold) as a complementary inflation-protection investment. Ben Davies has commented before on a coming short squeeze in the gold and silver markets. So has Ted Butler. And Robert Lenzner. Is it finally time, or is it profit taking in the silver market that has been hovering around $30 for a while? On the whole, it sounds like there is bearish sentiment and bullish sentiment on gold and silver, which sounds like a perfectly normal market condition. That is why the sharp price movements over very small time frames, as noted in the charts above, is disturbing. Even if a large share of the market decided to take profits and sell, it is not likely to have happened within a 15 minute window at 8am in the morning. This smells of market manipulation to me. On balance, I remain bullish on gold and silver. I don't buy paper versions of these investments as I think those markets are fractional reserved upon meager physical metal backing. I recommend investing in the physical metals. And the current price action sounds like a perfect opportunity to purchase gold and silver on the cheap. I will continue to follow gold and silver news and vette it out in a reasonable manner. If the markets turn bearish upon a real economic recovery, then I may change my position. 45 And I will write about it when I do. But for now, I am not buying the gold and silver markets top story. I think we are firmly going the other direction, regardless of what this morning's price activity is saying. FINANCIAL DERIVATIVES The term derivatives refer to a large number of financial instruments whose value is derived from the underlying assets. Derivative instruments like the options and futures facilitate the trading in financial contracts. The most important underlying instruments in the market are in the form of Equity, treasury bills, and foreign exchange. The trading in the financial derivatives has attracted the prominent players of the equity markets. The primary purpose of a derivative contract is to transfer risk from one party to another i.e. risk is transferred from a party that wants to get rid of it to another party i.e. willing to take it. The major players seen in the derivatives segment are the SPECULATORS whose sole objective is to buy and sell for a profit alone. The HEDGERS are the other breeds of players, who aim merely to have a hedge positions. They are risk free investors whose intention is to have a safety mechanism and wish to protect their portfolio. Nevertheless, they are pursued as a cheap and efficient way of moving risk within the economic system. But the world of derivatives is riddled with jargons making it more awesome. The trading in equity through the derivatives in India was introduced in the year 2000 by the Securities and Exchange Board of India [SEBI] and this was described as the “India’s derivative explosion”. Although this took a definite form in 2000 but the idea was initiated in the year 1995. it was then in the year 2000 that SEBI permitted the trading the in the options on the platforms of India’s premier exchange platforms i.e., the National Stock Exchange Of India limited [NSE] and The Bombay Stock Exchange [BSE] in the individual securities. But the futures contracts took 17 long months to get launched on November 09’ 2001. 46 The trading in options and futures in the individual stocks were permitted to trade on the stable stocks only. The small and highly volatile stocks were an exemption from the trade in derivatives. Futures and options are important tools that help the investors to derive profit. The futures facilitate the investor to enter into a contract to deliver the underlying security at a future date whereas, the options allow it to his discretion as to whether he wants to buy (call) or sell (put) the contract. The current trading behavior in the derivatives segment reveals that single stock futures continues to account for a sizeable proportion. A recent report indicates that the trading in the individual stock futures in the Indian exchanges has reached global volumes. One possible reason for such a behavior of the trader could be that futures closely resemble the erstwhile ‘BADLA’ system. COMMODITY DERIVATIVES Commodity market is an important constituent of the financial markets of any country. It is the market where a wide range of products, viz., precious metals, base metals, crude oil, energy and soft commodities like palm oil, coffee etc. are traded. It is important to develop a vibrant, active and liquid commodity market. This would help investors hedge their commodity risk, take speculative positions in commodities and exploit arbitrage opportunities in the market. The need for a futures market in the commodities, especially, in the primary commodities was emphasized because such a market not only provides ample opportunities for effective management of price risk, but also, assists inefficient discovery of prices which can serve as a reference for the trade in the physical commodities in both the external as well as in the internal market. India, a commodity based economy where two-third of the one billion population depends on agricultural commodities, surprisingly has an under developed commodity market. Unlike the physical market, futures markets trades in commodity are largely used 47 as risk management (hedging) mechanism on either physical commodity itself or open positions in commodity stock. There was an effort to revive these markets but all went in vain due to improper infrastructure and facilities. However, after India joined the WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION the need to protect the agricultural community against the price fluctuations cropped up. The National agricultural policy 2000 was formulated and proposed to expand the coverage of the futures market to minimize the volatility in the commodities prices and hedging the risk arising out of the fluctuations in the prices. As a result of this there is a standardized form of commodity futures trading in the country, today and a lot number of people are active in the commodities exchanges, taking it to a great high. The active players in these exchanges are Traders, Speculators and the Hedgers. It is said that now-a days the prices of the commodities in the Physical Market (Mandis) is derived in accordance to the spot prices in the commodity exchanges. Clearly, in the nascent stage, the derivatives market in India is heading in the right direction. In the terms of the number of contracts in a single commodity/stock it is probably the largest market globally. It is no longer a market that can be ignored by any of the serious participants. The Indian economy, now, is at the verge of greater expansion the any other economies in the globe today. This has attracted a large number of institutional investors, both – the Indian as well as foreign, to invest in to the Indian stocks and commodities, thereby bringing in a lot of forex reserves. As predicted by the popular investment Gurus’ and the great Economists world wide, “India will be a major player in the global economy by the end of this decade”. We can conclude that, with the institutional participation set to increase and a broader product rollout inevitable, the market can only widen and deepen further. 48 TRADING INSTRUMENTS Derivatives in the recent times have become very popular because of their wide application. Before getting into the hard talks about the commodities trade, let us know about the trading instruments in the derivatives, as they are similarly applicable to the commodities derivatives. There are 4 types of Derivatives instrument: Forward contract Future contract Options contract Swap Futures and Options are actively used in many exchanges whereas; Forwards and Swaps are mostly trade Over the Counter (OTC). FORWARDS CONTRACT A spot or cash market is the most commonly used for trading. A majority of our day-to-day transactions are in the cash market. In addition to the cash purchase, another way trading is by entering into a Forward contract. A Forward contract is an agreement to buy or sell an asset on a specified date of a specified price. These contracts are usually entered between a financial institution and its corporate clients or two financial institutions themselves. In the context to the Commodity trading, prior to the standardization, the trade was carried out as a forwards contract between the 49 Associations, Producers and Traders. Where the Association used to act as counter for the trade. A forward contract has been in existence in the organized commodities exchanges for quite sometimes. The first forward contract probably started in Japan in the early 18th century, while the establishment of the CHICAGO BOARD OF TRADE (CBOT) in 1848 led to the start of a formal commodities exchange in the USA. Forward contracts are very useful in HEDGING and SPECULATION. The essential idea of entering into the forward contract is to Hedge the price thereto avoid the price risk. By entering into a forward contract one is assured of the price at which the goods/assets are bought and sold. The classic Hedging example would be that of an exporter who expects to receive payment in foreign currency after three months. As he is exposed to greater amount of risk in the fluctuations in the exchange rates, he can, with the use of forwards, lock-in the rate today and reduce the uncertainty. Similarly, if a speculator has the information of an upswing in the prices of the asset, he can go long on the forward market instead of the cash market and book the profit when the target price is achieved. The forward contract is settled at the maturity date. The holder of the short position delivers the assets to the holder of the long position on the maturity against a cash payment that equals to the delivery price by the buyer. The price agreed in the forwards contract is the DILIVERY PRICE. Since the delivery price is chosen at the time of entering into the contract, the value of the contract becomes zero to both the parties and costs nothing to either the holder of the long position or to the holder of the short position. The salient features of a forwards contract are: It is a bilateral contract and hence is exposed to counter-party risk. Every contract is unique and is custom designed in the terms of: expiration date and the asset type and quality. The contract price is not available in the public domain. On the expiration, the contract is to be settled by the delivery of the asset. 50 Of the party wishes to reverse the contract, he has to go to the same counter-party, which may result o attract some charges. FUTURES CONTRACT “Financial futures represent the most significant financial innovations of the last twenty years.” - As quoted by MERTON MILLER, a noble lauret’ 1999. The father of financial derivatives is Leo Me lamed. The first exchange that traded in the financial derivatives was INTERNATIONAL MONETARY MARKET, wing of the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, Chicago, in the year 1972. The futures market was designed to solve the problems, existing in the forwards market. A financial future is an agreement between two parties to buy or sell a standard quantity of a specified good/asset on a future date at an agreed price. Accordingly, future contracts are promises: the person who initially sells the contract promises to deliver a specified underlying asset to a designated delivery point during a certain month, called delivery month. The underlying asset could, well be, a commodity, stock market index, individual stock, currency, interest rates etc.. The party to the contract who determines to pay a price for the goods is assumed to take a long position, while the other who agrees to sell is assumed to be taking a short position. The futures contracts are standardized in the terms of: Quantity of the underlying assets. Quality of the underlying assets. Date and month of the delivery. Units of the price quotations and minimum price change, and Location of the settlement. 51 It is due to the standardization that the futures contract has an edge with the forward contract, in the terms of: Liquidity, safety and the security to honoring the contract which is otherwise not secured in an OTC trading forwards contract. In short, futures contract is an exchange-traded version of the usual forward contract. There are however, significant differences between the two and the same can be appreciated from the above discussion. Benefits to Industry from Futures trading: Hedging the price risk associated with futures contractual commitments. Spaced out purchases possible rather than large cash purchases and its storage. Efficient price discovery prevents seasonal price volatility. Greater flexibility, certainty and transparency in procuring commodities would aid bank lending. Facilitate informed lending. Hedged positions of producers and processors would reduce the risk of default faced by banks. Lending for agricultural sector would go up with greater transparency in pricing and storage. Commodity Exchanges to act as distribution network to retail agri-finance from Banks to rural households. Provide trading limit finance to Traders in commodities Exchanges. 52 OPTIONS CONTRACT Options have existed over a long period but were traded over the counter (OTC) only. These contracts are fundamentally different from that of futures and forwards. In the recent years options have become fundamental to the working of global capital markets. They are traded on a wide variety of underlying assets on both, the exchanges and OTC. Options like the futures are also available on many traditional products such as equities, stock indices, commodities and foreign exchange interest rates etc., options are used as a derivate instrument only in financial capital market in India and not in commodity derivatives. It is in the process in introduction. Options, like futures, also speculative in nature. Options is a legal contract which, facilitate the holder of the contract, the right but not the obligations to buy or sell the underlying asset at the fixed rate on a future date. It should be highlighted that, unlike that the futures and forward contract the options gives the buyer of the contract, the right to enter into a contract and he doesn’t have to necessarily exercise the right to give, take the delivery. When a contract is made the buyer has to pay some money as a ‘Premium’ to the seller to acquire such a right. Options are basically of two types. Call options Put options Call options: A call options gives the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at a strike price specified in the option. The profit/loss depends on the expiration date of the contract if the spot price exceeds the strike price the holder of the contract books a profit and vice-versa. Higher the spot price more is the profit. Put options: A put option give the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price specified in the option. The profit/loss that the buyer makes on the option depends on the spot price of the underlying asset. If the spot price is below the strike 53 price he makes profit and vice-versa. If the spot price is higher than the strike price he will wait up to the expiry or else book the profit early. SWAPS: Swaps were developed as a long-term price risk management instrument available on the over-the-counter market. Swaps are private agreements between two parties to exchange cash flows in the future according to a pre-arranged formula. These agreements are used to manage risk in the financial markets and exploit the available opportunity for arbitrage in the capital market. A swap, generically, is an exchange. In the financial parlance it refers to an exchange of a series of cash flows against another series of cash flows. Swaps are also used in the asset/liability management to obtain cost-effective financing and to generate higher risk-adjusted returns. With swaps, producers can effectively fix, i.e. lock in, the prices they receive over the medium to long-term, and consumers can fix the prices they have to pay. No delivery of the asset is involved; the mechanism of swaps is purely financial. The swaps market originated in the late 1970’s, when simultaneous loans were arrange between British and the US entities to bypass regulatory barriers on the movement of foreign currency .the land mark transaction Between the World Bank and the IBM in august 1981, paved the way for the development of a market that has grown from a nominal volume in the early 1980’s to an outstanding turnover of US $ 46.380tn in 1999. The swaps market offers several advantages like: These agreements are undertaken privately while transactions using exchange traded derivatives are public. 54 Since the swaps products are not standardized, counter parties can customize cash-flow streams to suit their requirements The swaps can be regarded as portfolios of forward contracts. The two commonly used swaps are: Interest rate swaps: These entail swapping only the interest related cash flows between the parties in the same currency. Currency swaps: These entail swapping both principal and interest between the parties, with the cash flows in one direction being in a different currency than those in the opposite direction. PARTICIPANTS IN THE DERIVATIVE MARKET There are three major participants in the derivatives market. They are: Hedgers Speculators Arbitragers HEDGERS He is the person who enters the derivatives market to lock-in their prices to avoid exposure to adverse movements in the price of an asset. While such locking may not be extremely profitable the extent of loss is known and can be minimized. They are in the position where they face risk associated with the price of an asset. They use derivatives to reduce or eliminate risk. For example, a farmer may use futures or options to establish the price for his crop long before he harvests it. Various factors affect the supply and demand for that crop, causing prices to rise and fall over the growing season. The farmer can watch the 55 prices discovered in trading at the CBOT and, when they reflect the price he wants, will sell futures contracts to assure him of a fixed price for his crop. A perfect hedge is almost impossible. While hedging Basis risk could arise. Basis = Spot price of asset to be hedged – Futures price of the contract used. Basis risk arises as a result of the following uncertainties: The exact date when the asset will be bought or sold may not be known. The hedge may require that the Futures contract be closed before expiration. PRICE FUTURES PRICE BASIS SPOT PRICE EXPIRY DATE TIME SPECULATORS: A speculator is a one who accepts the risk that hedgers wish to transfer. A speculator takes positions on expectations of futures price movements and in order to make a profit. In general a speculator buy futures contracts when he expect futures prices to rise and sell futures contract when he expects futures prices to fall, but has no desire to actually own the physical commodity. Speculators wish to bet on the future movement in the price of an asset. They use derivatives to get extra leverage. They take positions in the market and assume risk to profit from fluctuations in the prices. Infact, the speculators consume the information, make forecast about the prices and put their money in these forecast. By taking positions, they are betting that the price would go up or they are betting it would go down. 56 Depending on their perception, they may long or short positions on the futures or /and options, or may hold spread positions. ARBITRAGEURS “Simultaneous purchase of securities in one market where the prices thereof are low and sale thereof in another market, where the price thereof is comparatively higher. These are done when the same securities are been quoted at different prices in the two markets, with a view to make a profit and carried on with the conceived intention to derive advantage from difference in prices of securities prevailing in the two markets”. -As defined by The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India. Arbitrageurs thrive on the market imperfections. They profit by trading on given commodities, or items, that are in the business to take advantage of a discrepancy between prices in two different markets. If, for example, they see the future prices of an asset getting out of line with the cash price, they will take offsetting positions in the two markets to lock in a profit. Thus, the arbitrage involves making risk-less profit by simultaneously entering into transactions in two or more markets. With the introduction of derivate trading the scope of arbitrageurs’ activities extends to arbitrage over time i.e., he can buy securities in an index today and sell the futures, maturing in the month or two. TRADING OF COMMODITY DERIVATIVES IN INDIA Trading of all the derivatives in India is carried over: Exchanges Over the counter 57 EXCHANGE TRADING An asset (commodity/stock), when is traded over an organized exchange is it is termed, to be traded on the Exchange. This type of trading is the general trading which we see on the major exchanges world over. The settlement in the exchange trading is highly standardized. OVER THE COUNTER TRADING An asset (commodity/stock) is traded over the counter usually because the company is small and unable to meet listing requirements of the exchanges and facilitates the trading in those areas where the exchanges are not located. Also known as unlisted the assets are traded by brokers/dealers who negotiate directly with one another over computer networks and by phone. Instruments such as bonds do not trade on a formal exchange and are thus considered over-the- counter securities. Investment banks making markets for specific issues trade most debt instruments. If someone wants to buy or sell a bond, they call the bank that makes the market in that asset. Exchange Vs OTC Trading The OTC derivatives markets have witnessed rather sharp growth over the last few years, which have accompanied the modernization of commercial and investment banking and globalization of financial activities. The recent developments in information technology have contributed to a great extent to these developments. While both exchange-traded and OTC derivative contracts offer many benefits, the former have rigid structures compared to the latter. It has been widely discussed that the highly leveraged institutions and their OTC derivative positions were the main cause of turbulence in financial markets in 1998. These episodes of turbulence revealed the risks posed to market stability originating in features of OTC derivative instruments and markets. 58 The OTC derivatives markets have the following features compared to exchange-traded derivatives: The management of counter-party (credit) risk is decentralized and located within individual institutions. There are no formal centralized limits on individual positions, leverage, or margining. There are no formal rules for risk and burden-sharing, There are no formal rules or mechanisms for ensuring market stability and integrity, and for safeguarding the collective interests of market participants, The OTC contracts are generally, not regulated by a regulatory authority and the exchange’s self-regulatory organization, although they are affected indirectly by national legal systems, banking supervision and market surveillance. COMMODITIES MARKET….. Global Perspective Oil accounts for 40 per cent of the world's total energy demand. The world consumes about 76 million bbl/day of oil. United States (20 million bbl/d), followed by China (5.6 million bbl/d) and Japan (5.4 million bbl/d) are the top oil consuming countries. Balance recoverable reserve was estimated at about 142.7 billion tons (in 2002), of which OPEC was 112 billion tons 59 The major commodities trading exchanges globally are: Chicago Board Of Trade (COBOT). U.S.A. New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX). U.S.A. London Metal Exchange (LME). United Kingdom. Tokyo Commodity Exchange (TOCOM). Japan International Petroleum Exchange (IPE). London Metal Exchange (LME). United Kingdom Sydney Futures Exchange (SFE). Australia Brazilian Futures Exchange (BBF). Brazil Winnipeg Commodity Exchange (WCE). Canada Marche a Terme International de France (MATIF). France Hong Kong Futures Exchange (HKFE). Hong Kong New Zealand Futures & Options Exchange (NZFOE). New Zealand Russian Commodity and Raw Materials Exchange. Russia Singapore International Monetary Exchange (SIMEX). Singapore South African Futures Exchange (SAFEX). South Africa Dalian Commodity Exchange. China Shanghai Metal Exchange (SME). China 60 Chicago Board Of Trade (CBOT) The Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT), established in 1848, is a leading futures and options on futures exchange. More than 3,600 CBOT members trade 50 different futures and options products at the exchange through open auction and/or electronically. Volume at the exchange in 2003 was a record breaking 454 million contracts. In its early history, the CBOT traded only agricultural commodities such as corn, wheat, oats and soybeans. Futures contracts at the exchange evolved over the years to include non-storable agricultural commodities and non-agricultural products like gold and silver. The CBOT's first financial futures contract, launched in October 1975, was based on Government National Mortgage Association mortgage-backed certificates. Since that introduction, futures trading has been initiated in many financial instruments, including U.S. Treasury bonds and notes, stock indexes, and swaps, to name but a few. Another market innovation, options on futures, was introduced in 1982. For more than 150 years, the primary method of trading at the CBOT was open auction, which involved traders meeting face-to-face in trading pits to buy and sell futures contracts. But to better meet the needs of a growing global economy, the CBOT successfully launched its first electronic trading system in 1994. During the last decade, as the use of electronic trading has become more prevalent, the exchange has upgraded its electronic trading system several times. Most recently, on January 1, 2004, the CBOT debuted its new electronic platform powered by the cutting-edge trading technology. As of 1st January 2004, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange is providing clearing and related services for all CBOT products 61 New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) The NYMEX in its current form was created in 1994 by the merger of the former New York Mercantile Exchange and the Commodity Exchange of New York (COMEX). Together the represent one of the world's largest markets in commodities trading. It deals in futures (and options) in oil products, such as crude oil, heating oil, leaded regular gasoline, natural gas, propane and in rare metals, such as platinum and palladium. It also deals in gold and silver, aluminum and copper, sharing with the London Metal Exchange a dominant role in the world metal trading. London Metals Exchange The London Metal Exchange is the world's premier non-ferrous metals market with highly liquid contracts and a worldwide reputation. It is innovative while maintaining its traditional strengths and remains close to its core users by ensuring its contracts continue to meet the high expectations of industry. As a result, it is highly successful with a turnover in excess of US$3,000 billion per annum. It also contributes to the UK’s invisible earnings to the sum of more than £250 million in overseas earnings each year. The origins of the London Metal Exchange can be traced as far back as the opening of the Royal Exchange in 1571. This is where metal traders first began to meet on a regular basis. However, it was in 1877 that the London Metal Market and Exchange Company were formed as a direct result of Britain's industrial revolution of the 19th century. This led to a massive increase in the UK’s consumption of metal, which required the import of enormous tonnages from abroad. Merchant venture’s were investing large sums of money in this activity and were exposed to great risk, not only because the voyages were hazardous but also because the cargoes could lose value if there was a fall in price during the time it took for the metal to reach Britain. 62 INDIAN PERSPECTIVE There are three major exchanges for the commodity trading in India. They are: The National Commodities and Derivatives Exchange Ltd. (NCDEX) Multi Commodities Exchange of India Ltd. (MCX) National Multi-Commodity Exchange Ltd. (NMCE) National Commodity & Derivatives Exchange Limited (NCDEX) The National Commodities and Derivatives Exchange Ltd is a professionally managed online multi commodity exchange promoted by ICICI Bank Limited (ICICI Bank), Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC), National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) and National Stock Exchange of India Limited (NSE). Punjab National Bank (PNB), CRISIL Limited (formerly the Credit Rating Information Services of India Limited), Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative Limited (IFFCO) and Canara Bank by subscribing to the equity shares have joined the initial promoters as shareholders of the Exchange. NCDEX is the only commodity exchange in the country promoted by national level institutions. This unique parentage enables it to offer a bouquet of benefits, which are currently in short supply in the commodity markets. The institutional promoters of NCDEX are prominent players in their respective fields and bring with them institutional building experience, trust, nationwide reach, technology and risk management skills. NCDEX is a public limited company incorporated on April 23, 2003 under the Companies Act, 1956. It obtained its Certificate for Commencement of Business on May 9, 2003. It has commenced its operations on December 15,2003 63 NCDEX is a nation-level, technology driven de-mutuali zed on-line commodity exchange with an independent Board of Directors and professionals not having any vested interest in commodity markets. It is committed to provide a world-class commodity exchange platform for market participants to trade in a wide spectrum of commodity derivatives driven by best global practices, professionalism and transparency. Forward Market Commission regulates NCDEX in respect of futures trading in commodities. Besides, NCDEX is subjected to various laws of the land like the Companies Act, Stamp Act, Contracts Act, Forward Commission (Regulation) Act and various other legislations, which impinge on its working. NCDEX is located in Mumbai and offers facilities to its members in more than 390 centers throughout India. The reach will gradually be expanded to more centers. NCDEX currently facilitates trading of thirty six commodities - Cashew, Castor Seed, Chana, Chilli, Coffee, Cotton, Cotton Seed Oilcake, Crude Palm Oil, Expeller Mustard Oil, Gold, Guar gum, Guar Seeds, Gur, Jeera, Jute sacking bags, Mild Steel Ingot, Mulberry Green Cocoons, Pepper, Rapeseed - Mustard Seed, Raw Jute, RBD Palmolein, Refined Soy Oil, Rice, Rubber, Sesame Seeds, Silk, Silver, Soy Bean, Sugar, Tur, Turmeric, Urad (Black Matpe), Wheat, Yellow Peas, Yellow Red Maize & Yellow Soybean Meal. At subsequent phases trading in more commodities would be facilitated. 64 Multi Commodities Exchange of India Ltd (MCX) MCX an independent and de-mutulised multi commodity exchange has permanent recognition from Government of India for facilitating online trading, clearing and settlement operations for commodity futures markets across the country. Key shareholders of MCX are Financial Technologies (India) Ltd., State Bank of India, NABARD, NSE, HDFC Bank, State Bank of Indore, State Bank of Hyderabad, State Bank of Saurashtra, SBI Life Insurance Co. Ltd., Union Bank of India, Bank Of India, Bank Of Baroda, Canara Bank, Corporation Bank. Head quartered in Mumbai, an expert management team with deep domain knowledge of the commodity futures markets leads MCX. Through the integration of dedicated resources, robust technology and scalable infrastructure, since inception MCX has recorded many first to its credit. Inaugurated in November 2003 by Mr. Mukesh Ambani, Chairman & Managing Director, Reliance Industries Ltd, MCX offers futures trading in the following commodity categories: Agri Commodities, Bullion, Metals- Ferrous & Non-ferrous, Pulses, Oils & Oilseeds, Energy, Plantations, Spices MCX has built strategic alliances with some of the largest players in commodities eco-system, namely, Bombay Bullion Association, Bombay Metal Exchange, Solvent 65 Extractors' Association of India, Pulses Importers Association, Shetkari Sanghatana, United Planters Association of India and India Pepper and Spice Trade Association. Today MCX is offering spectacular growth opportunities and advantages to a large cross section of the participants including Producers / Processors, Traders, Corporate, Regional Trading Centers, Importers, Exporters, Cooperatives, Industry Associations, amongst others MCX being nation-wide commodity exchange, offering multiple commodities for trading with wide reach and penetration and robust infrastructure, is well placed to tap this vast potential. Vision and Mission of the Multi Commodities exchange of India. The vision of MCX is to revolutionize the Indian commodity markets by empowering the market participants through innovative product offerings and business rules so that the benefits of futures markets can be fully realized. Offering 'unparalleled efficiencies', 'unlimited growth' and 'infinite opportunities' to all the market participants. At MCX we believe that performance excellence and affordability would be the key drivers in promoting and popularizing Commodities Futures trading in the country. Exchanges in the new economy will be driven by strong service availability backed by superior technology and MCX is well poised to emerge as the "Exchange of Choice" for the commodity futures trading community. 66 COMMODITIES SYMBOLS Gold, Gold HNI, Gold M, I-Gold, Silver, Silver HNI, Silver M Castor Oil, Castor Seeds, Castor Seeds (Disa), Cottonseed, Crude Palm Oil, Groundnut Oil, Kapasia Khalli (Cottonseed Oilcake), Mustard Seed (Hapur), Mustard Seed (Jaipur), Mustard /Rapeseed Oil, Mustard Seed (Sirsa), RBD Palmolein, Refined Soy Oil, Sesame Seed, Soyameal Soya Seed Cardamom, Jeera, Pepper, Red Chilli, Turmeric Aluminium, Copper, Nickel, Sponge Iron, SteelFlat, Steel Long (Bhavnagar), Steel Long (Gobindgarh), Tin Cotton Long Staple , Cotton Medium Staple, Cotton Short Staple, Kapas Chana, Masur, Tur, Urad, Yellow Peas, Basmati Rice, Maize, Rice, Sarbati Rice, Wheat Brent Crude Oil, Crude Oil, Furnace Oil Cashew Kernel, Rubber High Density Polypropylene (PP), Polyethylene (HDPE), Guar Seed, Guargum, Gur, Mentha Oil, Sugar M-30, Sugar S-30, 67 Multi-Commodity Exchange, MCX COMMODITY UNIT OF UNIT OF YIELD/Re. PRICE TRADING MOVEMENT QUOTATION YIELD/TIC TRADING or TIC SESSION VALUE PRECIOUS METALS GOLD-M 10gm 100gm 10.00 1.00 10.00 10:00AM-11:30PM GOLD 10gm 1000gm 100.00 1.00 100.00 10:00AM-11:30PM SILVER-M 1KG 5KG 5.00 1.00 5.00 10:00AM-11:30PM SILVER 1KG 30KG 30.00 1.00 30.00 10:00AM-11:30PM AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTS SOYA 1QT 10QT 10.00 0.05 0.50 10:00AM-5:00PM & SOYA OIL 10KG 1000KG 100.00 0.05 5.00 10:00AM-5:00PM & PALMOLEIN OIL CRUDE 10KG 1000KG 100.00 0.05 5.00 10:00AM-5:00PM & PALMOLEIN OIL RBD 10KG 1000KG 100.00 0.05 5.00 10:00AM-5:00PM & CASTOR 100KG 1MT 10.00 0.25 2.50 10:00AM-5:00PM & CASTOR OIL 10KG 1MT 100.00 0.10 10.00 10:00AM-5:00PM & GROUND NUT 10KG OIL 1MT 100.00 0.10 10.00 10:00AM-5:00PM & GAUR SEED 100KG 5MT 50.00 1.00 50.00 10:00AM-5:00PM & BLACK PEPPER 100KG 1MT 10.00 1.00 10.00 10:00AM-5:00PM & KAPAS 20KG 4MT 200.00 0.10 20.00 10:00AM-5:00PM & INDUSTRIAL METALS STEEL LONG 1MT 25MT 25.00 0.50 12.50 10:00AM-5:00PM & STEEL FLAT 1MT 25MT 25.00 0.50 12.50 10:00AM-5:00PM & COPPER 1KG 1MT 1000.00 0.05 50.00 10:00AM-11:30PM NICKEL 1KG 250KG 250.00 0.50 125.00 10:00AM-5:00PM & TIN 1KG 500KG 500.00 0.25 125.00 10:00AM-5:00PM 68 The National Multi Commodity Exchange of India ltd. The first state-of-the-art de-mutualized multi-commodity Exchange, NMCE commenced futures trading in 24 commodities on 26th November, 2002 on a national scale and the basket of commodities has grown substantially since then to include cash crops, food grains, plantations, spices, oil seeds, metals & bullion among others. NMCE was the first Exchange to take up the issue of differential treatment of speculative loss. It was also the first Exchange to enroll participation of high net-worth corporate securities brokers in commodity derivatives market. NMCE has also made immense contribution in raising awareness about and catalyzing implementation of policy reforms in the commodity sector.. It was the Exchange, which showed a way to introduce warehouse receipt system within existing legal and regulatory framework. It was the first Exchange to complete the contractual groundwork for dematerialization of the warehouse receipts. Innovation is the way of life at NMCE. National Multi Commodity Exchange of India Ltd. (NMCE), promoted by commodity-relevant public institutions, viz., Central Warehousing Corporation (CWC), National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India (NAFED), Gujarat Agro-Industries Corporation Limited (GAICL), Gujarat State Agricultural Marketing Board (GSAMB), National Institute of Agricultural Marketing (NIAM), and Neptune Overseas Limited (NOL). The Punjab National Bank (PNB) took equity of the Exchange to establish that linkage. Even today, NMCE is the only Exchange in India to have such investment and technical support from the commodity relevant institutions. These institutions are represented on the Board of Directors of the Exchange and also on various committees set up by the Exchange. The experienced and qualified professionals with impeccable integrity and expertise manage the day-to-day operations of the Exchange. None of them have any trading interest. 69 Vision National Multi-Commodity Exchange of India Limited is committed to provide world class services of on-line screen based Futures Trading of permitted commodities and efficient Clearing and guaranteed settlement, while complying with Statutory / Regulatory requirements. We shall strive to ensure continual improvement of customer services and remain quality leader amongst all commodity exchanges. Mission Continuous improvement in Customer Satisfaction. Improving efficiency of marketing through on-line trading in Dematerialization form. Minimizing of settlement risks. Improving efficiency of operations by providing best infrastructure. Rationalizing the transaction fees to optimum level. Implementing best quality standards and testing in tune with trade practices. Improving facilities for structured finance. Improving quality of services rendered by suppliers. Promoting awareness about on-line features trading services of NMCE across the length and breadth of the country. Turn over of the Indian commodity futures’ market Turnover on Commodity Futures Markets Exchange NCDEX NBOT MCX NMCE ALL EXCHANGES 2010-11 1490 53014 2456 23842 129364 70 (Rs. In Crores) 2011-12 54011 51038 30695 7943 170720 NCDEX TRADING SYSTEM A trading system is a system of rules and guidelines of the whole trading process. The system includes: First in the system, the TICKER for each commodity is shown on the trading terminal. Generally it is standardized for all the exchanges in a country, but nevertheless, it may differ between the exchanges in same country. Firstly, the Format for Tickers is like this: CCCGGGLLL CCC – three letters for the commodity. GGG – three letters for the grade. Wherever there is no particular grade, either STD (standard) or GR1 (grade 1) has been used. LLL – three letters for the delivery location. Eg. SYOREFIND -- SYO: Soy Oil, REF: Refined, IND: Indore Now let’s have a look at the format of the tickers for all the commodities that are traded in NCDEX: GLD100MUM SLV100DEL SYBGR1IND SYOREFIND RMSGR1JPR RMOEXPJPR RBDPLNKAK CPOSTDKDL CTMJ34BTD CTLS06ABD : “Gold”+“100% pure”+“Mumbai” : “Silver”+“100% pure”+“Delhi” : “Soy Bean”+“GR1”+“Indore” : “Soy Oil”+“Refined”+“Indore” : “Rape/Mustard”+“GR1”+“Jaipur” : “Rape/Mustard Oil”+“Expeller”+“Jaipur” : “RBD”+“Palm Olein”+“Kakinada” : “Crude Palm Oil”+“STD”+“Kandla” : “Cotton Medium Staple Length”+“J-34”+“Bhatinda” : “Cotton Long Staple Length”+“S-06”+“Ahmedabad” 71 “INSTRUMENT TYPE” in NCDEX is to denote whether the ticker is a futures contract or a spot price being disseminated or an options contract COMDTY – used for commodity spot price dissemination FUTCOM – used for futures on commodity OPTCOM – used for options on futures on commodity CONTRACT EXPIRY: Contract Expiry for the Futures & Options contract will be written as 20mmmYYYY. 20 -- 20th of every month a contract expires. mmm – used to denote the month, e.g. DEC, JAN etc YYYY – used to denote the year e.g. 2003, 2004 etc For the spot price, no expiry date will be displayed or required as the positions in spot market are for perpetuity (Spot market not yet started). WHAT TO QUOTE FOR BUY/SELL Gold – for buying futures of say 500 gm, you will need to enter “Quantity” as 500, and price in “Rs/10gm” Silver – for buying futures of say 25 Kg, you will need to enter “Quantity” as 25 and the price in “Rs/Kg” All oils and oilseeds – for buying futures of say 5 MT, you will need to enter “Quantity” as 5 and The price for Soy Bean in “Rs/Quintal” The price for Rapeseed/Mustard Seed in “Rs/20 Kg” The price for all edible oils in “Rs/10 Kg” 72 Cotton – for buying futures of say 44 bales, you will need to enter “Quantity” as 44 and the price in “Rs/Quintal” ORDER TYPES: There are major, two types of orders, regular lot orders and qualifiers. Regular lot order Market Order: It is a type of order where in both the buyer and seller agrees for a transaction at current market price (CMP). Limit Order: An order that can be executed only at a specified price or one favorable for the investor. Hence for a seller a limit price is above Current Market Price (CMP) and for a buyer it is below the Current Market Price (CMP) Qualifier Stop Loss: An order that is put to curb excess loss to the customer. Hence for a seller (who already has a buy) a stop-loss order is below CMP and for buyer (who already holds a sell) a stop-loss order is above CMP. Futures Spread (SB) – specified difference between two different calendar months in same commodity. It also called just ‘Spreads betting’. Immediate or Cancel (IOC) 2L Order (2L) – Opposite positions taken in two different months (arbitraging) e.g. buying March contract and selling April contract. 73 3L Order (3L) – Opposite positions taken in two different months and either buy/sell position taken in other month. E.g. buying March contract and selling April contract and buying in May contract. Hence in this case one position in either of the contracts is not arbitraged. TIME VALIDITY OF TRADES Day-Valid only for that day. Good Till Date (GTD) – Valid to the date specified (for specified no. of days), Max 7 days. Good Till Canceled (GTC) – Valid till cancelled, Max 7 days. SETTLEMENT PROCESS IN COMMODITIES FUTURES In this Education Series, we shall have a look into how settlement is done in case of commodities futures. The settlement procedure is more or less same as in case of stock futures, nevertheless, there are some key differences in the procedure by the virtue of the underlying asset, which is a commodity. Now, we will look into key two key issues which affect the settlement process. First being whether the underlying asset of the future is deliverable (this depends on exchange) and the other whether the underlying asset is in a physical form or only in electronic form. Table.1: Comparison between stock futures and commodity futures. Instrument Deliverable Electronic Form Physical From Stock Futures No* Yes No Commodity Futures Yes Yes Yes 74 In many developed financial markets like Japan, US, UK, Euro land, stock futures can account to delivery. From Table.1 it is clear that the stock futures in India do not end up in delivery, implying a person who has taken long position cannot ask for delivery of real stock after the expiry of the contract even if he is willing for taking delivery. Again since, the delivery is not possible, an investor cannot settle his short position with the real stock; neither can he take delivery of stocks if he has taken long position. He has to mark-to-market at the end of future contract settlement. But in case of commodity futures, delivery of underlying commodity is possible. The delivery can be taken both in the electronic form and physical form. In case of electronic form the delivery quantity is transferred to/from the investor’s DP account. In case of physical form, the delivery quantity is transferred to/from the stocking point. Now, we arrive at an important point, when and how are settlements done? Daily Settlements are done on mark-to-market basis. And at the expiry of the contract Final Settlement is done. Daily Mark to Market (MTM) Settlement is done for each Client: At the end of every trading day, for all the trades, this is done till the date of the Contract expiry. A daily settlement is done to take care of DAILY PRICE FLUCTUATION for all trades. 75 Final Settlement will be done for each Client: This on expiry of the Contract will handle the FINAL obligation of the Member for all trades in that contract. How is Daily MTM done? Calculating the daily profits and losses for the client/investor does the Daily Settlement. Profits and Losses are determined on the positions for client/investor, for each client and for each contract All trades are marked to the market at the Daily Settlement Price which is equal to Closing price for the day. A total Mark to Market Profit or Loss is calculated for the every client/investor. Table.2 Example of Daily MTM Branch 1 Branch 2 Client 1 Contract A Client 2 Contract B Contract A Client 3 Contract A Contract B Buy 400@50 Sell 200@150 Sell 700@48 Buy 200@63 Buy 150@160 Sell 200@55 Sell 150@190 Buy 500@40 ---- Sell 150@170 Closing rate 400 X 8 = 200 X 30 = 700 X 10 = A – 58 3200 (6000) (7000) 200 X 5 = 3000 B – 180 200 X 3 = 150 X 10 = 500 X 18= (1000) 150 X 10 = (600) 1500 9000 PROFIT PROFIT LOSS PROFIT LOSS PROFIT /(LOSS) 2600 (4500) 2000 (1000) 1500 TOTAL MTM LOSS (1900) 150 X 20 = (1500) PROFIT 2500 76 Settlements Procedure - Daily MTM Settlement Exchange Clearinghouse (NCDEX/MCX) Download of Margin and MTM files at EOD (End Of the Day) TWS* Margins Initial Margin Call Any special Margin Daily MTM settlement (Collection/Refund ))))on T+1)& Daily Profit/Loss for Positions closed out MTM of Open positions KARVY Commodities Broking Pvt. Ltd. “Clearing Bank A/c” at Closing Price Funds transaction flow BRANCH 1 Client 1 Makes arrangement for funds With the Head Office KCBPL BANK Client 1, 2 Banks credits the funds into KCBPL bank a/c BRANCH 2 *TWS – Trading Work Station Chart 1: Procedure for Daily MTM 77 Exchange Clearing House (NCDEX/ MCX) When is Daily MTM Settlement done? The information on MTM amount (paid or received) by the Broking Member (KCBPL) is given thru the Extranet at the end of the day, same information is passed on to the Broking Member (KCBPL) branches. Actual payment and receipt of funds will be made by the Client on the next trading day i.e. T+1. (‘T’ being the trade date) How does the Transfer of funds happen? Payment will be done through a designated Clearing bank of the Exchange. The Broking Member (KCBPL) makes arrangement for funds in his Settlement A/c with the bank. The Clearing Corporation (NSCCL) will send instruction to the Bank for debiting/crediting the Broking Member (KCBPL) account. What are the other payments to be made? Besides the MTM, the Broking Member (KCBPL) will make Daily Margin payments. Margin files will be downloaded on the Extranet Broking Member (KCBPL) arranges for funds in the Settlement A/c The Clearing Corporation debits the funds on the next day after the trading date. What happens in case of failure? If the Broking Member (KCBPL) fails to make the payment of MTM or Margin amount, trading terminal is disabled immediately. Trading will commence on deposit of funds by the Broking Member (KCBPL). Where is the information on Daily Settlement available? All information pertaining to Settlements is available on the Broking Member (KCBPL) Extranet. This is available in specific folders for the Broking Member (KCBPL). 78 How do I access the Extranet? Thru the VSAT / Leased Lines connectivity using FTP protocol Login using Trading member Id and password during non-trading hours. (Here Trading Member is KCBPL) Now let’s have a brief look at the sequence of Events. Opening new positions and Closing of open positions by Member During the period of contract till date of expiry. Calculated at the end of every Trading Day, Payments on T+1. Daily MTM Settlement and Margins Determination of positions for each Member On the Date of expiry after the trading hours. Final Settlement of all open positions As per settlement calendar for each contract. Chart.2 Settlements - Sequence of events From Chart.2 the last event in the sequence of events is the “Final Settlement” of all the open positions. “The Settlement done for Open Buy and Sell positions on the Contract Expiry Date is called Final Settlement.” By the virtue of commodities futures being deliverable, both in electronic form (DP A/c) and in physical form, the final settlement in case of commodities futures varies from stock futures. 79 The futures settlement in case of commodities futures is done in the following ways: Cash settlement: Most of the open positions end up in cash settlement at the end/expiry of a contract. In fact about 99% of the positions end up in cash settlement. Electronic Form: Some positions end up in delivery, the amount /volume of a commodity that a client marks for delivery is transferred into the clients DP A/c. Physical Form: Very less, almost negligible delivery happens in the physical form. (About 0.1-0.5% of total open positions) How final positions are determined? Broking Member A Client 1 Broking Member B Client 2 Client 3 Contract Y Day 1 Contract X 400 S Contract Y 700 B Contract X 400 S 200 B Day 2 - 400 S 400 B 200 B Date of Expiry 400 S 300 B - 400 B Contract X 400 S Contract Y 300 B 500 S 500 S Contract Y 500- 400 = 100S Can actual delivery of the commodity be done on Expiry? A Broking Member (KCBPL) can give and take delivery of commodities for an investor/client or on proprietary trades done, by completing the Delivery formalities and giving delivery information to the Exchange What are procedures required before Delivery? Opening a Clearing Member (KCBPL) Pool account for the purpose of settlements. Beneficiary Demat account for own transactions. Opening of Client’s Demat account with the empanelled DP. 80 How is the delivery information processed? The information submitted by the Members is matched at NCDEX at the end of the day All trades, which are matched, are locked for delivery A Delivery Request number is generated for all delivery information submitted Settlements – Deliveries Exchange Clearinghouse Workflow Download of KCBPL net positions on expiry KCBPL Delivery Information Counter party Information Matching of Information Submission of Delivery information and matching of Matched Information Information Direct delivery Between Buyers and Sellers How does the matching of delivery information take place? Validation of delivery information On Client’s Net Open Position On Delivery lot for commodity Excess quantity is rejected and is cash settled. Matching limited to the total capacity at the Warehouse Matching is done for the deliveries based on Commodity Location 81 Delivery thru Depository SETTLEMENT CALENDAR Commodity Physical Settlement schedule for Pay-in/Pay-outs Soya bean T+7 Refined Soya bean oil T +7 Rapeseed Mustard Seed T +7 Rapeseed Mustard Seed Oil T +7 RBD Palmolein T +7 PLATINUM T +7 Medium Staple Cotton T +10 Long Staple Cotton T +10 Gold T +2 Silver T +4 Settlement Pay-in Pay-in will take place on date as specified in Settlement Calendar. Commodities: Seller ensures Demat of commodities prior to pay-in. Instruction to DP by seller to move commodities to KCBPL Pool A/c. Pay-in of commodities on Settlement Date thru KCBPL pool A/c. Funds: Pay-in of funds – Thru the Clearing bank of the Member on the Pay-in day. Settlement Pay-out Pay-out will take place on date as specified in Settlement Calendar. Commodities Credit given into the Buyer member KCBPL Pool A/c. Instruction by KCBPL to transfer from pool A/c to buyer client’s Demat account. Subsequent Remat of commodities and physical movement handled by buyer. Fun 82 ADVANTAGES OF TRADING/INVESTING IN COMMODITIES Benefits to the Industry, Exporters and Importers: 1. Hedging the price risk associated with future contractual commitments. For instance, let’s take a case of a Soy Bean exporter whose export commitment is one month now (present market price is Rs.1700 per quintal). As per his analyst’s recommendations, the prices are expected to rise (to an extant of Rs.1800 per quintal) after one month, when he has committed for export. Now let’s assume that his export commitment is 10000 quintals. Time Market Price Today Export Commitment Nil After one month 10000 1800 1700 Instance 1: With no hedging. Sale Price: Rs. 1850. Cost Price: Rs. 1800. So, net profit/ quintal = Rs.50. Net Profit of deal=Rs.50x10000=Rs.5, 00,000. Instance 2: With Hedging: Sale Price: Rs.1850. Cost Price: Rs.1700. (where in the exporter goes long (buys) today) So, net profit/ quintal=Rs.150. Net Profit of deal=Rs.150x10000=15, 00,000. An increase of 200% net profit. 83 2. Efficient price discovery: With the starting of national wide commodities markets, regional price differences in commodities prices are controlled. Hence, now the cost of a commodity is almost same throughout the country. Prior to this there was lot of price differences of commodities at various places. Example, the price of Gold in Hyderabad was different from price of Gold in Mumbai, but now this disparity is curbed to an extant, though some price still exists between the exchanges. 3. Benefits to the Banks: Now the producer and consumer of the commodity can go for ‘Hedging’ their positions hence, the loaner of funds (Bank) is clear of the receivables. Thus, ‘Hedged’ positions of producers and consumers would reduce the risk of default faced by the banks. Lending for agricultural sector would go up with greater transparency in pricing and storage. 4. Benefits to the clients: The commodity prices move with strong broad based fundamentals. Hence, the commodity prices do not move in an erratic fashion. The price movements are also due to Global price movements of a particular commodity hence, things like insider trading, and price manipulations do not exist in commodities markets. A commodity is always tradable. And also never a commodity price can be ‘zero’. In case of stocks, a company may be de-listed, hence, it may go non tradable or the virtual price being ‘zero’ 84 FACTORS EFFECTING COMMODITIES MARKET Before starting this section let’s divide commodities into different classes: Precious Metals: Gold, Silver. Base Metals: Steel, Aluminum*, High Grade Copper, Nickel, Zinc, Tin. Agricultural: Grains: Soy, Soy Oil, Rice, and Rice Oil*. Softs: Cotton, Coffee*, Sugar. Energy: Crude Oil, Natural Gas. ** Factors affecting the prices of commodities: The factors affecting the prices of various commodities can be divided into two: Generic Factors: These are the factors affecting all the commodity prices in general. Demand and Supply. Indian Rupee Vs other currencies. Export/Import parity. Political environment. Specific Factors: These are the factors affecting a particular commodity or a class of commodities. Precious Metals: Stock market dynamics. Geo-political tensions. US dollar Vs other major currencies. Global macroeconomics. Miner’s reports. Agricultural: Climatic conditions. Crop production. Government regulations. Export rejection/orders. 85 Softs: Climatic conditions. Crop production. Import duty. Industrial Metals: Industrial demand. Substitute metals supply. Government regulations. Infrastructure projects. Energy: Production. New excavations. Geo-political tensions. New projects. 86 CHAPTER-IV DATA ANALYSES AND INTERPRETATION 87 Multi Commodities Exchange of India Ltd (MCX) Copper Price Date Open(Rs.) High(Rs.) Low(Rs.) Close(Rs.) 06/02/2013 452.00 05/02/2013 453.65 04/02/2013 452.95 02/02/2013 452.70 01/02/2013 448.90 31/01/2013 449.90 30/01/2013 448.85 29/01/2013 447.75 28/01/2013 446.80 25/01/2013 449.50 24/01/2013 448.50 23/01/2013 449.90 22/01/2013 447.70 21/01/2013 448.10 19/01/2013 448.90 18/01/2013 448.10 17/01/2013 447.90 16/01/2013 451.95 15/01/2013 449.95 14/01/2013 456.05 12/01/2013 454.40 11/01/2013 456.65 10/01/2013 456.15 09/01/2013 456.95 08/01/2013 459.70 07/01/2013 458.10 05/01/2013 458.90 04/01/2013 456.10 03/01/2013 460.35 02/01/2013 452.55 01/01/2013 451.05 31/12/2012 449.25 29/12/2012 447.45 28/12/2012 449.55 27/12/2012 447.15 452.55 453.80 456.00 453.00 453.40 453.70 451.50 448.50 449.55 450.40 449.20 451.00 450.20 448.75 448.90 450.70 450.05 452.00 451.05 456.40 454.80 457.15 459.45 459.20 460.00 459.00 459.25 459.80 462.20 459.90 451.70 451.70 447.45 449.95 449.30 449.15 451.70 451.55 452.60 448.30 448.50 448.05 445.40 446.30 445.00 447.00 448.10 447.55 446.50 448.90 447.80 445.60 448.15 447.50 449.65 454.25 454.05 455.60 455.50 456.30 456.30 458.55 455.50 457.00 452.55 450.65 448.20 447.45 446.60 447.15 449.45 451.95 454.35 452.95 453.20 449.10 450.85 447.70 448.30 446.60 448.25 448.55 449.75 446.65 448.90 448.60 449.15 448.40 450.80 449.95 454.55 454.30 457.25 455.60 457.25 458.65 458.95 458.40 457.30 457.65 451.40 451.45 447.45 447.45 448.70 88 TQ 188000 103000 342000 60000 395000 240000 291000 175000 123000 155000 80000 180000 58000 53000 2000 97000 217000 107000 137000 153000 13000 135000 198000 223000 154000 111000 18000 190000 335000 340000 31000 84000 0 41000 28000 TV(Rs Lacs) 846.61 466.35 1,552.84 271.71 1,779.88 1,082.41 1,310.11 781.95 550.93 693.56 358.51 810.88 260.28 237.12 8.98 435.70 971.06 481.41 615.36 692.38 59.08 614.91 905.06 1,019.13 705.83 507.85 82.60 870.65 1,542.52 1,553.12 139.85 377.92 0.00 183.67 125.61 OI(In Lots) 416 411 419 302 285 241 247 307 357 393 402 408 334 345 346 345 342 340 332 330 304 299 285 291 260 240 224 222 206 151 131 114 105 105 109 26/12/2012 444.90 24/12/2012 446.95 22/12/2012 446.45 21/12/2012 445.05 20/12/2012 446.15 19/12/2012 453.70 18/12/2012 456.20 17/12/2012 454.70 15/12/2012 453.50 14/12/2012 455.00 13/12/2012 467.25 12/12/2012 453.70 448.00 447.40 446.45 447.35 447.50 453.80 456.50 456.70 453.60 455.00 467.25 456.00 444.30 443.85 446.45 443.25 440.75 447.00 454.00 452.90 453.50 453.30 451.35 452.35 446.60 444.50 446.45 447.10 441.45 447.55 454.50 453.85 453.55 453.90 451.95 454.35 78000 104000 1000 78000 169000 103000 40000 43000 3000 27000 45000 48000 347.55 462.72 4.46 347.26 749.97 463.06 182.10 195.63 13.61 122.61 203.83 218.12 109 119 121 121 124 113 82 77 76 78 77 77 FUTURE MARKET BUYER SELLER 05/02/2013(Buying) 452.00 452.55 05/02/2013(Cl., period) 449.15 449.45 Profit 2.85 Loss 3.10 Loss 500 x2.85=1425, Profit 500 x3.10=1550. Because buyer future price will increase so, he can get profit. Seller future price also increase so, profit decrease, Incase seller future will decrease, and he can get profit. The 89 closing price of Copper Metal at the end of the contract period is 416.00 and this is considered as settlement price. Multi Commodities Exchange of India Ltd (MCX) Gold Price Open(Rs.) High(Rs.) Low(Rs.) Close(Rs.) 05/02/2013 31,579.00 04/02/2013 31,432.00 02/02/2013 31,481.00 01/02/2013 31,551.00 31/01/2013 31,630.00 30/01/2013 31,655.00 29/01/2013 31,713.00 28/01/2013 31,714.00 25/01/2013 31,810.00 24/01/2013 32,059.00 23/01/2013 32,174.00 22/01/2013 32,800.00 21/01/2013 32,124.00 19/01/2013 32,038.00 18/01/2013 32,115.00 17/01/2013 32,125.00 16/01/2013 32,320.00 15/01/2013 32,280.00 14/01/2013 32,279.00 12/01/2013 32,234.00 11/01/2013 32,291.00 10/01/2013 32,190.00 09/01/2013 32,229.00 08/01/2013 32,270.00 07/01/2013 32,325.00 05/01/2013 32,270.00 04/01/2013 32,150.00 03/01/2013 32,529.00 02/01/2013 32,050.00 01/01/2013 32,067.00 31/12/2012 31,917.00 29/12/2012 31,916.00 31,667.00 31,626.00 31,484.00 31,648.00 31,708.00 31,683.00 31,713.00 31,739.00 31,825.00 32,059.00 32,190.00 32,800.00 32,214.00 32,072.00 32,149.00 32,190.00 32,320.00 32,298.00 32,280.00 32,234.00 32,360.00 32,360.00 32,300.00 32,273.00 32,379.00 32,270.00 32,212.00 32,529.00 32,468.00 32,131.00 32,103.00 31,918.00 31,430.00 31,345.00 31,466.00 31,438.00 31,425.00 31,410.00 31,583.00 31,646.00 31,664.00 31,816.00 32,036.00 32,116.00 32,066.00 32,038.00 32,057.00 31,990.00 32,263.00 32,266.00 32,160.00 32,234.00 32,181.00 32,172.00 32,181.00 32,220.00 32,200.00 32,270.00 32,050.00 32,264.00 32,050.00 32,067.00 31,917.00 31,895.00 90 31,485.00 31,556.00 31,475.00 31,492.00 31,460.00 31,652.00 31,658.00 31,678.00 31,726.00 31,866.00 32,082.00 32,226.00 32,135.00 32,060.00 32,093.00 32,182.00 32,291.00 32,285.00 32,202.00 32,234.00 32,237.00 32,345.00 32,213.00 32,246.00 32,309.00 32,270.00 32,151.00 32,417.00 32,414.00 32,098.00 32,029.00 31,909.00 TQ 64000 29000 4000 36000 69000 111000 33000 15000 23000 37000 17000 9000 34000 4000 12000 62000 5000 7000 16000 1000 25000 28000 18000 6000 8000 1000 33000 8000 53000 7000 32000 5000 TV(Rs Lacs) 2,025.02 913.09 125.90 1,134.95 2,178.31 3,507.84 1,044.57 475.35 730.21 1,182.47 545.74 290.03 1,092.17 128.24 385.17 1,989.57 161.46 226.00 515.48 32.23 807.36 903.13 580.28 193.47 258.48 32.27 1,060.68 259.33 1,713.79 224.68 1,024.07 159.55 OI(In Lots) 218 192 187 186 183 169 126 121 123 123 118 128 129 137 137 135 110 110 109 107 107 104 90 82 84 79 79 76 74 80 75 77 28/12/2012 31,950.00 27/12/2012 31,777.00 26/12/2012 31,760.00 24/12/2012 32,041.00 22/12/2012 32,005.00 21/12/2012 31,714.00 20/12/2012 32,077.00 19/12/2012 32,086.00 18/12/2012 32,550.00 17/12/2012 32,450.00 15/12/2012 32,346.00 14/12/2012 32,348.00 13/12/2012 32,319.00 12/12/2012 32,586.00 11/12/2012 32,500.00 10/12/2012 32,499.00 08/12/2012 32,356.00 07/12/2012 32,360.00 31,950.00 31,877.00 31,890.00 32,041.00 32,011.00 31,992.00 32,077.00 32,111.00 32,674.00 32,500.00 32,351.00 32,361.00 32,361.00 32,586.00 32,543.00 32,637.00 32,356.00 32,360.00 31,832.00 31,777.00 31,760.00 31,943.00 32,005.00 31,714.00 31,552.00 31,910.00 32,275.00 32,443.00 32,346.00 32,288.00 32,274.00 32,586.00 32,428.00 32,499.00 32,356.00 32,351.00 91 31,873.00 31,816.00 31,861.00 31,968.00 32,008.00 31,946.00 31,696.00 31,981.00 32,445.00 32,468.00 32,349.00 32,305.00 32,314.00 32,586.00 32,516.00 32,563.00 32,356.00 32,356.00 22000 9000 13000 4000 2000 22000 14000 38000 17000 4000 2000 30000 8000 1000 11000 5000 0 2000 701.85 286.34 414.10 127.87 64.02 701.28 444.81 1,217.23 552.56 129.87 64.70 969.04 258.51 32.59 357.66 162.82 0.00 64.71 75 62 60 60 58 58 58 55 35 33 30 30 17 15 14 7 7 7 FUTURE MARKET BUYER SELLER 05/02/2013(Buying) 31579.00 31667.00 05/02/2013(Cl., period) 31430.00 31485.00 Profit 149.00 Loss 182.00 Loss 500 x149.00=74500, Profit 500 x182.00=91000. Because buyer future price will increase so, he can get profit. Seller future price also increase so, profit decrease, Incase seller future will decrease, and he can get profit. The closing price of Gold Metal at the end of the contract period is 16500.00 and this is considered as settlement price. 92 Multi Commodities Exchange of India Ltd (MCX) Silver Price Date Open(Rs.) High(Rs.) Low(Rs.) Close(Rs.) 06/02/2013 60,875.00 05/02/2013 61,080.00 04/02/2013 61,005.00 02/02/2013 61,100.00 01/02/2013 60,670.00 31/01/2013 61,601.00 30/01/2013 60,858.00 29/01/2013 60,540.00 28/01/2013 60,989.00 25/01/2013 61,544.00 24/01/2013 62,201.00 23/01/2013 62,412.00 22/01/2013 62,045.00 21/01/2013 62,100.00 19/01/2013 61,910.00 18/01/2013 61,819.00 17/01/2013 62,069.00 16/01/2013 62,154.00 15/01/2013 61,345.00 14/01/2013 61,102.00 12/01/2013 60,872.00 11/01/2013 61,145.00 10/01/2013 60,598.00 09/01/2013 60,930.00 08/01/2013 60,870.00 07/01/2013 60,980.00 05/01/2013 60,575.00 04/01/2013 60,220.00 03/01/2013 61,898.00 02/01/2013 60,786.00 01/01/2013 60,448.00 31/12/2012 60,550.00 29/12/2012 60,290.00 28/12/2012 60,504.00 27/12/2012 60,100.00 26/12/2012 60,249.00 61,080.00 61,415.00 61,350.00 61,110.00 61,622.00 61,736.00 61,798.00 60,732.00 61,136.00 61,548.00 62,201.00 62,540.00 62,301.00 62,232.00 61,981.00 62,147.00 62,300.00 62,356.00 62,061.00 61,585.00 60,872.00 61,182.00 61,310.00 60,937.00 61,151.00 60,992.00 60,650.00 60,270.00 62,030.00 62,164.00 60,603.00 60,580.00 60,340.00 60,524.00 61,000.00 60,450.00 60,820.00 60,800.00 60,650.00 61,100.00 60,524.00 60,350.00 60,461.00 60,540.00 60,480.00 60,900.00 61,580.00 62,200.00 61,911.00 62,025.00 61,910.00 61,819.00 61,201.00 61,800.00 61,345.00 60,922.00 60,840.00 60,530.00 60,553.00 60,405.00 60,750.00 60,531.00 60,575.00 59,543.00 61,280.00 60,786.00 60,448.00 60,250.00 60,290.00 60,105.00 59,900.00 59,946.00 93 60,959.00 60,986.00 61,273.00 61,105.00 60,943.00 60,542.00 61,724.00 60,637.00 60,698.00 60,990.00 61,646.00 62,355.00 62,213.00 62,153.00 61,946.00 61,977.00 62,154.00 62,287.00 62,011.00 61,376.00 60,851.00 60,628.00 61,188.00 60,527.00 61,001.00 60,802.00 60,613.00 60,105.00 61,505.00 61,796.00 60,530.00 60,443.00 60,315.00 60,200.00 60,833.00 60,052.00 TQ 0 1000 1000 0 2000 3000 1000 1000 2000 1000 1000 1000 0 0 0 0 1000 1000 2000 1000 0 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 0 2000 1000 2000 0 0 0 1000 1000 1000 TV(Rs Lacs) 274.22 476.73 841.48 36.66 1,173.12 1,586.51 884.05 327.48 1,002.69 697.49 686.20 823.69 261.08 167.81 37.17 185.93 833.43 540.35 926.90 496.54 54.77 657.53 639.42 400.77 512.24 383.25 36.37 1,419.86 573.54 1,072.91 108.95 181.33 36.19 687.27 706.56 523.65 OI(In Lots) 87 87 84 83 83 66 83 75 75 85 95 111 110 108 108 106 107 120 113 116 111 110 121 110 115 111 109 109 78 82 72 71 71 70 93 78 24/12/2012 60,699.00 22/12/2012 60,640.00 21/12/2012 60,288.00 20/12/2012 62,462.00 19/12/2012 63,206.00 18/12/2012 64,630.00 17/12/2012 64,199.00 15/12/2012 64,094.00 14/12/2012 64,653.00 13/12/2012 64,950.00 12/12/2012 65,195.00 11/12/2012 65,314.00 10/12/2012 65,750.00 08/12/2012 65,330.00 60,699.00 60,750.00 61,000.00 62,580.00 63,400.00 64,756.00 64,371.00 64,211.00 64,653.00 65,093.00 65,797.00 65,372.00 65,795.00 65,408.00 60,319.00 60,640.00 60,013.00 59,961.00 62,295.00 63,315.00 64,101.00 63,909.00 64,100.00 64,327.00 65,195.00 64,976.00 65,750.00 65,330.00 94 60,490.00 60,709.00 60,483.00 60,149.00 62,459.00 63,441.00 64,276.00 64,078.00 64,353.00 64,611.00 65,539.00 65,148.00 65,767.00 65,363.00 0 0 0 2000 1000 1000 0 0 0 1000 0 0 0 0 108.88 127.49 271.88 1,062.45 622.36 594.38 308.31 211.46 231.85 368.97 314.08 273.83 59.19 58.83 79 80 74 78 60 58 54 50 46 41 40 35 35 34 FUTURE MARKET BUYER SELLER 05/02/2013(Buying) 60875.00 61080.00 05/02/2013(Cl., period) 60820.00 60959.00 Profit 55.00 Loss 121.00 Loss 500 x55.00=25500, Profit 500 x121.00=60500. Because buyer future price will increase so, he can get profit. Seller future price also increase so, profit decrease, Incase seller future will decrease, and he can get profit. The closing price of Silver Metal at the end of the contract period is 274.22 and this is considered as settlement price. 95 CHAPTER-V FINDINGS SUGGESSIONS CONCLUSIONS BIBLIOGRAPHY 96 FINDINGS Due to the increasing of inflation in the country the Gold , copper and silver got very much importance and it was increased and the commodities market. It shown that the more of the given share is known as commodities i.e. 67% and other got very less as compared to commodities. The value of the commodity market increased because of increasing in the values of the commodities and also the availability is also not easy because it is a prestigious metal. Due to the increase in the purchase of products got very much importance for commodity and it was increased Majority of the Investor’s trade in the Commodities Market but few Done & Left due to Losses & Settlement Problems. Investors purchased commodities from Religare Enterprises Ltd because of the company’s policies and information availability. Due to the increase in the population in the country the commodity products got very much importance and it was increased and also increased interest in the purchase of oil and oil seeds.. Most of the investors feel that commodity trading id very good and remaining says good for investing Trading in Commodities Futures is More Beneficial & More Leveraging got more percentage. Due to the increase in the services in the country the Services they prefer from a Financial Advisory Institution is telephone. Due to the increase in the population in the country the general market got very much importance and it was increased and also increased interest in the purchase of Jewelers. Most of the investors preferring Religare Enterprises Ltd for investing in the commodity market. 97 CONCLUSION Commodities market, contrary to the beliefs of many people has been in existence in India through the ages. However the recent attempt by the Government to permit Multi-commodity National levels exchanges has indeed given it, a shot in the arm. Commodity includes all kinds of goods. FCRA defines “goods” as “every kind of movable property other than actionable claims, money and securities”. Futures trading are organized in such goods or commodities as are permitted by the Central Government. Firstly, the price movements are more predictable, purely based on demand and supply of that commodity, unlike in other markets where price manipulations are very much possible, hence the investor is fixed. To that extent market price risk is reduced. Secondly, the markets are working virtually round the clock,(NCDEX works from 10:00 AM to 4:00 PM and next session from 7:00 PM to 11:00PM)so any drastic news is digested. In case of other markets this provision is not there, just think of September 11th episode, next day equity markets opened far down and the Investors are left hanging. The future contracts available on a wide spectrum of commodities like Gold, Silver, Cotton, Steel, Soya oil, Soya beans, Wheat, Sugar, Channa etc., provide excellent opportunities for hedging the risks of the formers ,importers, exporters, traders and large scale consumer. Religare Enterprises Ltd is another venture of the prestigious Religare Enterprises Ltd. With our well establish presence in the multifarious facets of the modern financial services industry from Stock Broking to registry services. 98 SUGGESTIONS Commodity market presently deals with FUTURES contract and most probably OPTIONS are provided, it would be convenient to the investors. As the fund managers take decisions with mutual fund investment, it would be another option for him to invest through mutual funds in commodity market. If Government takes this commodity market into awareness for the farmers, it would be better for them to take their own decisions for commodity which they want to trade. As there is an option for the trader to take the physical delivery, it would be better if the Government cuts the tax rate for the physical delivery of goods. Avoid buying shares of the company which are not traded on your stock exchange. Investor must show interest in steady and fast growth shares only. Avoid buying Turn rounds (making loss continuously), Cyclical (cycles of good and bad performance), Dog shares (very inactive or passive). Avoid companies with low PIE ratio relative to the market as always. If the investor is confident of EPS moving up and expects PIE to increase as well stick to the shares and be patients. 99 BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. Donald E. Fisher, Ronald J. Jordan, Securities Analysis and Portfolio Management,, 1999, sixth edition, futures and options Page no: 404-435,489,493. Prentice hall of India 2. Sharpe W.F. Alexander J. Bailey, investments, 1998, 5th edition, Derivatives, Prentice Hall of India,. 3. SCHAUM"S out lines, investments,2nd edition, new chapters on future And options. Religare finapolies, Monthly editions, Broachers of Religare trade. WEBSITES: RELIGARE LEARNING CENTRE www.icrier.org/pdf/Working%20Paper%20249.pdf www.icrier.org/pdf/Working%20Paper%20249.pdf www.iimahd.ernet.in/~jrvarma/papers/vik23-1.pdf www.religare.com www.religarecommodities.com www.ncdex.com www.mcx.com 100