Plant and Animal Cells
advertisement

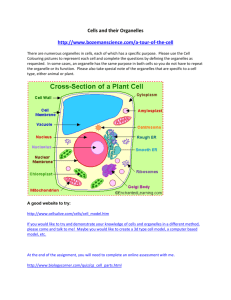
Mr. Vallee’s Plant and Animal Cells Student Handout http://www.purchon.com/biology/cells.htm http://www.brainpop.com Plant and Animal Cells Anatomy of generalized Plant and Animal Cells http://www.cellsalive.com/ http://www.purchon.com/biology/cells.htm There are three main regions: 1. Organelles - Structures inside of cells with a particular function in life process of cells (like an organ in a body – heart, liver, kidney) 2. Cell membrane (plasma)– the outer cell boundary that holds the parts of the cell together, also separates the cell from its surroundings a. fragile/transparent b. like a baggie, but more 3. Nucleus – controls the cells activities/located near the center. 1. surrounded by cell membrane 2. enclosed in its own membrane 3. shape conforms to shape of cell 4. cell reproduction chromosomes – contain info (blueprint) about characteristics of the organism, when cells reproduce, identical chromosomes go into each new cell (DNA). Other regions of a cell: Cytoplasm – jelly-like substance containing many chemicals to keep cell functioning. Like the factory area of the cell. 1. Has 3 elements a. cytosol – fluid that suspends other elements b. inclusions – chemical substances c. organelles 2. Contains several organelles (little organs) a. Mitochondria – releases energy from food (sausage shaped) HOW? 1. Takes in: Food, Oxygen, Water = Energy 2. Then: Energy produces waste (carbon dioxide) b. Vacuoles – storage of water, food, waste c. Golgi apparatus - flattened sacs modify/package proteins; sacs fill up > sacs erupt > go outside cell Two Organelles that make plant/animal cells different 1. Plant has a cell wall – rigid, gives it strength 2. Plant has chloroplasts – makes food Lysosome – small, ball-shaped organelles that help the cell break down nutrients and old cell parts. They are present in animal cells, but are rare in plant cells. Endoplasmic Reticulum – is a system of membranes and tubes. The membranes twist and turn through the cell providing passages through which materials can pass.