Business Research Process: Steps & Problem Formulation
advertisement

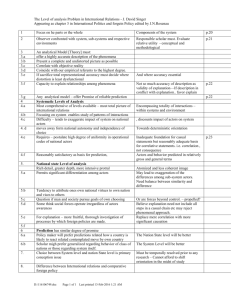
1 The Research Process Sequence of steps in busieness research Formulate Problem Decision Problem Research problem Dermine Research Design Explorative research Descriptive research Cusal research Dermine data Collection Method Secondary Data Primary data Design data Collection Forms Quantitative Data Qualitative Data Design Sample and Collect data Sample Frame and sample Probability versus nonprobability sample Analyze and Interpret Data Editing/Quality assurance of data Coding Tabulation Data Analysis Prepare the Research Report (proposal) Structure Scientific Reqirements/Theory/Models Literature 2 Confer Exhibit 3.1, page 50 3 Decision Problem and Research Problem Drivers for problem formulation: 1. Unaticipated change, basically in the environment of the focal firm (suppliers,competitors, customers) 2. Planned change (estimation, effects, outcome) 3. Serendipity (random ideas or information) 4 Differetn Problem Levels: 1) Individual orientation, PSYCHOLOGY 2) Individual-individual, SOSIAL PSYCHOLOGY 3) Individual and group, ORGANIZATION THEORY, ORGANIZATION PSYCHOLOGY 4) Group/department, ORGANIZATION SOCIOLOGY 5) Inter-group, ORGANIZATION THEORY 6) Group/department and organization, ECONOMIC THEORY, PRINCIPAL-AGENT THEORY, ORGANIZATION THEORY 7) Organization/firm, ECONOMIC THEORY, BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION 8) Firm-firm, ECONOMICS OF ORGANIZATION, ECONOMIC THEORY, GAME THEORY 9) Firm and environment ECONOMIC THEORY, CONTRACT LAW, INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS 5 Decision Problem: The problem facing the decision maker (organization) for which the research is intended to provide answers or information Research Problem: A statement of the decision problem into research terms A practical example: Introduction of a new product because sales are below the target Revision of the target? Withdraw the product? Revise some elements in the marketing mix? 6 Further investigation: Assumption about ineffective advertising Lack of awareness among potential users? Lack of interest among potential users? The decision problem should focus on what needs to be done? Bad performance in one specific supplier firm: The ability/skills in the supplier firm? The motivation in the supplier firm to carry out satisfactory services for the purchasing organization The research problem should aim at providing information which enable the decision maker to take relevant decisions or carry out relevant actions in order to solve the problem 7 Examples of failures: Taste of food and drinks Image of food and drinks Instant coffee 8 How can you avoid to make wrong specification of the research problem? Wait until you have explored the decision problem sufficiently before you state your research problem The typical research failure is to start the research process by making a proposal stating the methods which is to be used to complete the research A more fruitful way of doing research is to examine the decision maker’s situation carefully in the first place with focus on: 1. The decision maker (organization) and its environment 2. Alternative courses of action 3. The objective of the decision maker 4. The consequences of alternative actions 9 Start by making a research request step: 1. Action: The actions that are contemplated on the basis of the research 2. Origin: The events that led to a need for action give a deeper understanding of the decision problem 3. Information: The questions which need to be answered in order to take relevant decision 4. Use: The way each piece of information will be used to help make the proper decisions 5. Target and subgroups: Localize the groups from whom relevant information can be gathered 6. Economy: Estimate the time and money that are available for Conducting the research 10 Example: Decision problem: Sales reductions for a specific product group 1. Action: Drop the product? Improve marketing mix? Improve distribution and logistics? 2. Origin: Increased competition? Recession in the economy? The product life cycle is in the ending stage? Turn over and problems in the sales force of the company Sales development over time? 11 3. Information: The information need is determined by the origin of the problem which might narrow your research agenda when you look at the correspondence between action and origin Suppose that we know that the competitors are winning market shares, that the market size is maintained for the product, and that we are loosing sales volume in specific distribution channels A marketing and/or logistic problem 12 4. Use: What kind of information is relevant now? Our firm has to pay attention to the actors in a specific distribution channel, e.g. industrial distributors in international markets Find sales figures for different distribution actors in this channel Quality rating (bench marking) of the product Sales promotion support Prices and margin for the distribution actors Currency development Logistic performance, delivery time and lead time and order costs Integration or long term relationships between dominant actors in the distribution channel 13 5: Targets and subgroups Relevant information and informants: Within the firm: Statistics providing sales development figures for product groups and customers/distribution actors Interviews or focus groups: Top manager Marketing manager Sales manager Logistic manager Outside the firm: Competitors/marketing intelligence Interviews: Distributors Final customers Consultancy firms 14 6. Economy: Start with most available data Make priorities among the different information sources 15 Research Proposal: 1. Tentative project title 2. Statement of the research problem Describe the general problem under consideration Why is this problem of any relevance? Literature, new papers, journals, statement from the case firm/decision maker, some verification is necessary 3. Purpose and limits of the project Focus and purpose of the project should be elaborated in more details Scope and limitations, what is left out and what is the main focus Research questions or hypotheses 4. Outline Tentative framework for the entire project Literature review Research model 16 5. Data sources and research methodology Setting for the study Primary/secondary data Specification of informants Data collection 6. Estimated time and scheduling Time schedule for the different stages of the project 7. Cost estimates (research consulting firms) Specification of costs for carrying out the project